Once again the US is in a critical election year and once again it’s the economy that is the number one issue that voters care about. That means that once again both parties are filling the TV airwaves with ads claiming that they are the ones who can best handle the economy. I know that you’ve seen the Republican ads claiming that under Biden inflation was the worst in 40 years, it was but only for one month.

The Democrats meanwhile claim that unemployment under Biden has been at its lowest level in 60 years, it was but over the last few months it’s been creeping up. Meanwhile, under the Democrats wages have been steadily rising, but have they been rising enough to offset inflation? It’s all so confusing and with both sides only talking about the statistics that makes them look good it’s hard to know what to think.

Well I’m going to try to give it a shot. I have to tell you this is the most difficult post I’ve ever attempted. Economists not only have a large number of different quantities, Inflation, Unemployment, GDP and the like that they keep track of but they have several different ways of reporting those measurements. For example the Consumer Price Index, considered the best gage of inflation, is reported every month but announced as being ‘on an Annual Basis’. How can something that’s measured every month be on an annual basis? And most of the other quantities that economists talk about, like GDP and wages, but not unemployment, have to be adjusted for inflation. It’s no wonder that few people can make heads or tails about the claims being made by the Republicans and Democrats. However at least I will try to bring all the stats together, not just the ones that favour one side, and hopefully I’ll be able to explain it all enough for you to make the decision that’s right to you!

I have to start with inflation because, as I just said several other quantities have to be adjusted for inflation in order to make a fair comparison between what happened during the Trump administration from 2017-2020 and the Biden administration from 2021-2024. We all have a basic idea of what inflation is, prices keep going up, as time passes the cost of just about everything from food to gas to cars and even homes keeps rising year after year. That means that a dollar in 2024 buys a little bit less than a dollar would back in 2023 and a lot less than a dollar would have back in say the year 2000.
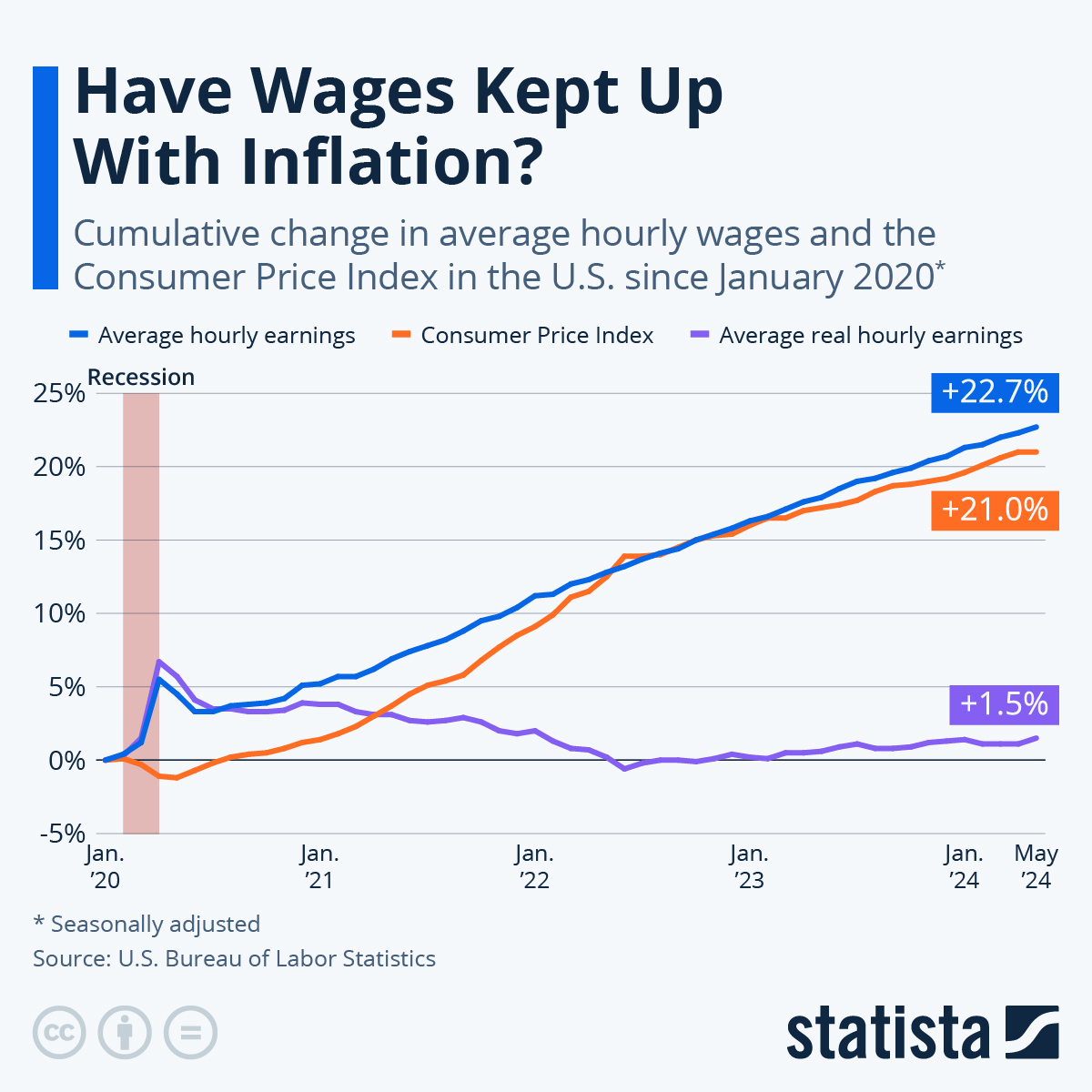
As I said inflation also affects several other economic measures as well, such as wages. Let’s say that last year your boss gave you a raise of 4%, sounds pretty good. Unfortunately inflation over the last year came in at 4.1% so you actually lost 0.1% of your pay. In economic terms your wage increase did not keep pace with inflation. On the other hand if you received a raise of 4% and inflation stayed below the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%, then you did indeed get an actual 2% increase in your income, your raise minus inflation.
