The Neolithic Period, or New Stone Age was that time in Prehistory when we humans first began the transition from hunter gatherer clans to agricultural societies. It was also the time therefore when some peoples settled down to live in permanent ‘villages’ instead of living as nomads moving from place to place with the seasons as the local resources ripened.
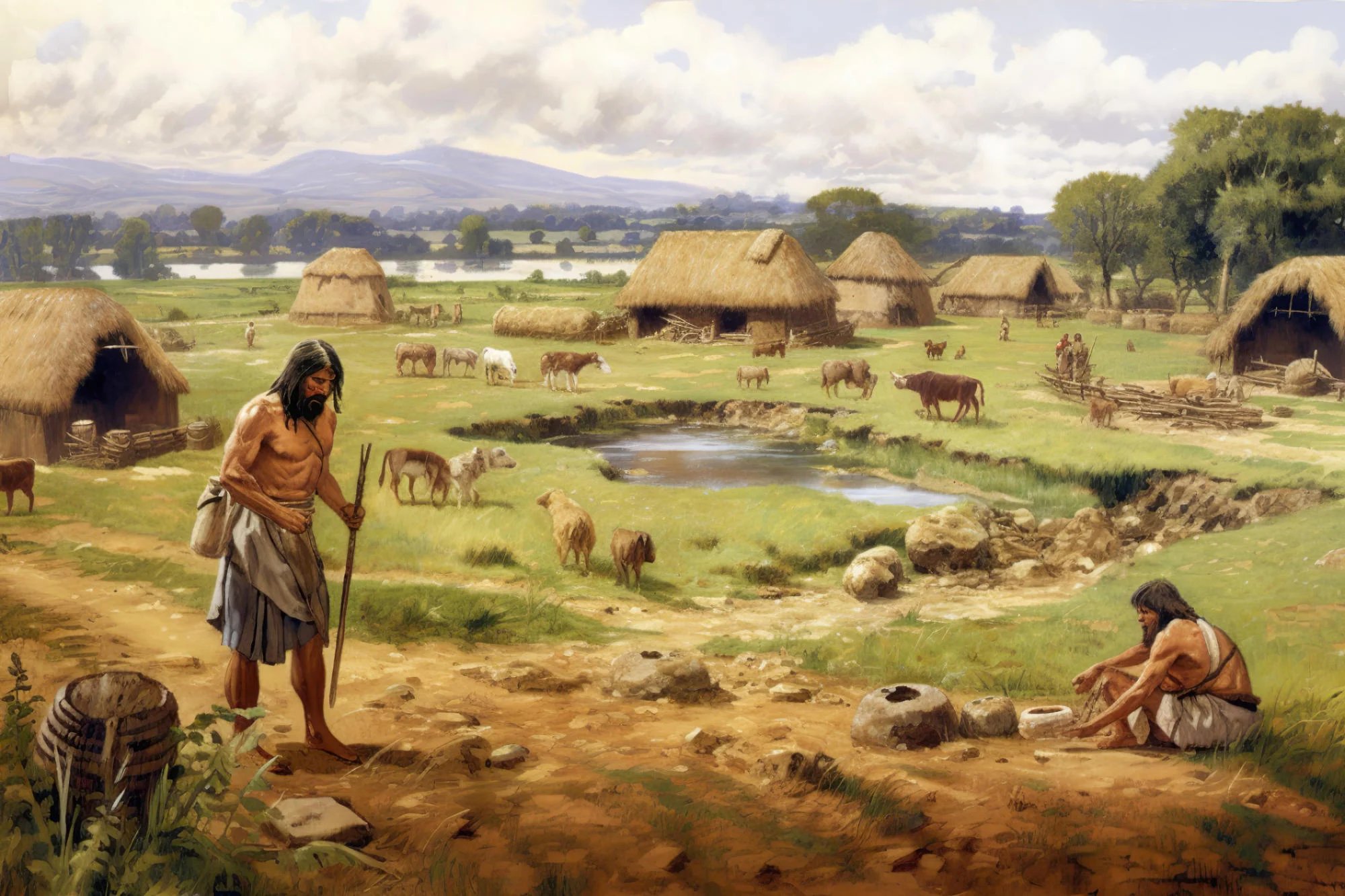

And once humans began to live permanently in one place they could begin to build, not just villages in which to live but also monuments to honour their gods or record some important event. It is well known from anthropology that by building such monuments those people were also saying ‘This is our Land!” In this post I will be talking about several of such Neolithic structures and as usual I will start with the oldest first and then move forward in time.

