In my post of just two weeks ago, January 4th 2020, I talked about the possibility that the Red Giant star Betelgeuse might be about to explode as a Type 2 Supernova (SN2). At the end of that post I made an offhand remark about writing a post about Type 1 Supernovas (SN1) in order to clarify the difference between the two types. Well I recently came across a couple of papers concerning SN1s so I decided that now was as good a time as any to fulfill my promise.
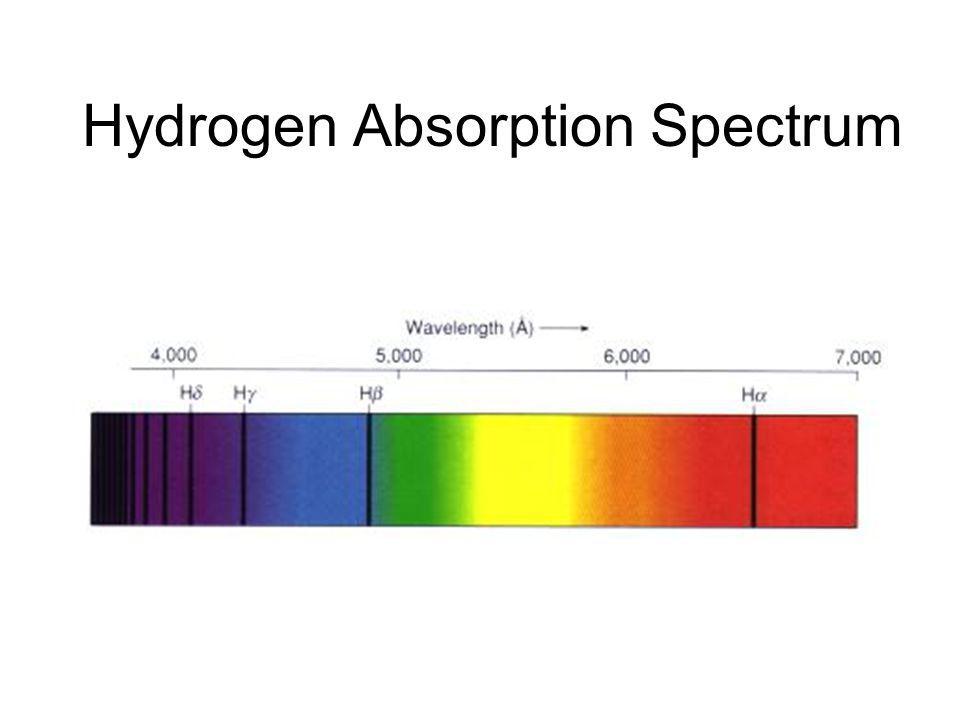
First of all I suppose I should start by describing how an astronomer distinguishes one type of supernova from the other when they observe one. They do this by breaking up the light from the Supernova into its spectral lines that show the elements giving off the light. In SN1s the spectral lines of hydrogen will be completely absent while in SN2s the spectra will indicate a fair amount of hydrogen. Other observational differences have been seen in a few individual Supernovas, ones near enough to observe additional details, but the presence or absence of Hydrogen is the consistent difference. Everything else is really just theory.
