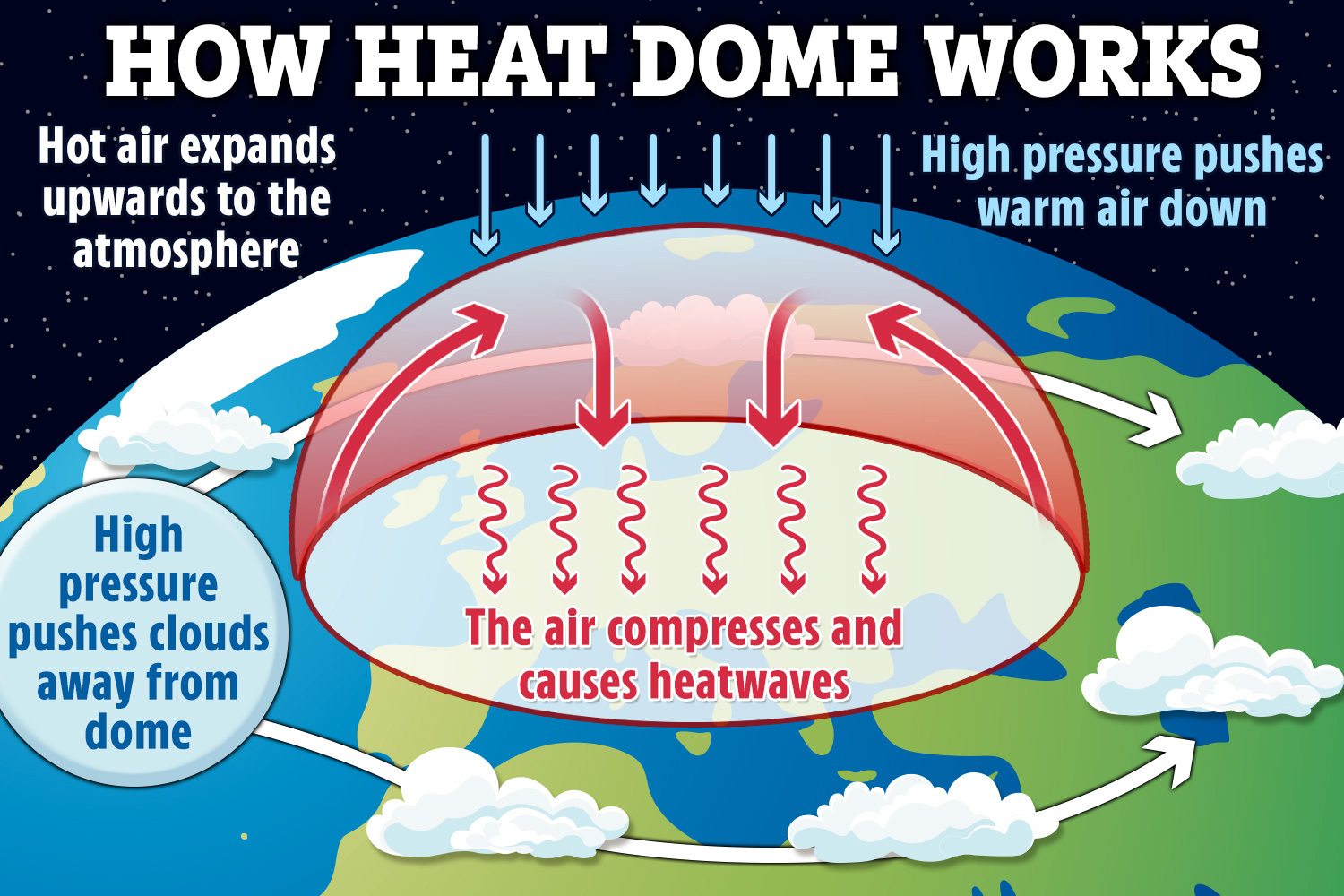
If you think about it, it wasn’t too many centuries ago that relations between sovereign nations meant either going to war or maybe two nations ganging up for a war on another. Diplomatic correspondence between the rulers of nations going back as far as the late Bronze Age, 1200-1300 BCE, has been unearthed by Archaeologists and those letters make it plain that the kings and Pharaohs of those days considered themselves to be above any laws, national or international. The idea was that a country and its ruler could do whatever other countries let them get away with. Might literally made right when it came to relations between nations.