Göbekli Tepe is in fact considered to be the oldest stone structure known to archaeology, see my post of July 5th 2017. The site is located in southern Turkey and has been dated to more than 11,000 years ago; the name by the way means ‘Potbelly Hill’ in Turkish. The site consists of a series of oval stone walls with large ‘T’ shaped pillars inside the ovals. Both the pillars and some of the walls are covered by carvings, many of the carvings are those of local animals while others appear to be abstract symbols. The site is undergoing almost constant excavation and it is expected that many more discoveries are waiting to be unearthed.
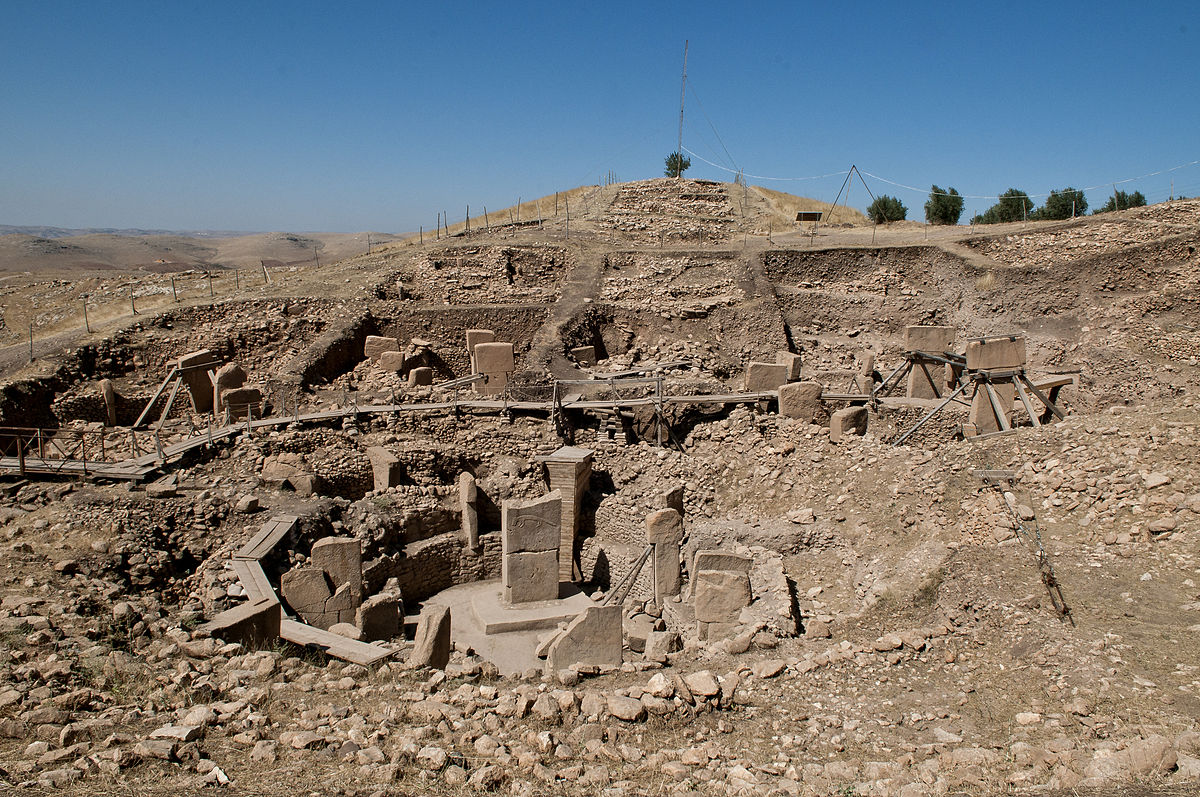

The motive behind the building of Göbekli Tepe is of course unknown after all these thousands of years but that hasn’t stopped archaeologists from trying out various theories. The temple like layout of the site certainly suggests that it could have been used as a place of worship, perhaps the animals craved into stone were sacred totems of some sort. Another possibility is that the structures were built as a calendar, that is some way the pillars and carvings could be used to keep track of the seasons. In an agricultural society being able to know when to plant and when to harvest is of the greatest importance.

A new study in the journal Time and Mind by archaeologists from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland has developed evidence supporting the idea of Göbekli Tepe being a calendar. At the same time the paper further suggests that the building of the site was a response to an astronomical event that occurred a thousand years before the earliest known part of Göbekli Tepe was built. This event occurred sometime around 10,800 BCE when an asteroid or comet fragment is known from geological evidence to have struck the island of Greenland triggering a worldwide ‘mini-ice age’. This drastic change in the climate is thought to have contributed to the extinction of large fauna such as the Wooly Mammoth and Saber Toothed Tiger.