Inflation also affects our whole nation’s growth in the same way. We’ve all heard of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) which is the sum total of all goods and services bought and paid for in a year, everything and every time money changes hands it contributes to the GDP. The growth of our country’s economy is measured in the percentage growth of GDP and if GDP actually goes down we are basically in a recession. But even an increase in GDP has to be higher than the rate of inflation or else, as with wages above, the country’s income actually got smaller. On the other hand two quantities that are not effected by inflation are unemployment and job growth. The percentage of people who are unemployed is the same no matter what happens to the value of the dollar. The same is true for the number of jobs created, or lost.
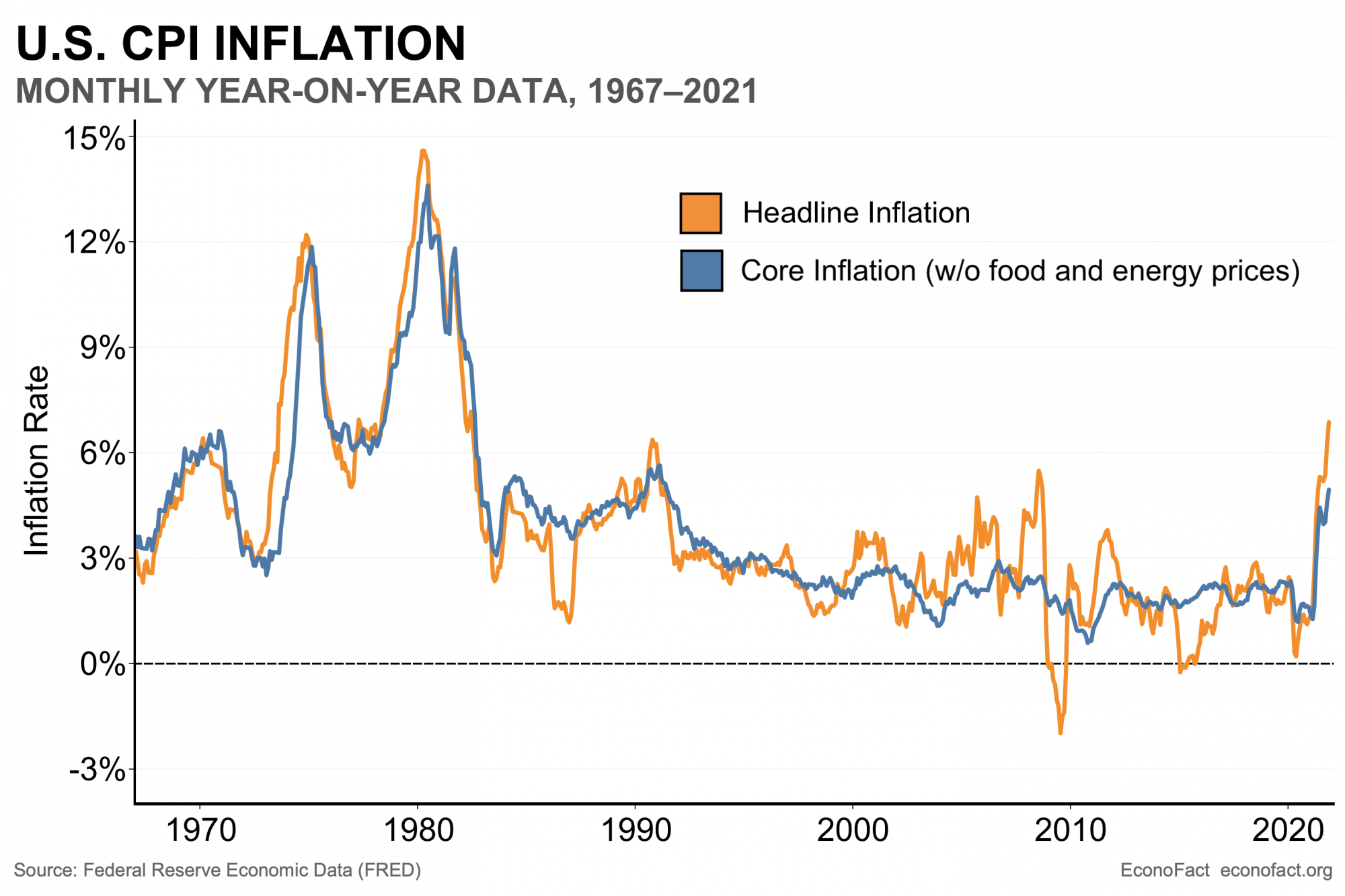
Throughout this post I have taken the various economic quantities effected by inflation and adjusted their values so that everything is given in terms of 2024 dollars. So now let’s take a look at how inflation has increased during the four years of the Trump administration and the first three and a half years of the Biden administration, remember Biden’s term is not yet over. Chart 1 shows how inflation increased for each president.
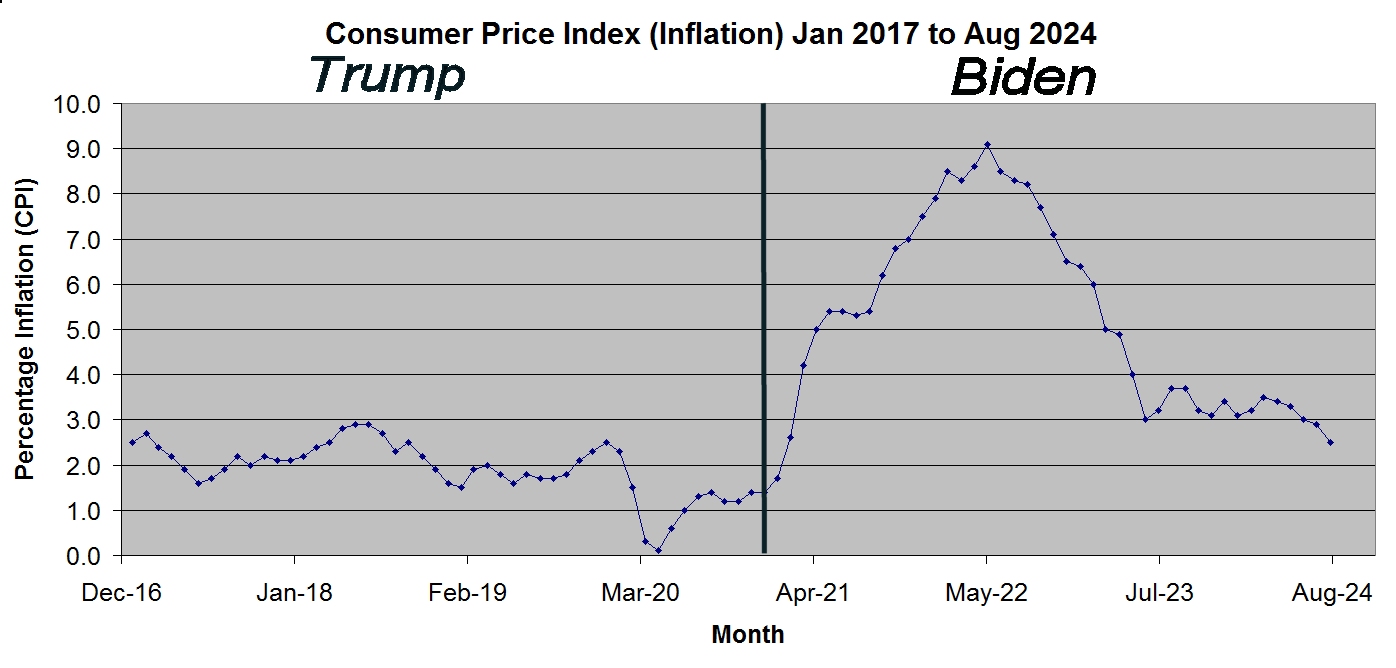