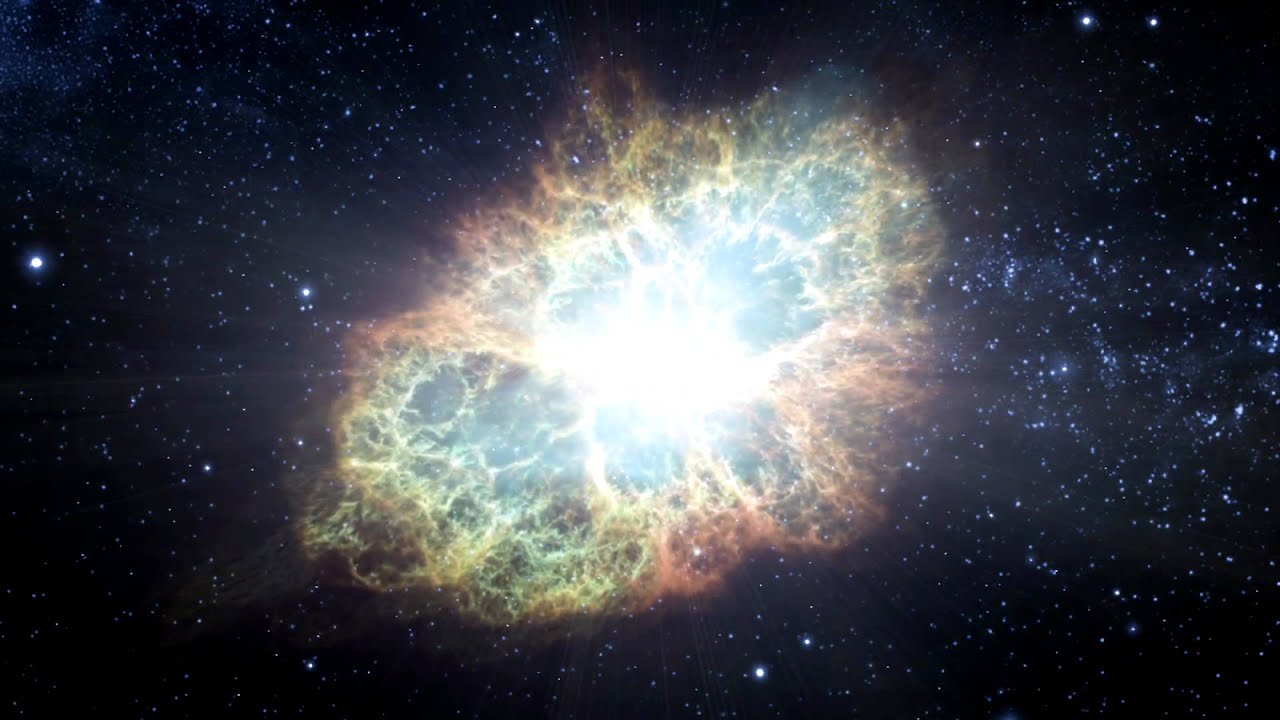
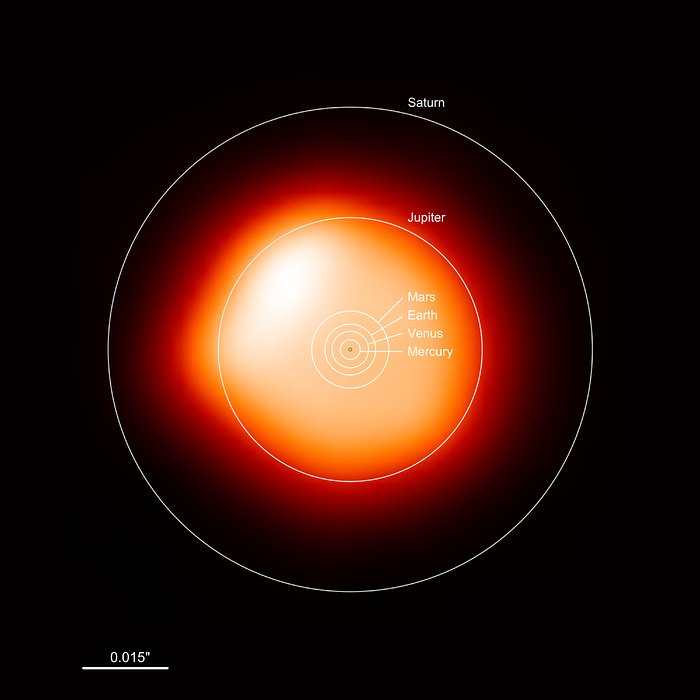
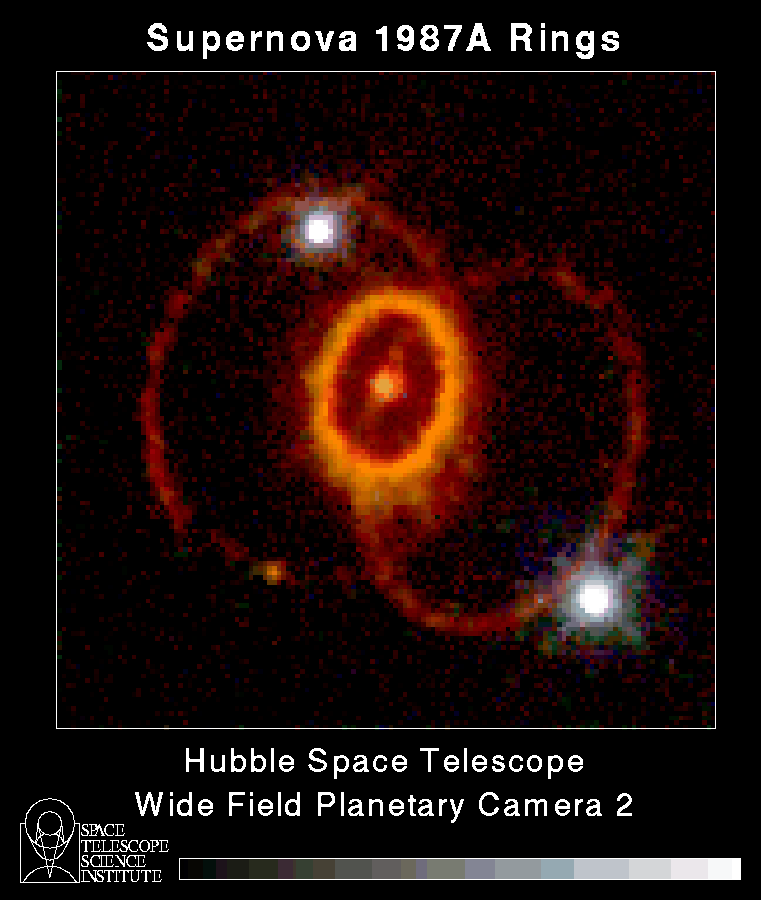
So let’s examine the theories, SN2s first. As I discussed in my post about Betelgeuse, SN2s begin as stars that are ten times or more as massive as our Sun. Such stars race through their nuclear fuel very quickly, millions instead of billions of years. As the star begins to run out of its fuel it puffs up into a red giant like Betelgeuse is now. When that fuel is completely used up the star’s core collapses because of gravity but that collapse triggers an explosion of the star’s outer layers as a Supernova. Since the outermost layers of the star still possess some hydrogen, that element’s spectral lines are seen in the Supernova’s light letting astronomers know that it is an SN2.

SN1s could hardly be more different. For one thing a SN1 can only occur in a double star system. In addition one of the stars must have already gone completely through it’s energy production life span and is now a burnt out cinder known as a white dwarf. White dwarfs can be as massive as our Sun but are crushed down to the size of a planet like Earth. Because they are so dense, and under such immense gravitational force, the material of a white dwarf is not made up of normal atoms as here on Earth, with electrons orbiting around a nucleus. Instead the electrons are squeezed into their nuclei and all of the nuclei are pushed much closer together than in normal matter, because of this the spectra of a white dwarf shows no sign of the presence of hydrogen.

