With the Covid-19 virus continuing to spread, causing an ever growing number of illnesses and deaths across our planet the science of epidemiology has gone from being a little known branch of medicine to arguably becoming the most vital topic in the world. Literally ‘the study of what is on or among the people’ epidemiology was once the most successful branch of medicine, helping to eliminate such deadly diseases as cholera, typhus and yellow fever. Indeed the doctors and scientists who developed epidemiology succeeded in controlling many infectious diseases without any kind of a cure or in some cases having the slightest idea as to what was causing the illness.

The ancient Greeks recognized that while some diseases could spread from person to person throughout a population, other illnesses like epilepsy or cancer were not infectious. It wasn’t until 1543 however that an Italian doctor named Girolamo Fracastoro speculated that diseases could be spread by living particles too small to be seen that floated through the air. The invention of the microscope and the discovery that there actually were microscopic living creatures lent considerable weight to Fracastoro’s theory.
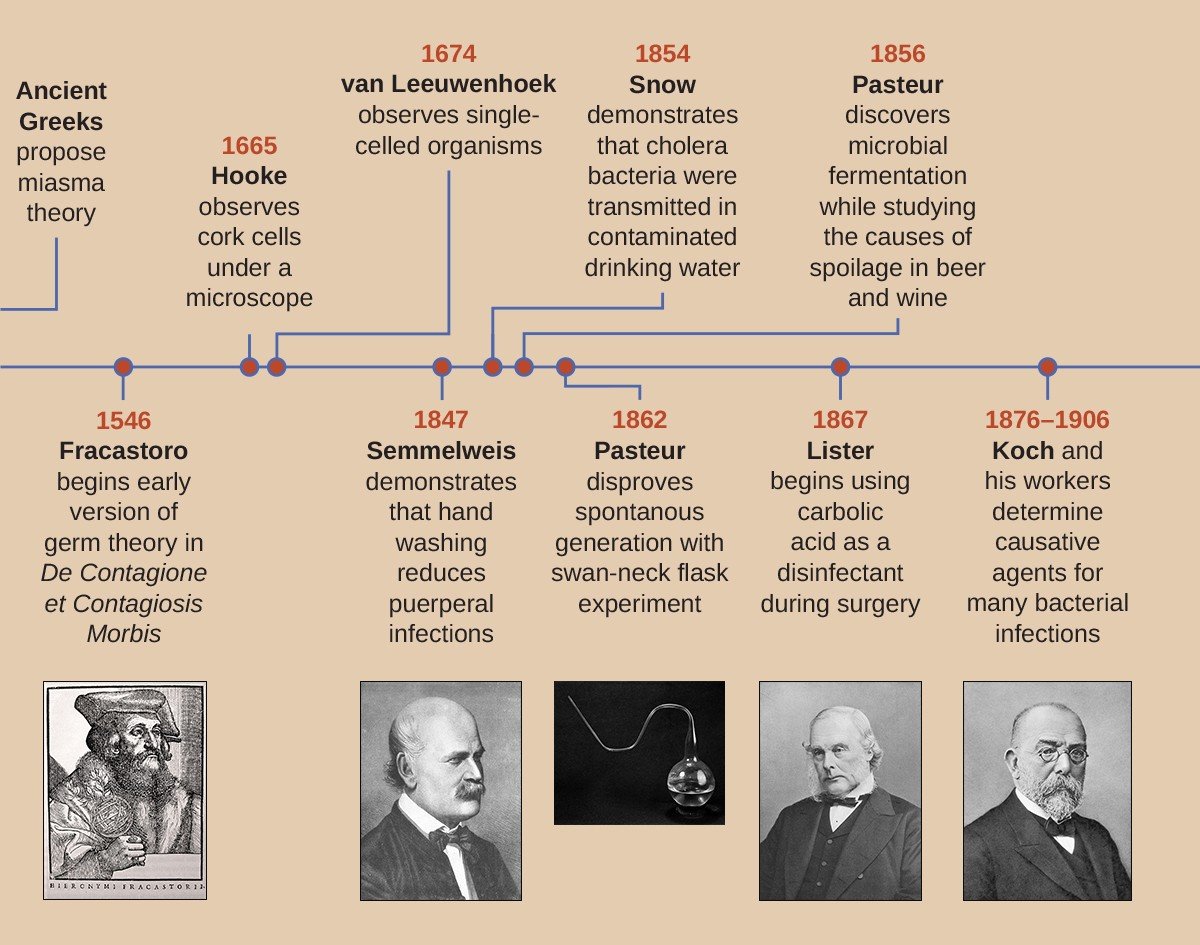
About a hundred years later in 1662 a part time mathematician, his day job was haberdasher, named John Graunt performed a statistical analysis of the mortality rolls of the city of London before and after the great plague of 1665-66. Graunt’s work provided much evidence supporting some theories about the spread of infection while at the same time disproving others and it established the use of mathematics in the study of diseases.