On the surface it looks as if inflation has been much higher during Biden’s term as President. Indeed the Republicans have been using this fact as their main attack against Democrats in general claiming that inflation under Biden reached its highest level in 40 years. It is worth noting however that the one bad year that Biden had with inflation also was the year that the US and the rest of the world came out of the Covid-19 pandemic.
You will remember that during the pandemic a considerable portion of the economy shut down and once the threat of Covid had lessened there were a number of issues getting people back to work, fixing supply chain problems and etc. For example, during Covid people cut back a lot on travel, even such ordinary trips as going to a restaurant for dinner. Further evidence that it was Covid that triggered the inflation comes from the fact that the rest of the world saw as high or higher inflation. The European Union, the UK, China and Japan all suffered from a spike in inflation.
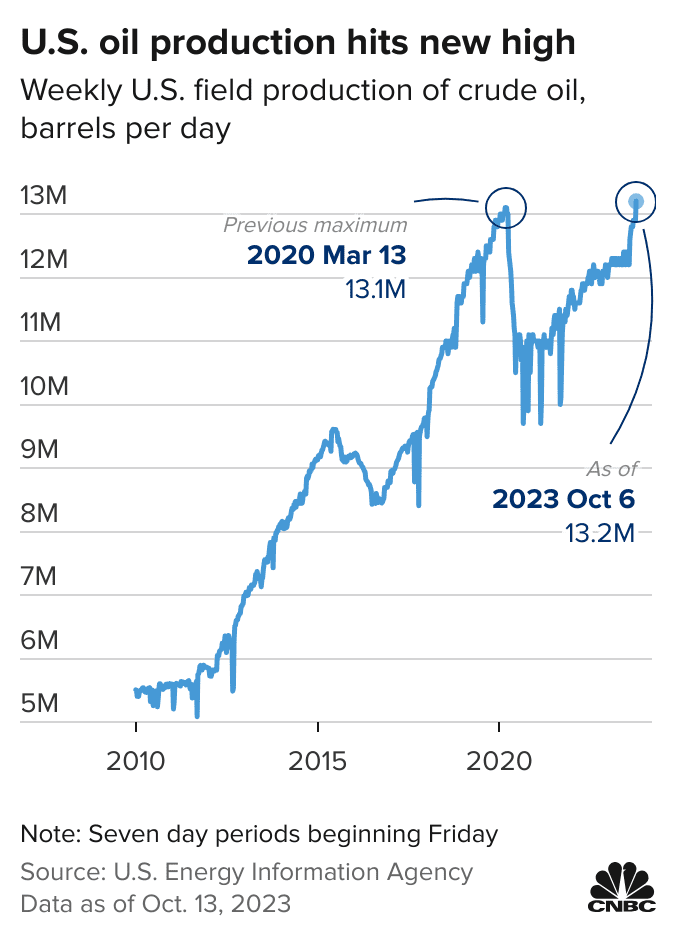
Because of this oil companies cut back on their production of gasoline and then, when the pandemic ended people immediately wanted gas again. Unfortunately it took the oil companies some time to bring production back to pre-covid levels. That time lag led to a big increase in gas prices that contributed to inflation. That supply issue was eventually solved however and for the past two years gas prices have dropped slowly but surely helping to stabilize inflation.
