NASA has just scored another success in its long term goal of exploring the planet Mars. The Insight space probe survived its ‘Seven Minutes of Terror’ ride through the atmosphere of Mars to a successful landing at about 2:50PM EST or 1950 hours Astronomers Time (GMT) on the 26th November 2018. Unlike NASA’s best known missions to the Martian surface Insight is not a rover vehicle but instead a stationary platform for instruments which it is hoped will discover a great deal about the interior of the red planet.
Insight’s journey to Mars began back on May 5th 2018; see launch image below, and the spacecraft traveled nearly 500 million kilometers to reach its destination. Now Mars hasn’t exactly been easy on the probes we’ve sent to study it, more than half of all missions sent there have ended in failure. One of the big reasons for this is the Martian atmosphere which is too thin to bring a spacecraft to a full stop, the way we use Earth’s atmosphere, yet it is still much thicker than the Moon’s making it difficult to use rockets all the way down.
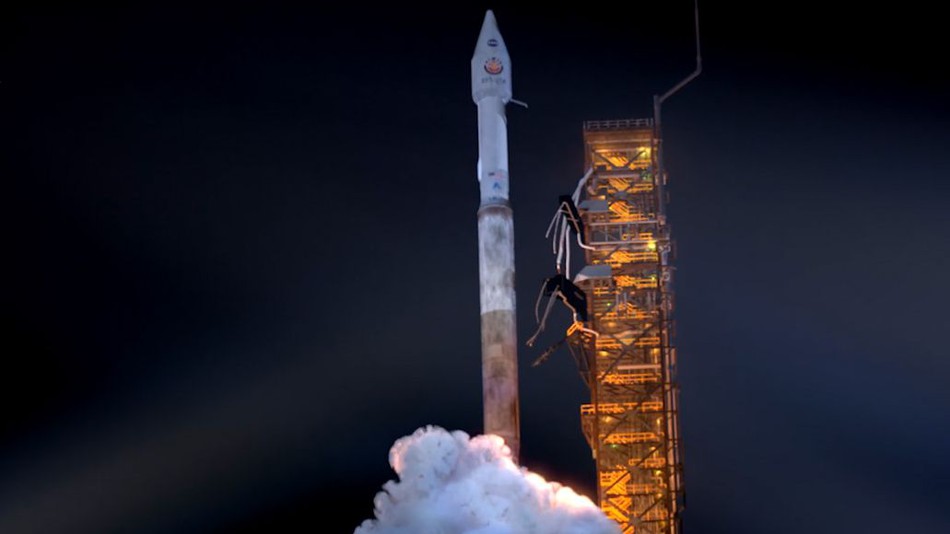

Another reason the scientists and engineers who built Insight at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory consider the actual landing to be so nerve wracking is that they have no way of controlling Insight during those dangerous seven minutes. All that the people at Mission Control can do is watch while the spacecraft either performs each of the steps programmed into it at just the right moment, or the whole mission fails.
You see, as the spacecraft enters Mars’ atmosphere the planet is about eight light-minutes distance from Earth. That means that it takes any signal from Insight eight minutes to reach Earth and be received. So if anything does go wrong by the time Mission Control knows about it, and a correction can be sent back to Insight 16 minutes will have passed and the spacecraft will be nothing more than a hole in the Martian surface.