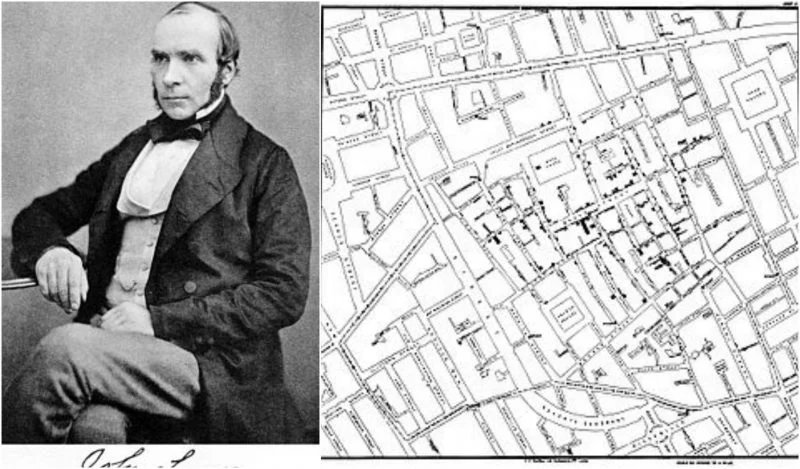
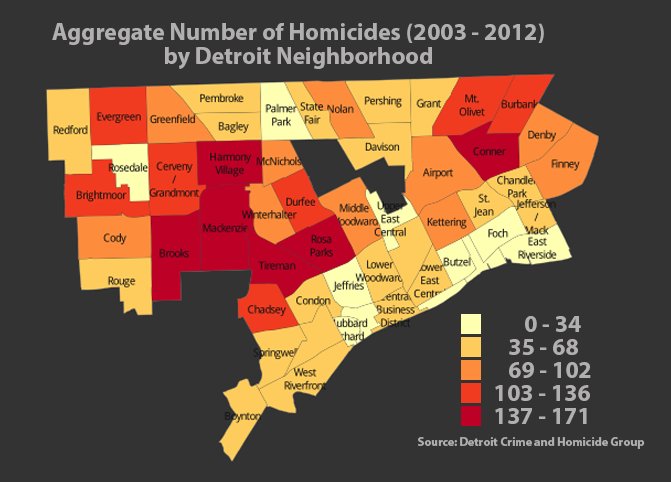
Another Londoner named John Snow became known as the father of modern epidemiology thanks to his work in 1854 leading to his discovering the cause of a number of cholera outbreaks striking the Soho section of London every few years. By simply marking the home addresses of cholera victims on a street map of London, see map below, Snow correctly concluded that the source of the infection was a water pump located on broad street. By disinfecting the water with chlorine and removing the pump’s handle Snow succeeded in ending the outbreak.

Another early pioneer was the Hungarian doctor Ignaz Semmelweis who dramatically reduced the infant mortality rate at his Viennese hospital by insisting on rules that promoted cleanliness. Then in the first decade of the 20th century Walter Reed achieved great success in fighting yellow fever in Cuba not by curing his patients who had contracted the deadly disease but by eradicating the mosquitoes who carried the disease from person to person.

You get the point; the purpose of epidemiology is not to treat the sick but instead to stop the spread of a disease in order to keep other people from becoming sick! That means that often times great advances in epidemiology are made by mathematicians rather than physicians. It has also allowed epidemiology to become the technique used to study social diseases such as obesity, deaths caused by smoking and even gun violence.
Right now of course the lessons learned from epidemiology are the only weapons we have with which to fight the viral disease Covid-19. Until we have either a vaccine or some really effective anti-viral drug all that each of us can do to protect ourselves is to practice the guidelines developed by epidemiology.