So now that we’ve considered the Democrat’s biggest economic liability going into this election let’s a look the Republicans’ biggest liability. That’s unemployment and if you’re going to blame Biden for the worst inflation in 40 years then you have to blame Trump for the worst unemployment since the Great Depression of the 1930’s, 80 years ago.
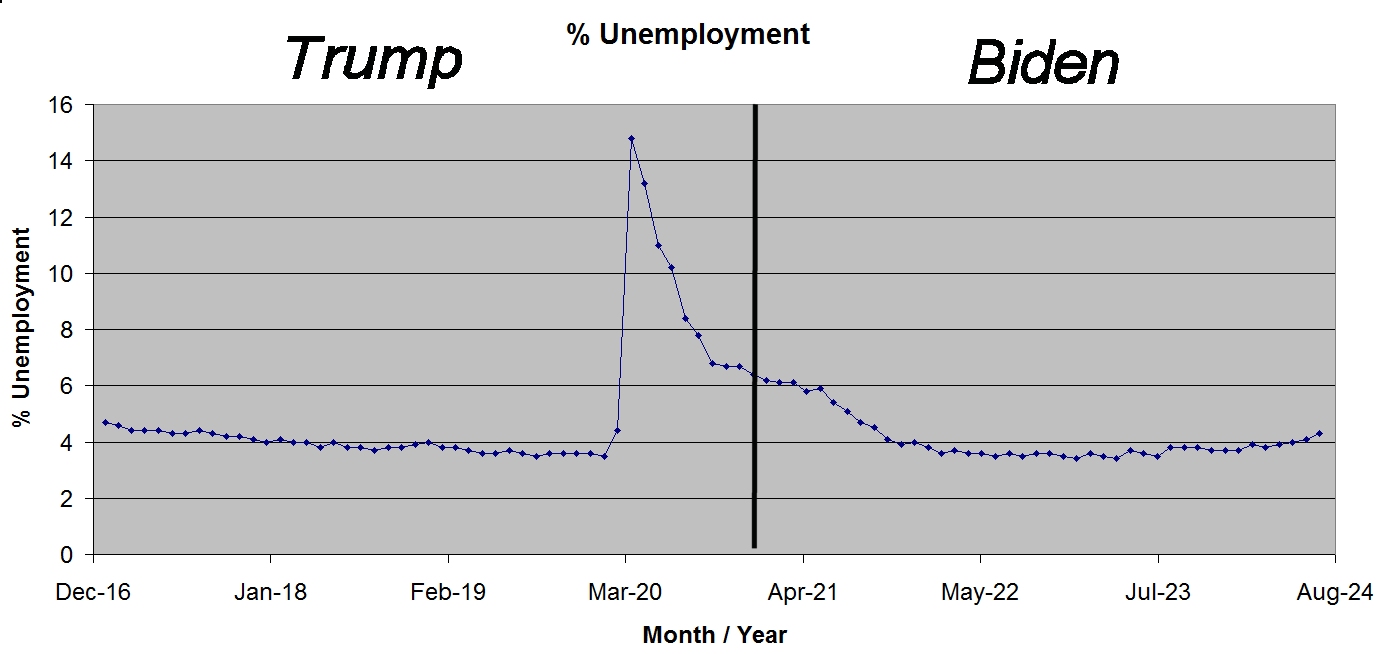
Actually unemployment for Trump’s first three years in office was quite good. The unemployment level his first year was a bit over 4% but dropped below 4% for Trump’s second and third year. Then in 2020, Trump’s fourth and final year in office unemployment skyrocketed to nearly 15%, literally the worst unemployment figure since the Great Depression back in the 1930s. So what happened to cause such a tremendous number of people to lose their jobs, well of course it was Covid.

With the pandemic spreading, with deaths and hospitalizations increasing the hospitality industry, restaurants, hotels, movie theaters etc, virtually closed because people could not gather together for fear of getting infected. Baseball games were played without fans in the seats so there were no concession stands that needed any workers; symphony orchestras stopped performing so there was no need for musicians. The fact that unemployment didn’t go higher than 15% during Covid was remarkable and shows the strength of the American economy. Once Covid became less of a threat unemployment quickly dropped. Indeed for almost two years during Biden’s term of office unemployment dropped to its lowest level since the 1960s. A statistic the Democrats are happy to remind us all about.