There’s another peculiarity about white dwarfs as well. White dwarfs can only be so massive, a value known as Chandrasekhar’s number, which is equal to about 1.4 times the mass of our Sun. Any heavier and the white dwarf will continue to collapse down into a neutron star or black hole. That collapse triggering its outer layers to explode as an SN1.
So where would an otherwise stable white dwarf star get the extra mass needed to make it exceed Chandrasekhar’s number and explode as a SN1? From its companion star that’s where, which is why SN1 only occur in binary star systems. Astronomers have in fact observed binary systems where a white dwarf’s intense gravity is pulling matter away from its companion, a situation that will eventually lead to a SN1.
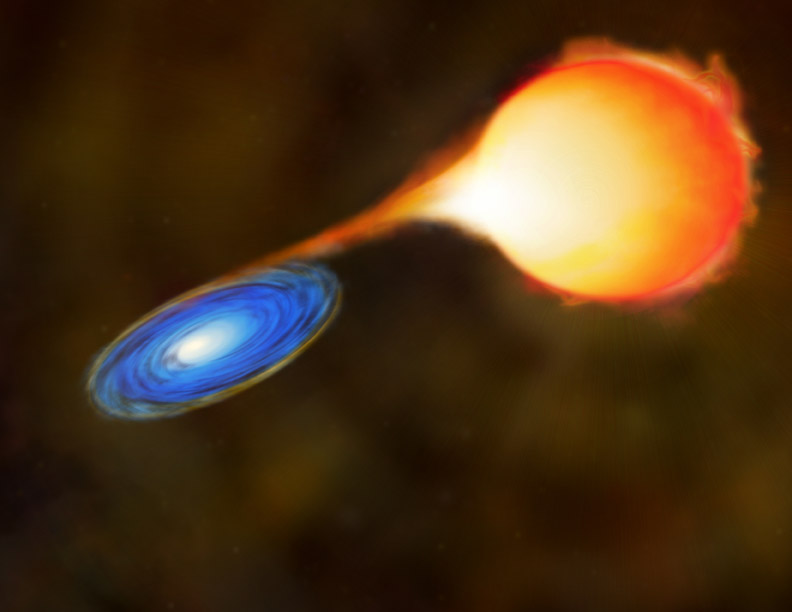

And now astronomers Bradley E. Schaefer, Juhan Frank and Manos Chatzopoulos of the Department of Physic and Astronomy at Louisiana State University have used some very precise measurements of the faint star V Sagittae in the constellation Sagitta to actually predict that it will explode as a SN1 in or about the year 2083. In fact V Sagittae is already rapidly increasing in brightness, currently shining at 10x the brightness it did when it was first accurately measured back in 1907.