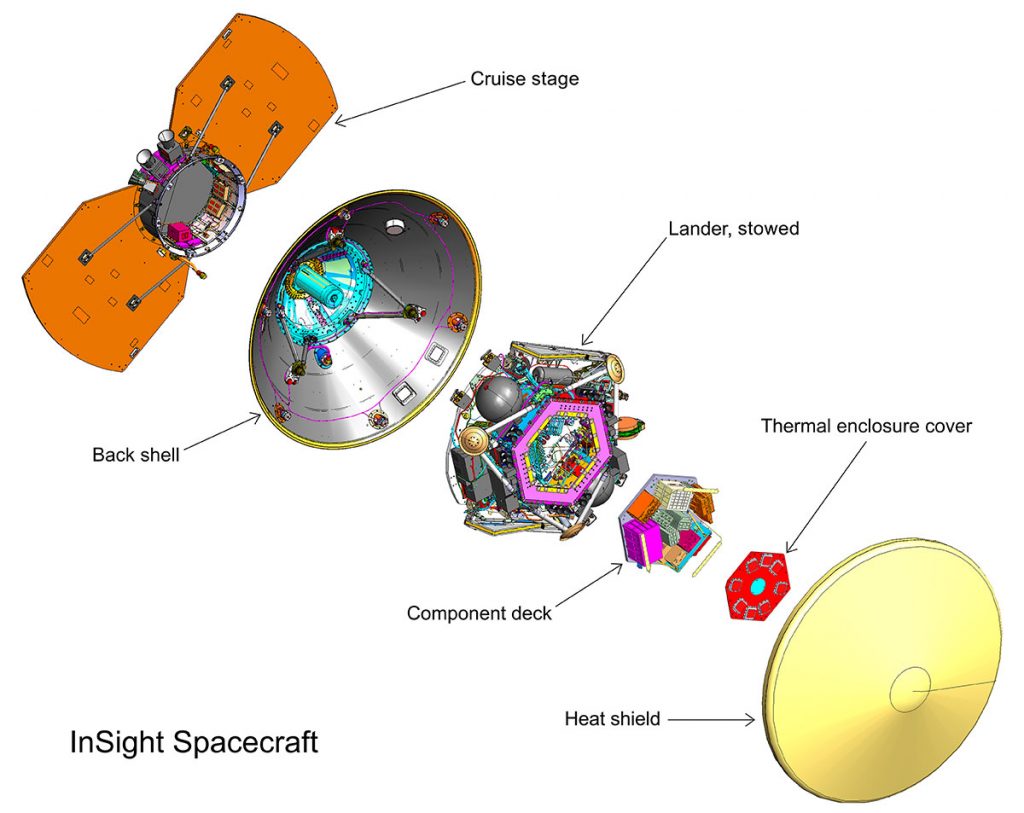
The sequence of events actually begins just before Insight hits the atmosphere as the spacecraft’s cruise stage and backshell are discarded. These protected the lander during its voyage from earth while providing it with power, see image above. Entering the atmosphere at about 20,000 kilometers per hour air resistance caused the spacecraft’s heat shield temperature to rise to more than 5,000 degrees Celsius. Once the craft had been slowed to about 1,500 kph a parachute was deployed and the heat shield detached.
At this point the lander’s legs deployed and its onboard radar began to measure the remaining distance to the ground. When the radar measured the distance as 600 meters Insight released its parachute and used 12 small rockets to control its descent the rest of the way.
Now remember, because of the time delay in a radio signal traveling from Mars to Earth by the time Mission Control had received the signal that Insight had entered the atmosphere the lander was actually already safely on the ground. Think of that; imagine yourself in Mission Control watching as the telemetry comes in. Everything looks good but your information is eight minutes late. You have no idea if anything went wrong after the signals you’re looking at were sent. You can only hope for the best!
