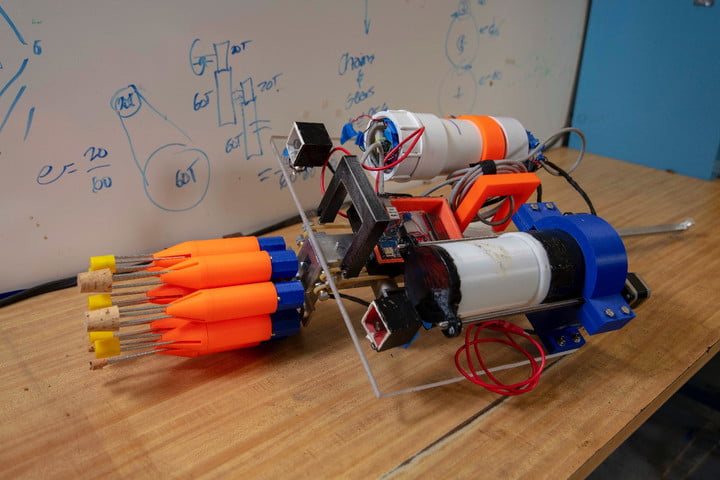
Invasive species are defined as populations of living creatures that have been transported from their natural habitat and become established in another ecosystem perhaps thousands of kilometers away. Sometimes this movement is a natural occurrence, such as when a few finches were somehow blown onto the Galapagos Islands, became established and evolved into some fifteen recognized species. Indeed such rare but natural transplanting of species is considered to be a driving force in evolution as the relocated population adapts to its new environment.
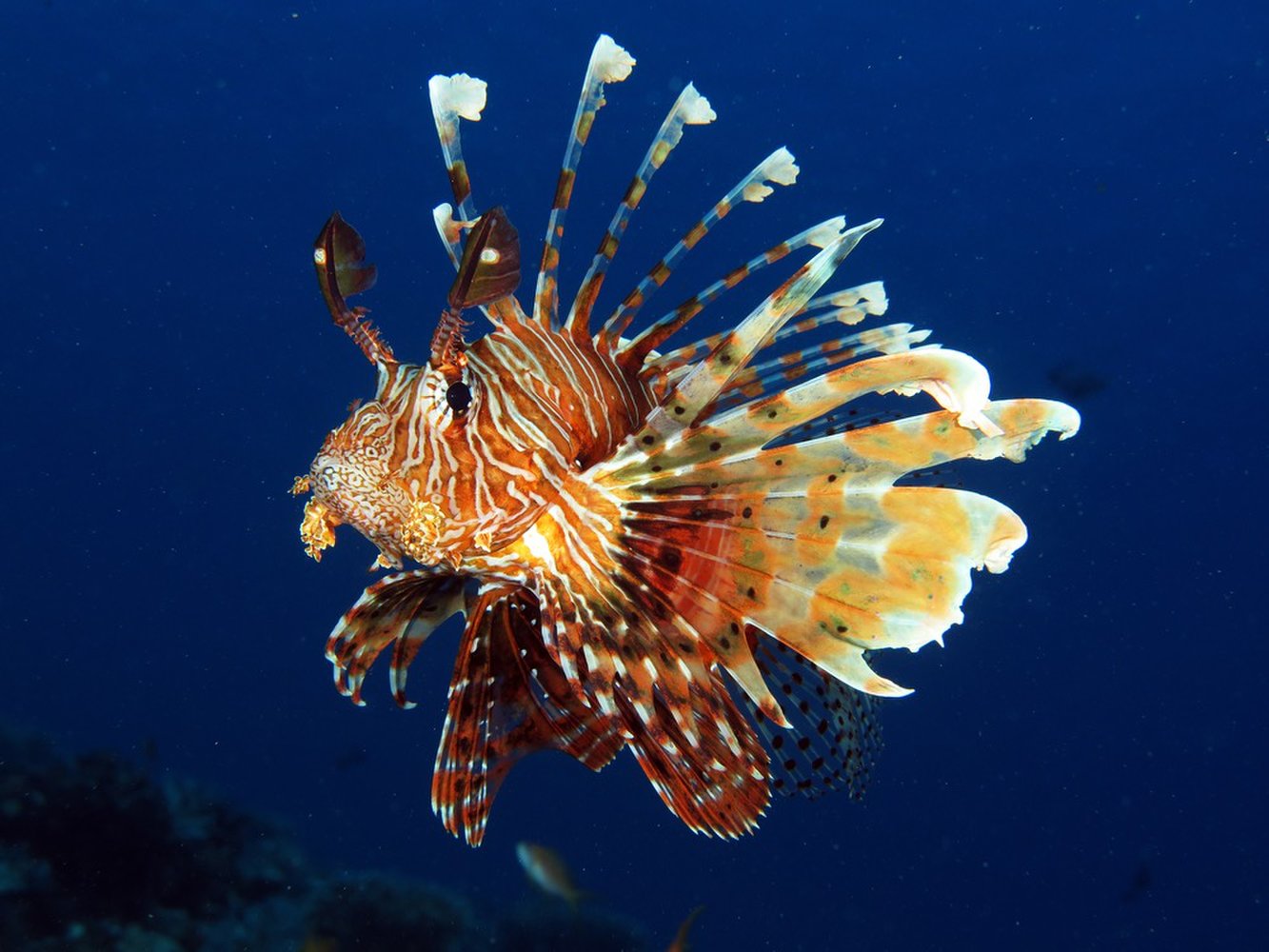
More often however it is human beings who have transported the creatures either intentionally or accidentally. One example of the latter category would be the common salt water aquarium fish the lionfish, any member of the 12 species of the genus Pterois but particularly P volitans and P miles. See images below.