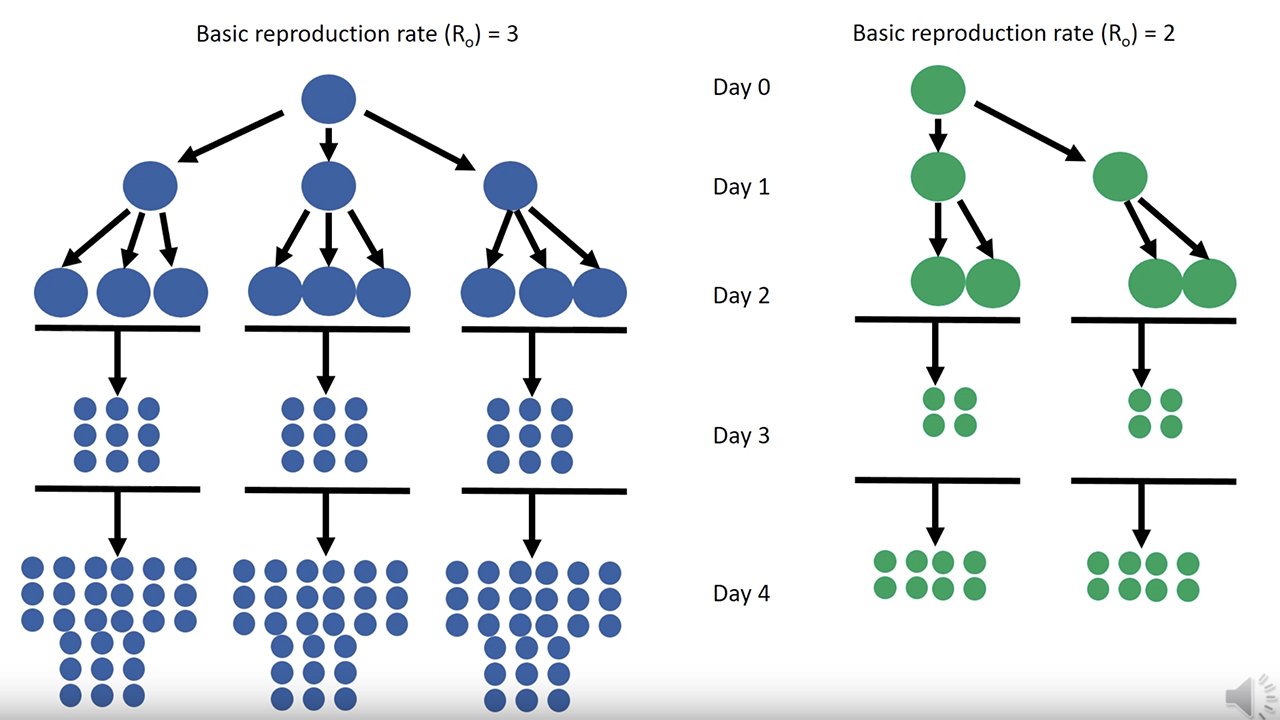
With that in mind it would be a good idea for all of us to understand some of the technical concepts that epidemiologists use to understand how a disease spreads and how we can reduce and control that spread. Probably the factor that is most important in determining, and controlling the spread of a disease is known as its Basic Reproduction Number oftentimes referred to as R-naught or just R0.
Simply put, for each person who becomes infected with a disease, R-naught is the average number of healthy people they will in turn infect. In others words, if you catch a cold and become infectious, R-naught is the number of members of your family, or your co-workers or just people you come into contact with that will catch a cold from you. This also means that if R0 for a disease is greater than one, then the number of people infected is going to grow. For example if R0 for a disease is two then one person will infect two people, those two will go on to infect four and the four will infect eight and so on until almost everyone has, or has had the disease.
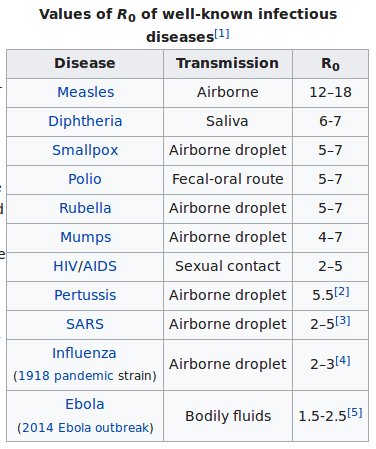
Under normal conditions in human society there are many diseases that have an R0 much greater than one. The table below shows the estimated R0 numbers for some well-known diseases.
Obviously the goal of epidemiology is to find methods and procedures that a community can take that will reduce R-naught for a disease below one. Perhaps the simplest technique is called ‘Social Distancing’ and it just means having everyone in a community reduce the amount of contact that they have with everyone else. No shaking hands when you meet someone, no hugs for friends you haven’t seen in years, also no parties and no big crowds at sports events or concerts. Social distancing works because less contact between people makes it less likely that a germ will pass between them.