Insight did land safely however, the landing went flawlessly and five minutes after JPL received the signal that the landing was accomplished the probe sent back its first image, see below. The image is covered with dust because of particles kicked up by the landing but you can see the Marian sky at the top along with something of the ground around the lander. Once the protective lens cover was removed the second image is much clearer, also below.
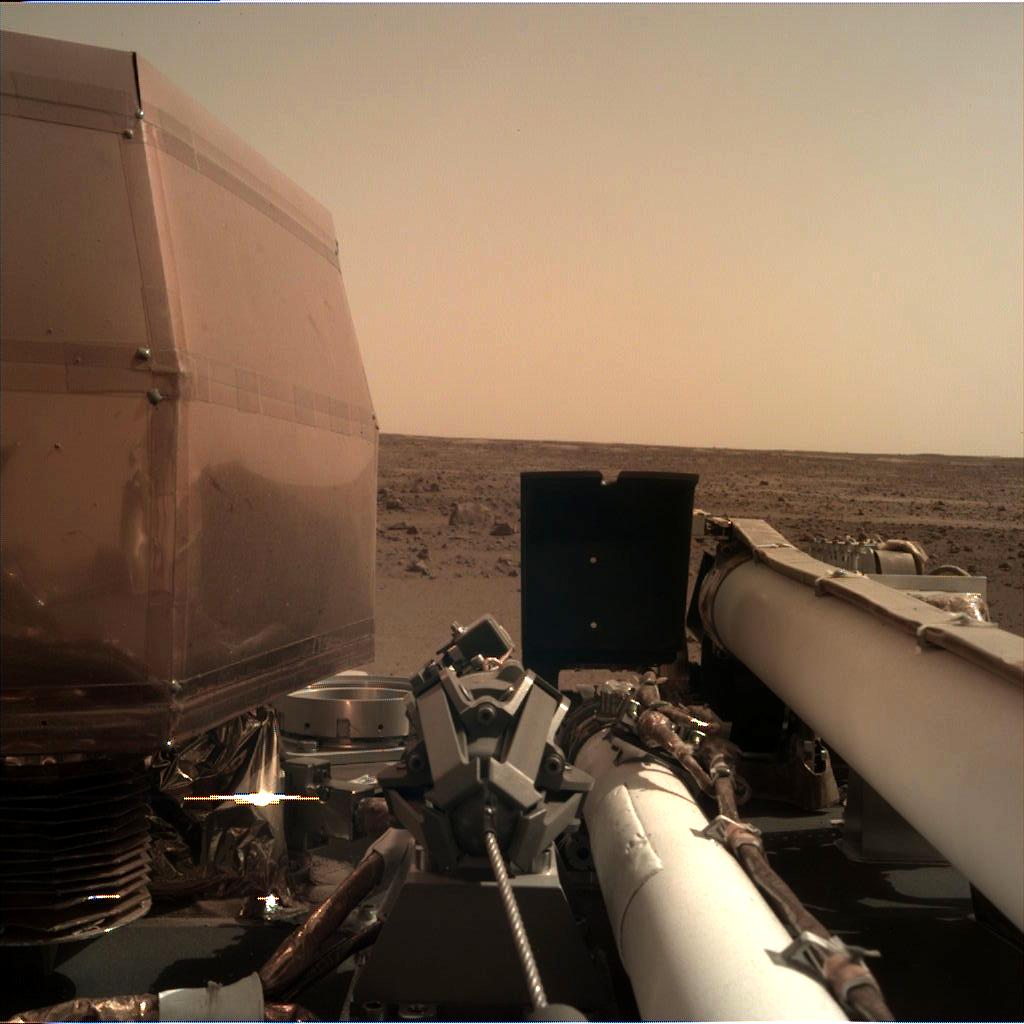


So Insight is on the Martian surface, its solar panels have been deployed to provide it with power, and soon it will be ready to deploy its instruments and begin its scientific mission. See image of lander below.
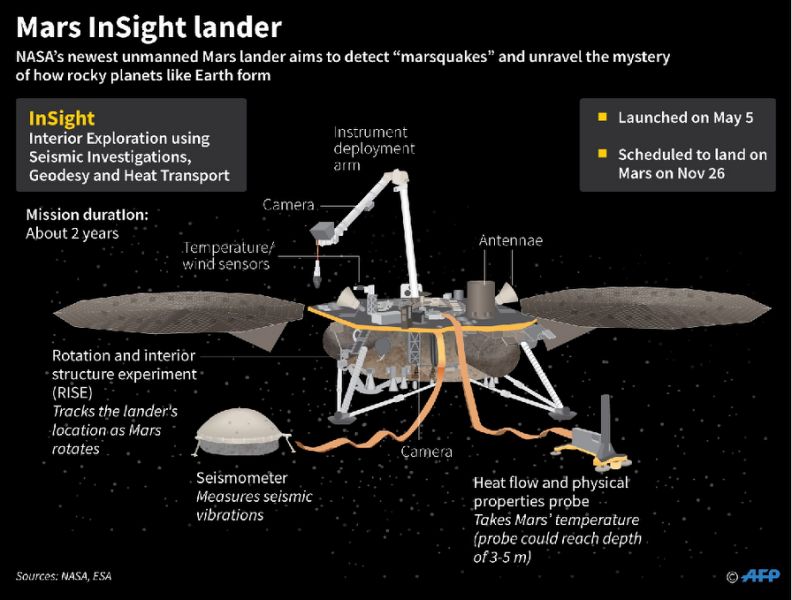
That mission is to study what goes on beneath the surface of Mars and learn some of the secrets of the Martian interior. The lander’s instruments include a seismograph and a temperature probe that could drill down as far as five meters below the surface. Instruments such as these have before now only been deployed on the Earth and Moon, by the Apollo astronauts.
With the landing of the Insight probe the pace of Mars exploration seems to be gaining momentum, and not just on Mars. Here on Earth people are once again becoming excited by space travel. Whereas just a few years ago a space mission would barely get a mention on the news the Insight landing was covered live by both CNN and FOX. And there’s still more to come. On new years day of 2019 the New Horizons spacecraft, which has already visited Pluto, will pass by the Kuiper belt object Ultima Thule and mid next year astronauts will once again fly into space from America soil.
I’m sure the news media will be covering that!