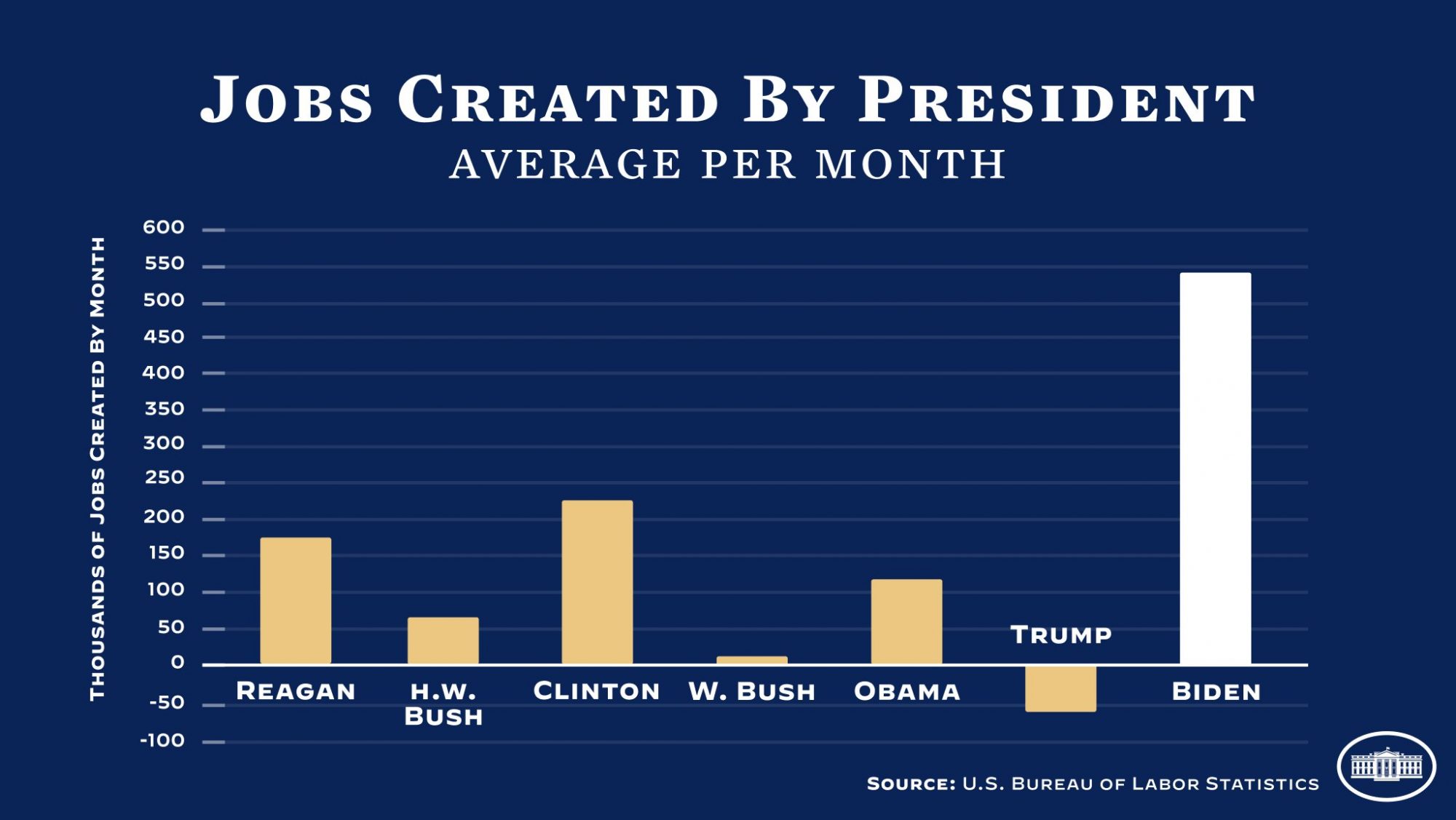
So, if you’re going to blame Biden and the Democrats for the worst inflation in 40 years then you have to blame Trump for the worst unemployment in 80 years. The plain fact is that no one is to blame, that both unemployment and the inflation that followed were caused by Covid. The lesson to be learned here is that there are factors outside the control of anyone, even the President that shape our economy.