The very concept of international law took a long time to develop and the very first time that two nations resolved a conflict by legal rather than martial means occurred between the USA and UK shortly after the American civil war. You see during that war British shipyards had constructed five warships for the Confederacy, the commerce raider CSS Alabama becoming the most successful. This was despite the fact that the British government never officially recognized the Confederacy as a legitimate nation. During the war the Alabama would sink over 60 Union merchant vessels.

After the Confederacy was defeated the US decided to sue the British government for the destruction those five ships had caused. Now one country suing another was unheard of, if one country had a conflict with another they started a war they didn’t sue the other country. How would a suit between two nations even be conducted, what court would hear the suit?

Neither the US nor UK wanted to go to war however so in 1872 they agreed to let an arbitration panel convened in Geneva Switzerland both hear the evidence and decide what damages, if any the UK owed the USA. In the final settlement Britain paid $15.5 million dollars to US shipping interests and insurance companies to settle the case.
This peaceful resolution of the “Alabama Claims” would over the next 150 years lead to the establishment of an ever growing number of international institutions ranging from the World Court at the Hague in the Netherlands to the World Trade Organization to the United Nations itself. And if these institutions have not yet succeeded in ending war they have at least firmly established the concept of international law.

The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is one of those international institutions with a mission intended to stimulate economic development and world trade. Founded in 1961 with 38 member nations and its headquarters in Paris France the OECD has grown to 139 members with a combined GDP of approximately $54 Trillion dollars. While having little power itself to enforce the statutes enacted by its members the OECD does compile and publish vast amounts of data concerning the state of the world’s economy.