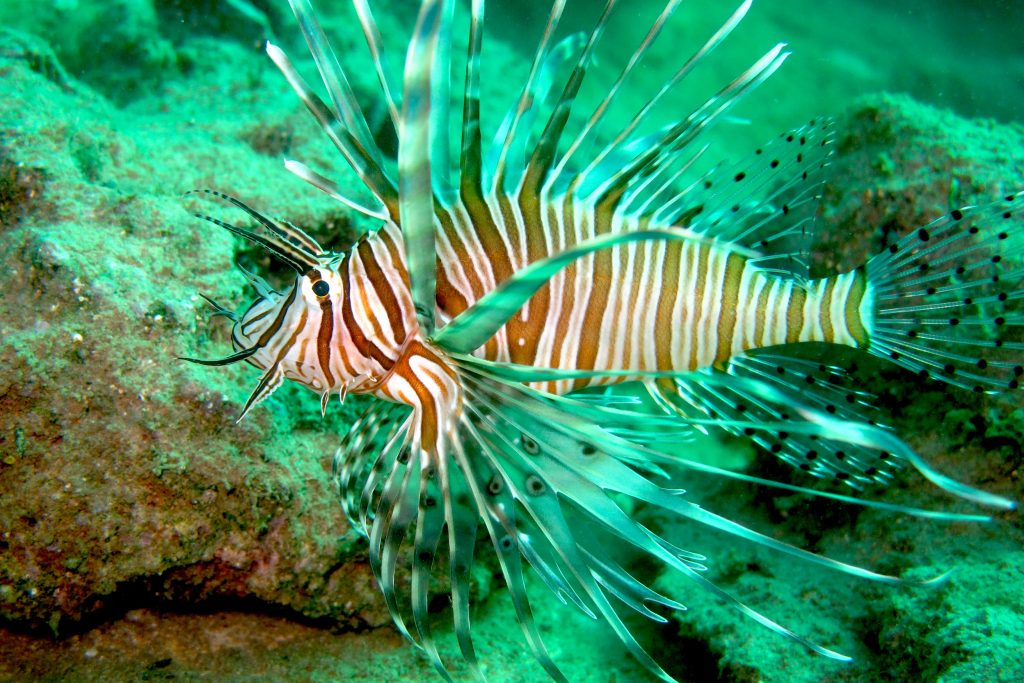


Lionfish are native to the Indian and western Pacific oceans where they are a predatory species feeding on small fish and invertebrates. Adult lionfish are generally 20-40cm in length and can weigh more than a kilogram. Their numerous spiny fins and colourful stripes have made them a popular aquarium fish, even though the animal’s spines are venomous and can produce a painful sting along with vomiting, nausea, convulsions and numerous other ill effects. Because of the danger of their spines Lionfish should only be kept by the most experienced of aquarium Hobbists.