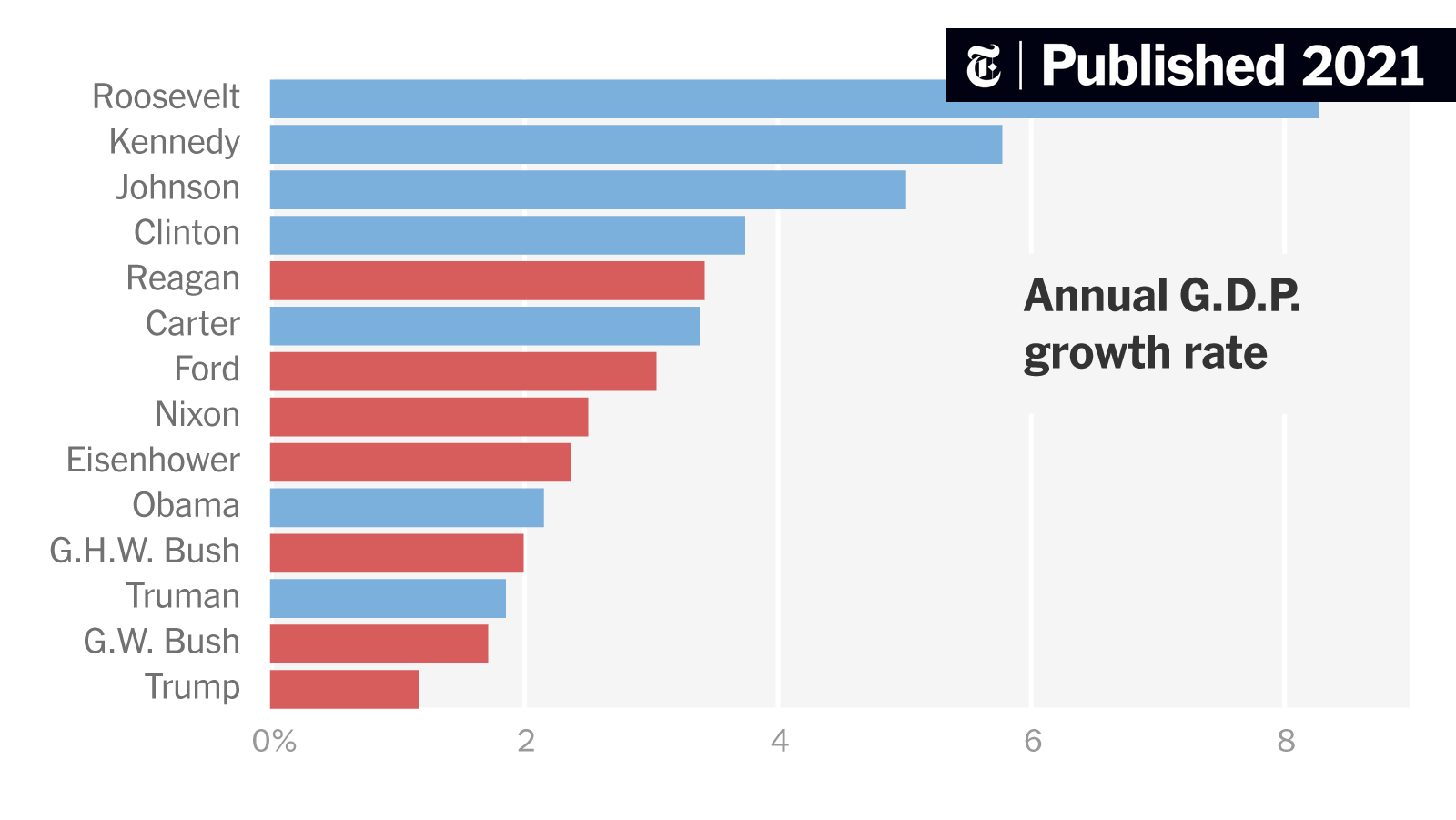
In my next post I’ll continue to discuss some other economic factors such as wages, GDP and the Deficit and how both Trump and Biden handled them.