Now the OECD is at the center of a large effort to establish for the first time an internationally agreed upon minimum tax level of 15% on the profits of multinational corporations. Why is that significant, well you see wealthy corporations, like wealthy individuals are always searching for ways to reduce the amount of taxes they have to pay. At the same time some small countries, with a small population can keep their tax levels low in the hopes of luring big companies to set up their headquarters there. While ordinary people, and companies are pretty much stuck with paying the taxes of wherever it is they live, corporations with factories in half a dozen different countries and sales offices in even more can pick whichever country has the lowest taxes rates and declare it to be their ‘home country’. It’s the same sort of game rich people have always played. Whether it be having a Swiss bank account or by using ‘holding companies’ to own other companies and help hide where the money comes from and to whom it’s going the rich are always looking for ways to cheat the system.
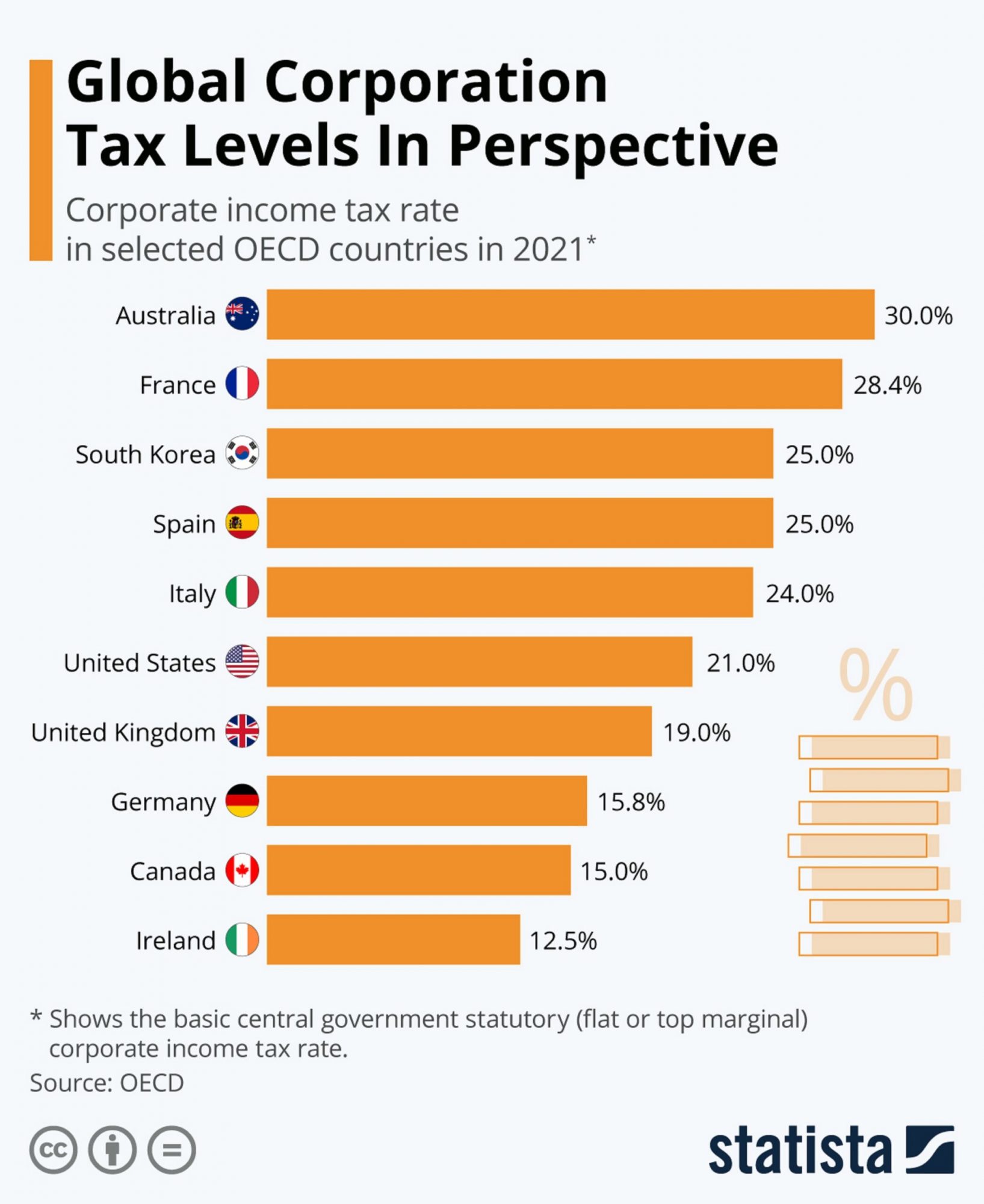
So the effort to establish a minimum corporate tax rate is an attempt to level the playing field, to force the multinationals to pay their fair share and distribute that money to where its needed. Over the last thirty years the United States has been one of the nations hardest hit by the current state of affairs with companies like Microsoft, Apple and Amazon being founded in the US but as they became multi-billion dollar corporations moving their headquarters to other countries for tax purposes. It’s not surprising therefore that the Biden administration is leading the effort to pass the new 15% minimum corporate tax rate.

So far 132 of the 139 members of OECD have agreed to the new tax rate but one nation is standing in the way and I hate to say it but it’s Ireland. You see ever since gaining independence from the UK the small nation of 5 million people has profited by its position close to some of the world’s richest nations while keeping its own taxes low. In fact Microsoft, Apple and Amazon are all currently headquartered in Ireland largely because of the countries 12.5% corporate tax rate. If Ireland agrees to increase its rate to 15% the country could actually lose tax revenue as some of the big corporations might go back where they came from.

But even if Ireland and the other remaining holdouts do finally agree to the minimum tax rate that still doesn’t mean that it’s a done deal. You see the agreement will still have to pass the US Senate, The European Union’s Parliament as well as legislative bodies in other nations. In other words an internationally agreed upon minimum corporate tax rate could still be years away, if it ever happens. Sometimes you have to wonder why it is that we humans can’t seem to get anything done without a bunch of lawyers and politicians arguing and filibustering. But I guess its better fighting wars all the time.