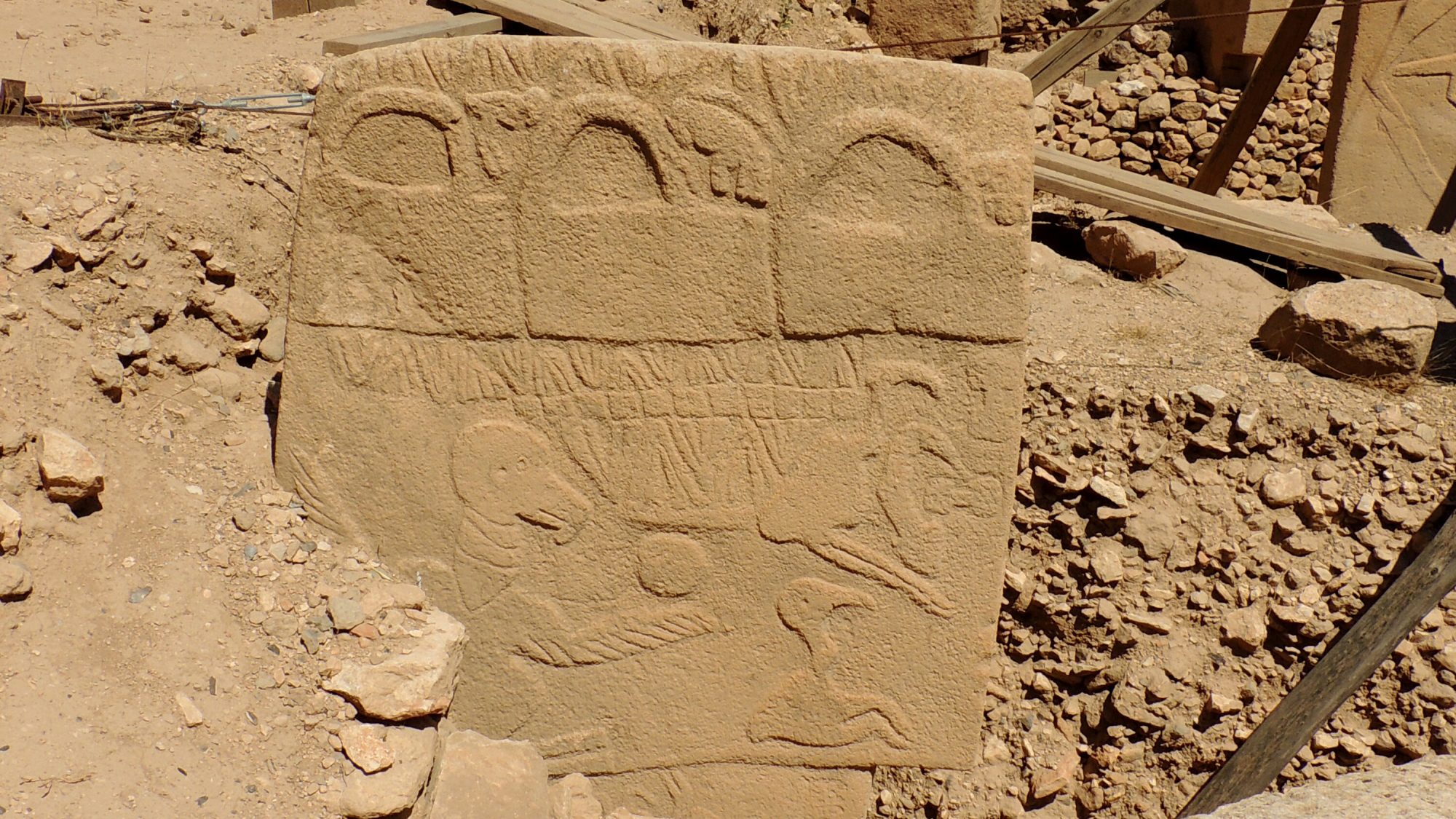
The evidence for Göbekli Tepe being a calendar comes from an interpretation ‘V’ shaped carvings on pillar 43 in the largest enclosure. The V shaped carvings appear to be arranged to record a lunar month of 29 or 30 days, below the V’s are squares that appear to represent the number of lunar months in a year plus another 10 V’s to make up for the extra time needed to get to 364 days. Finally there is a bird like figure with a V around its neck that the paper asserts represents the summer solstice bringing the total number of days to 365, the right number of days for a year. Using the carvings on the pillar could allow the ancient people of Göbekli Tepe to keep track of both the lunar months and a solar year.

The evidence for Göbekli Tepe being a record of the comet strike was found at the top of the same pillar which according to the article depicts a meteor swarm emanating from the constellations of Aquarius and Pisces. That is the location in the sky that is thought to be where the comet strike came from. According to Dr. Martin Sweatman, co-author of the study, “This event might have triggered civilization by initiating a new religion and by motivating developments in agriculture to cope with the cold climate.” In any case the event must have had a profound effect of people throughout the world and could well have inspired the people of Göbekli Tepe to try to record it somehow.