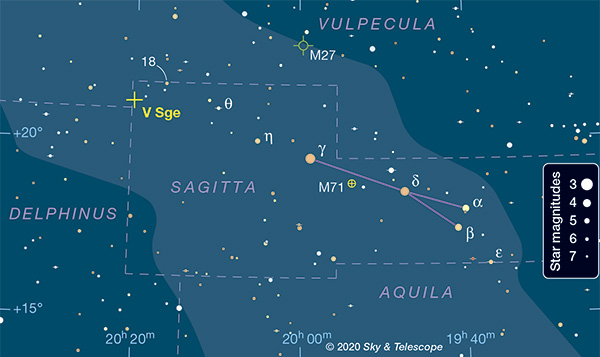
This rapid increase is likely to continue over the next decades as the white dwarf devours its companion. Eventually the star, which currently cannot even be seen with the naked eye, will become as bright in our sky as the star Sirius, or perhaps even the planet Venus, but not for long. How accurate the prediction about when V Sagittae will go Nova remains to be seen but you can be certain that astronomers will be keeping a close eye upon it for many years to come.
Another interesting thing about SN1 is that since they only occur when a white dwarf’s mass goes above Chandrasekhar’s number then all SN1 should be pretty much the same. That is, each SN1 should release the same amount of energy. If that is true then a SN1 can be used as a ‘standard candle’ to accurately measure distances throughout the Universe.
You see the distance to an object in deep space is the most difficult thing there is to measure in astronomy. We have many theories about the Universe that cannot be either confirmed or falsified simply because we can’t measure distances accurately enough to really be certain we know exactly what is going on. But if we know precisely how much energy an object puts out no matter where it is in the Universe, like a SN1, then we can measure how bright it appears in our sky and a simple formula tells us how far away it is.
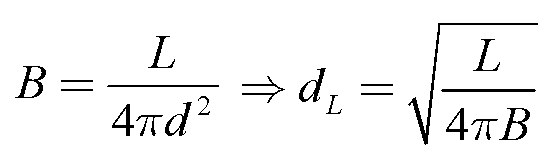
Astronomers did just that back in the 1990s, using SN1 to accurately measure the rate at which the Universe is expanding. It was those measurements that indicated that the expansion of the Universe was actually accelerating, that ‘Dark Energy’ was pushing the Universe apart faster. This was the first and still the best evidence for the existence of Dark Energy.