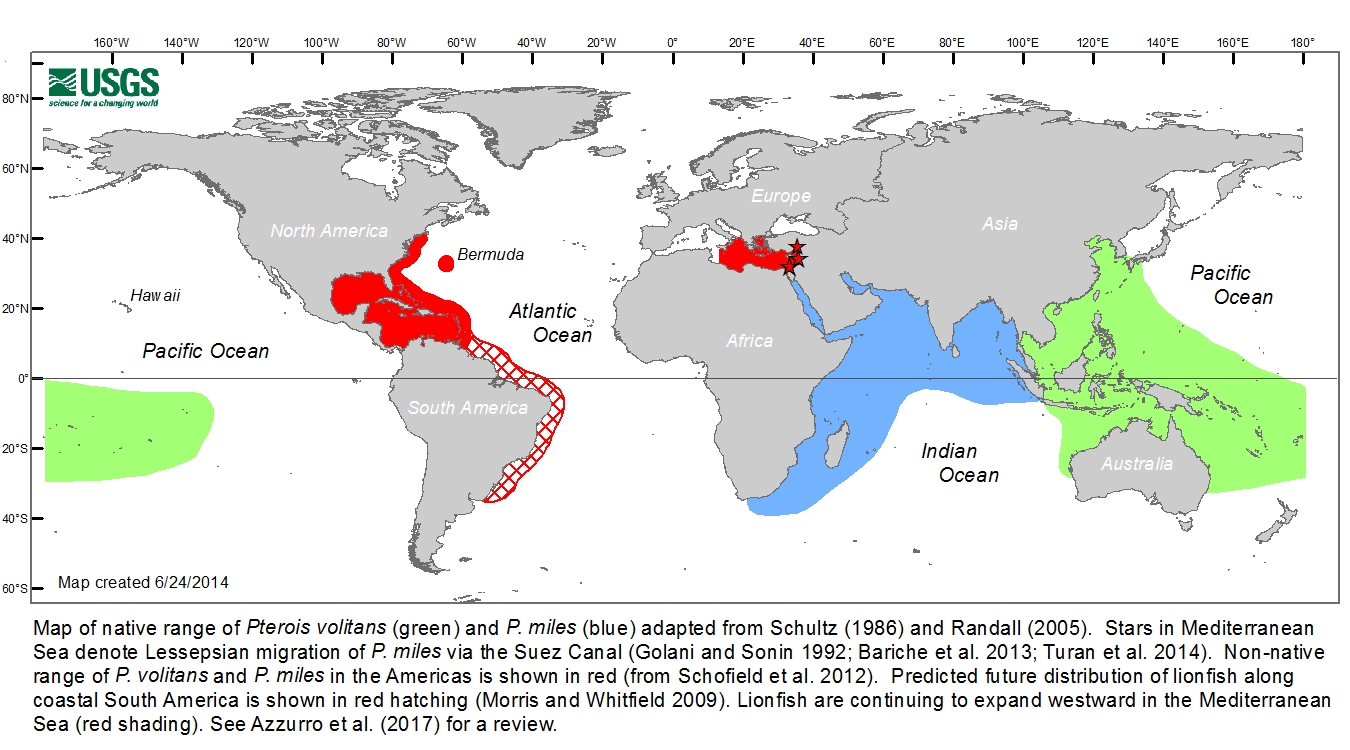
Even though lionfish are popular pets it appears as if some aquarium keepers along Florida’s Atlantic coast must have decided that they were more trouble than they were worth and decided to release their pets into the ocean. Once free the lionfish began doing what fish do and without their natural predators the lionfish population has exploded. Lionfish are now regularly found along the US coastline from Cape Hatteras in North Carolina to Texas and throughout the Caribbean islands.
The destruction caused by lionfish consists mainly in their preying on native species, particularly on the young fish of valuable game species. It is estimated that the increasing lionfish population could lead to a reduction of 80% in the biodiversity of Gulf and Caribbean coral reefs.
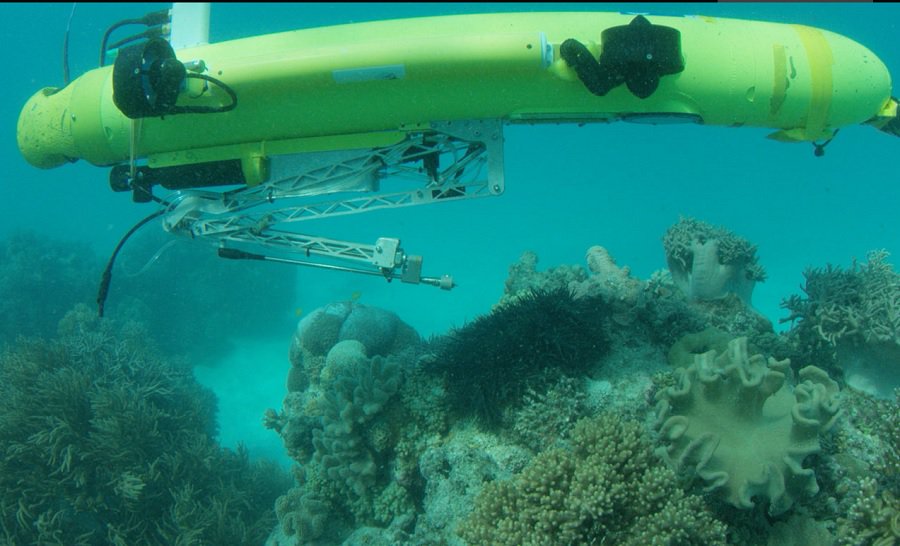
To combat their spread government and private conservation groups are developing programs to eradicate the lionfish from the waters they are now infesting. Currently biologists and fishermen are working to develop special traps and even robotic hunters that will catch lionfish without harming native species. At present however the most efficient technique for dealing with lionfish is spearfishing by scuba divers.