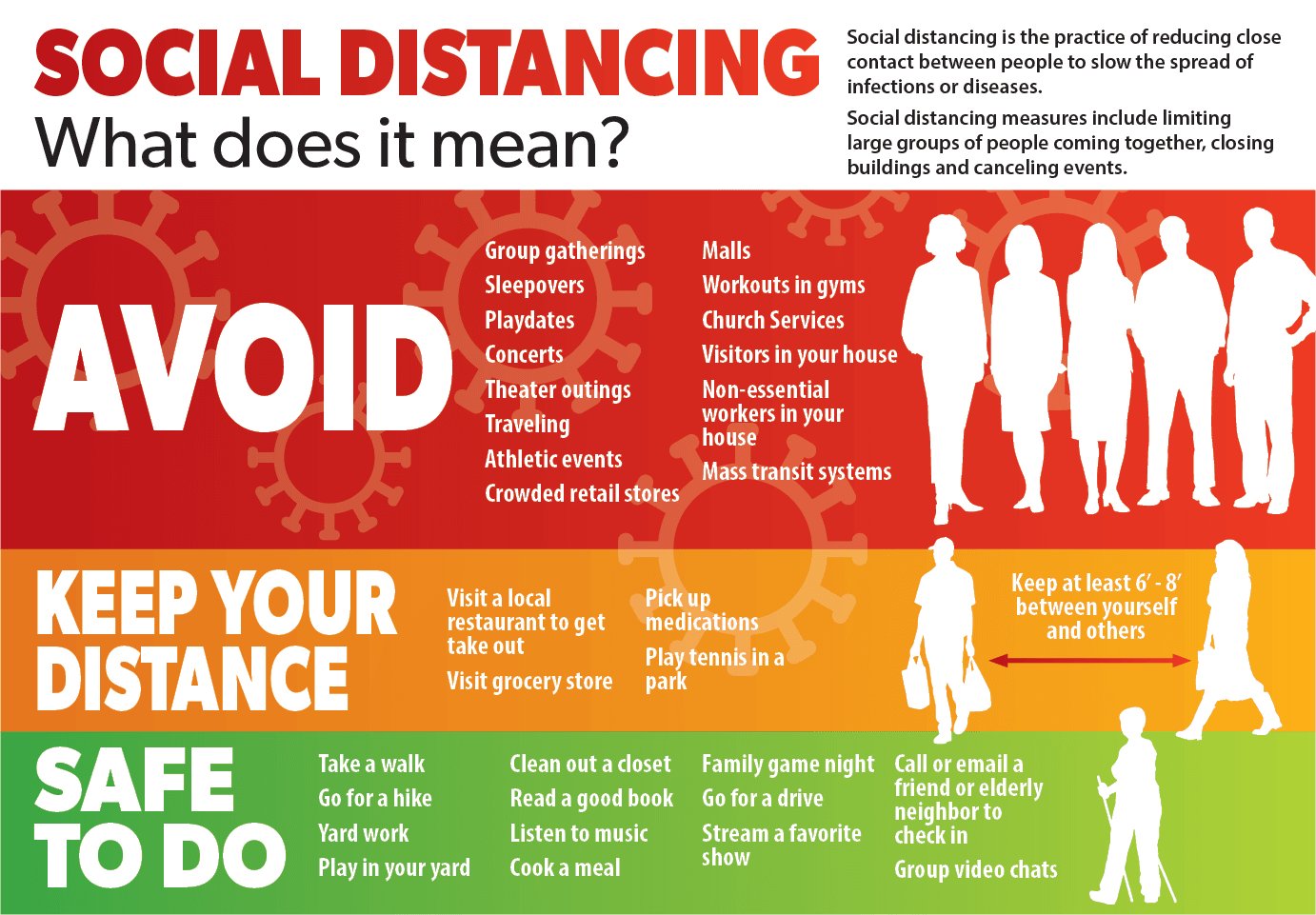
Looking back at the table you can see how many diseases spread through particles or droplets in the air. Those particles can only travel through the air for about three or four meters so if everyone stayed more than four meters apart those diseases could not spread. R0 would go very close to zero.
Of course such extreme social distancing is not really possible, we live in families and the jobs of many people are so essential that society cannot get along without them. We live in a society and that society requires a certain amount of contact between its members. That’s why other procedures, such as washing hands, disinfecting everything other people touch, and wearing face masks become so important. In fact anything that we can do to reduce R-naught is important, it is at present the only way we have to fight Covid-19.
Now for many viral diseases those people who are infected and recover acquire an amount of immunity to being re-infected. In such cases, once a majority of the population has been infected the spread of the disease is inhibited because there are now fewer victims left to infect. Not only that but actually the people who have become immune get in the disease’s way, getting between those who are infectious and those who have not yet been infected, effectively generating a macabre form of social distancing. This acquired immunity of the majority of a population is known as ‘Herd Immunity’.Herd immunity should be considered the last resort in fighting a disease however because it results in the maximum number of deaths and hospitalizations of sick people. Basically getting to herd immunity means not fighting a disease and just letting people get infected.