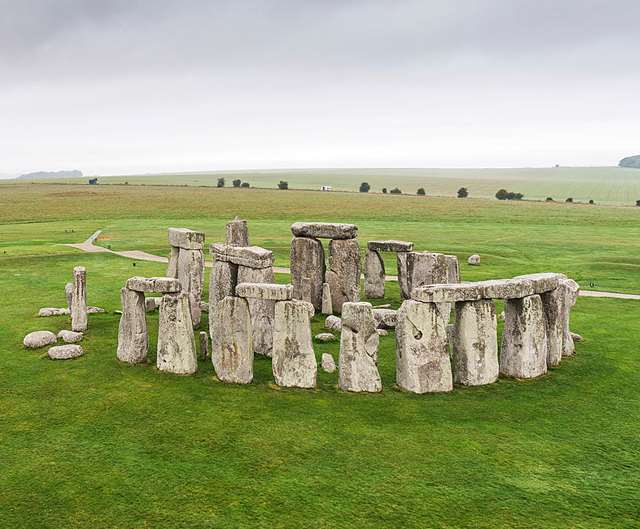
While we’re on the subject of ancient stone monuments there’s some news about the best known such structure, Stonehenge. Back in my post of 30 December 2023, I discussed how recent research had revealed that one of the most important of the so-called ‘bluestones’ at Stonehenge, the altar stone, was chemically so different from the other bluestones that it could not have come from the same quarry in Wales as the other bluestones did. So the hunt was on to find the place of origin for the altar stone.

Now a Ph.D. student in geology from Curtin University in Australia named Anthony Clarke has announced that he has traced the altar stone back to its source in northern Scotland. According to Mr. Clarke, who grew up in Wales not far from the quarry where the other bluestones came from, the altar stone is chemically identical to sedimentary rocks from the Orcadian basin nearly 700 kilometers from Stonehenge in northern Scotland.
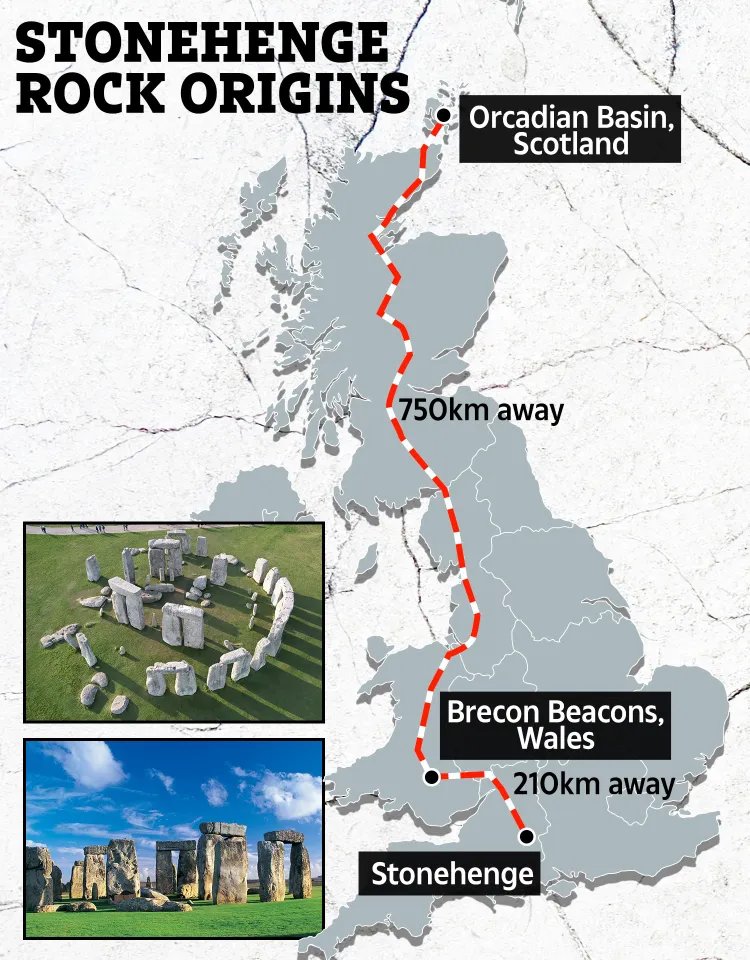
So after having solved the mystery of where the altar stone came from we now have to figure out how it got to Stonehenge, and why was a rock from so far away used there anyway. The terrain in northern Scotland is rather rugged even today so the 5,000 kilogram stone was probably brought by water, still a difficult undertaking in a culture that had not yet invented the wheel.

As to the question of why a stone from so far away was incorporated into Stonehenge, that is something we will probably never know for certain. Neither we will know for certain the reasons for the building of Göbekli Tepe. We can learn much from the ancient rocks left to us by our remote ancestors but their motives may remain hidden for the rest of time.