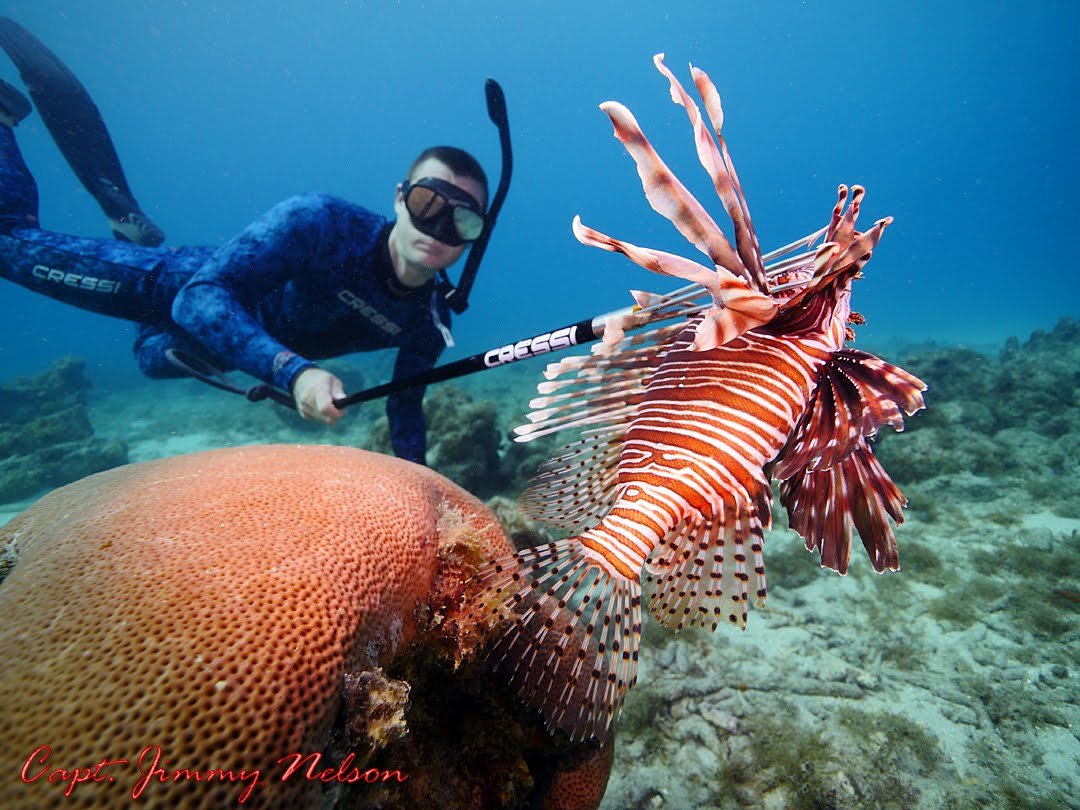

One helpful fact is that lionfish are quite tasty if you fillet them properly; remember they are venomous. So if oceanic scientists do actually develop a technique for large scale culling of lionfish don’t be surprised if someday you see lionfish offered at your local fishmarket.

Until then contests and fishing tournaments are being organized to increase interest in harvesting lionfish all along the eastern and gulf coasts. The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary has even gone so far as to license divers to hunt lionfish within its boundaries, a thing almost unheard of for a wildlife sanctuary.

Eventually lionfish will simply become a normal part of the marine environment along the southern US coast. In time other animals will learn to prey on them and that will impose a control on their population. In fact it appears that sharks may be immune to the lionfish’s venom, some scientists are even trying to teach sharks to prey on lionfish.
How much damage the lionfish will do to the biodiversity of the Gulf and Caribbean before then however can only be guessed at right now. A lot of trouble because of a few people who didn’t want to take care of the animals they bought thinking that they looked really cool!