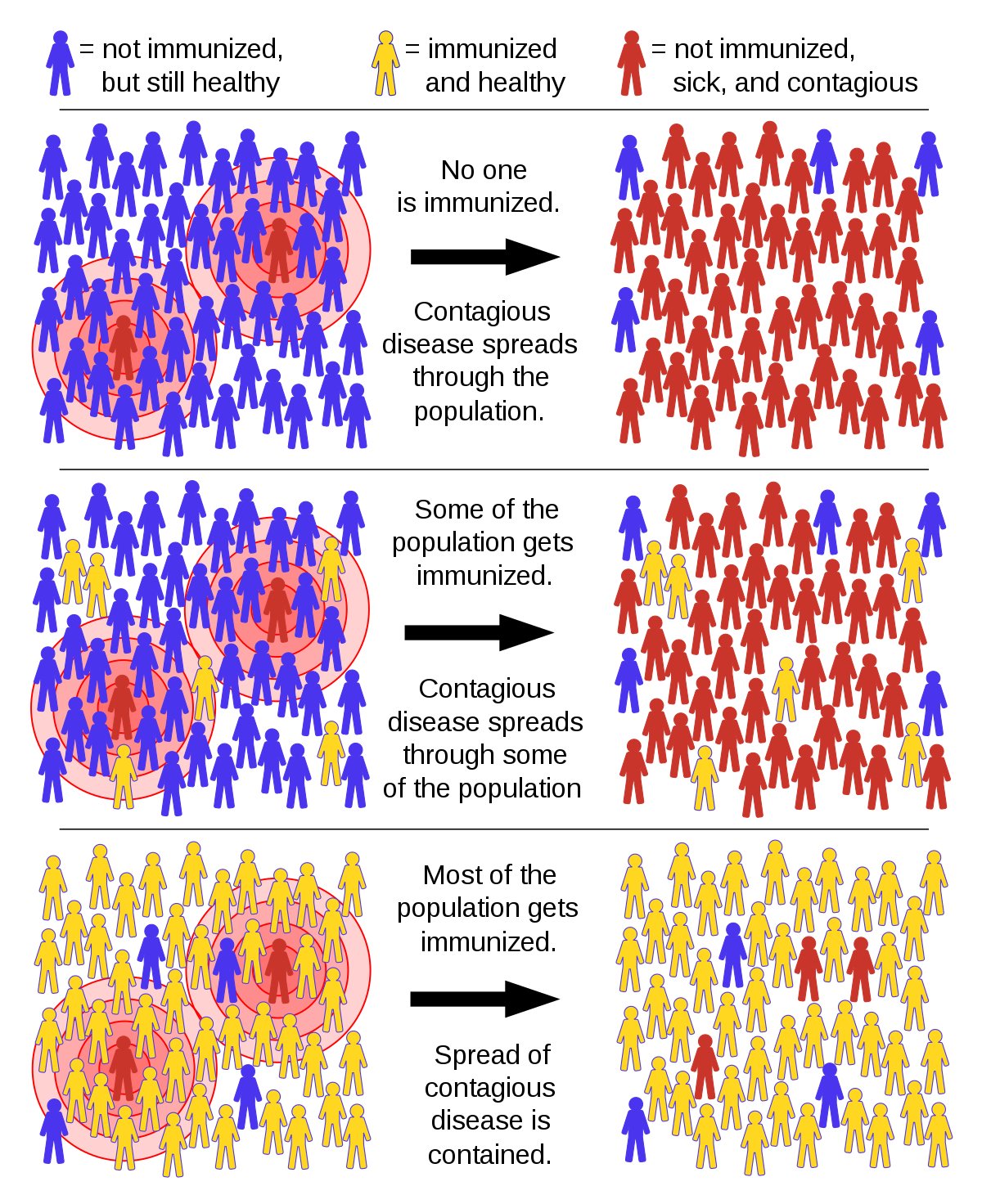
Surprisingly there are many people who believe that is the best solution to Covid-19. Indeed the entire nation of Sweden has decided to forego all social distancing measures and just let the disease die out on its own.
One last point, when and if a vaccine is developed that is effective against Covid-19 it will grant immunity to people who have not yet been infected by the disease. In epidemiological terms a vaccine therefore works by getting a population to herd immunity without people dying or being admitting to a hospital, without them getting sick at all. Something I’m certain that we are all looking forward to!