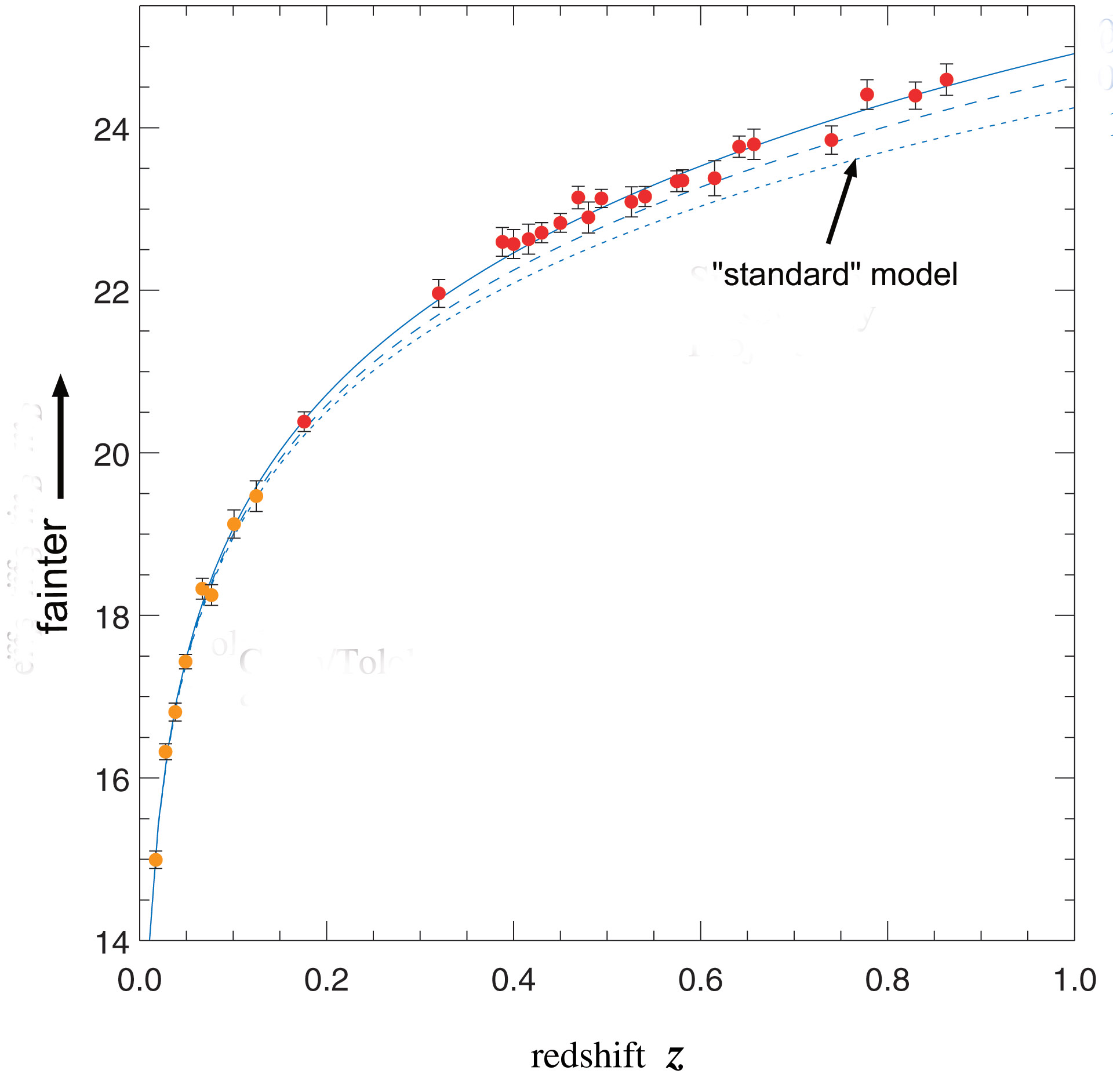
Now a new study threatens to upend all of that. Astronomers from the Department of Astronomy at Yonsei University in South Korea along with the Korean Astronomy and Space Science Institute have made highly detailed measurements from 60 SN1 events and have found that the absolute luminosity of an SN1 changes with the age of the Universe at which time the SN1 occurred. In other words SN1 have evolved over time. In fact if the changes in luminosity with time described in the paper are taken into account then the acceleration of the Universe simply disappears, there’s no such thing as Dark Energy!
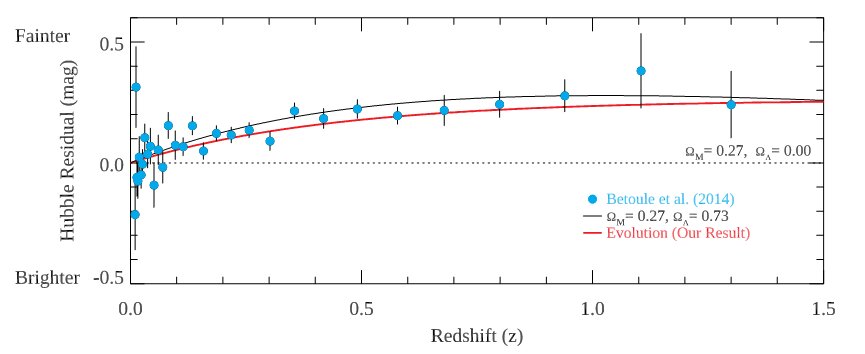
If this study is true it would undo much of the Astronomy of the last 30 years, but other astronomers have to review it first, check the data, make some more measurements to be certain. Whether or not SN1 can be used as a ‘standard candle’ is an important matter for Astronomers but regardless of the answer to that question they are still an awesome example of the many different objects in our Universe.