It was ten years ago now in December of 2015 that Space X Corporation first pulled off the astounding feat of safely landing the first stage of their Falcon 9 rocket. Only a little more than a year later in March of 2017 Space X went one step further and reused a Falcon 9 first stage, even safely landing the booster stage for a second time. Since then the Hawthorn, California company has landed and reused hundreds of first stages, the current score is 528 soft landings but the figure keeps on going up every couple of days. Space X has already launched over one hundred Falcon 9s so far this year. All this reuse of the most expensive part of a launch system has allowed Space X to dramatically reduce the cost of getting a payload into space, dollars per kilo to orbit.
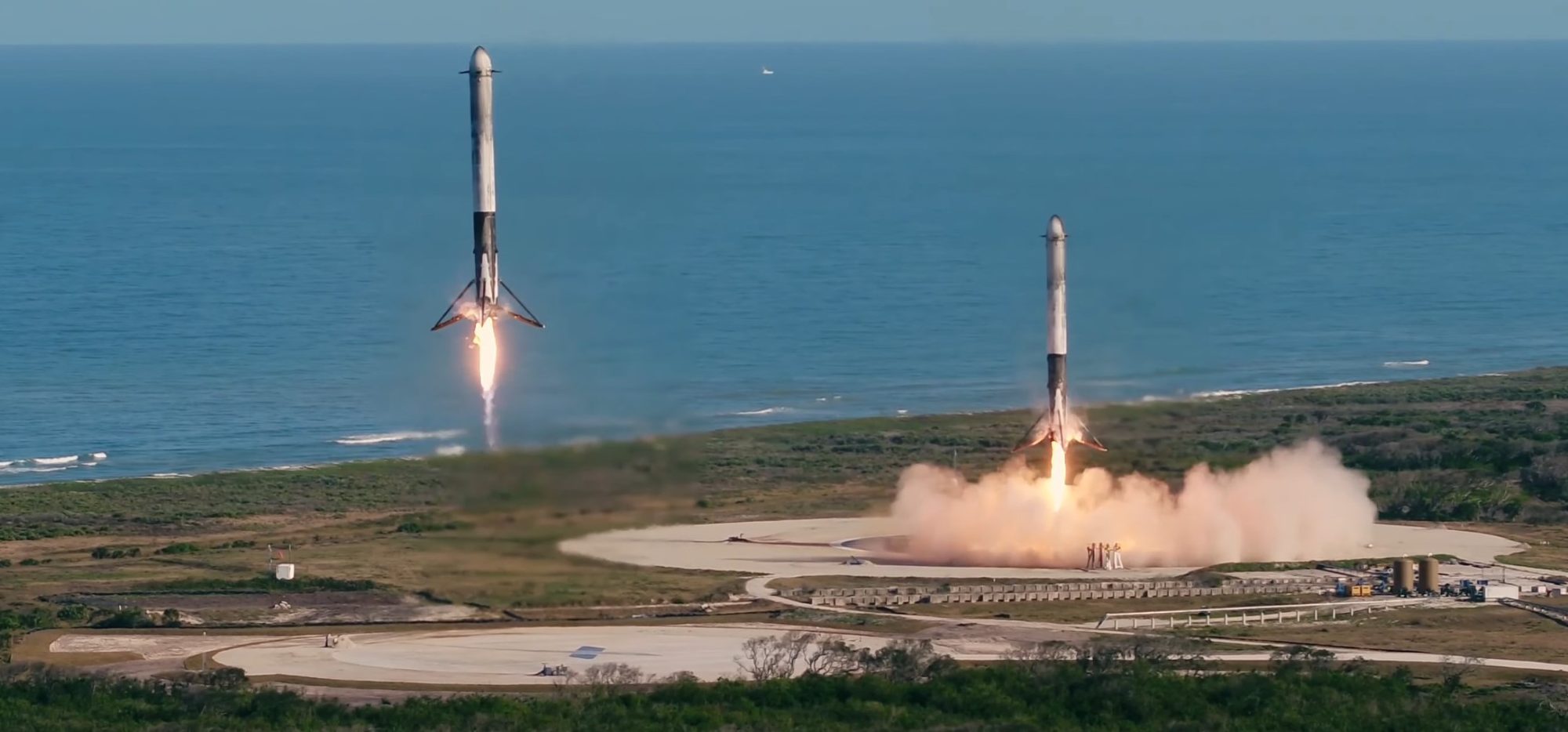

Because of that reduction in cost Space X is able to just put more things into orbit, whether it be Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites or other commercial satellites of even people. Space X not only routinely sends astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) but it has also carried out eight privately funded space missions.

Thanks to their monopoly on reusable rockets right now more than half of all space launches are by Space X simply because of its ability to reuse its Falcon 9 first stage. That monopoly may not last much longer however for there are currently several corporations and nations that are working hard to develop their own version of a reusable rocket.

In fact Blue Origin Corporation has just succeeded in accomplished that task during the second test launch of their New Glenn rocket this month. On the 13th of November, after several delays due to weather and even a coronal mass ejection from the Sun, New Glenn carried out all of its mission objectives including a pinpoint landing of the first stage on a drone landing ship in the Atlantic.
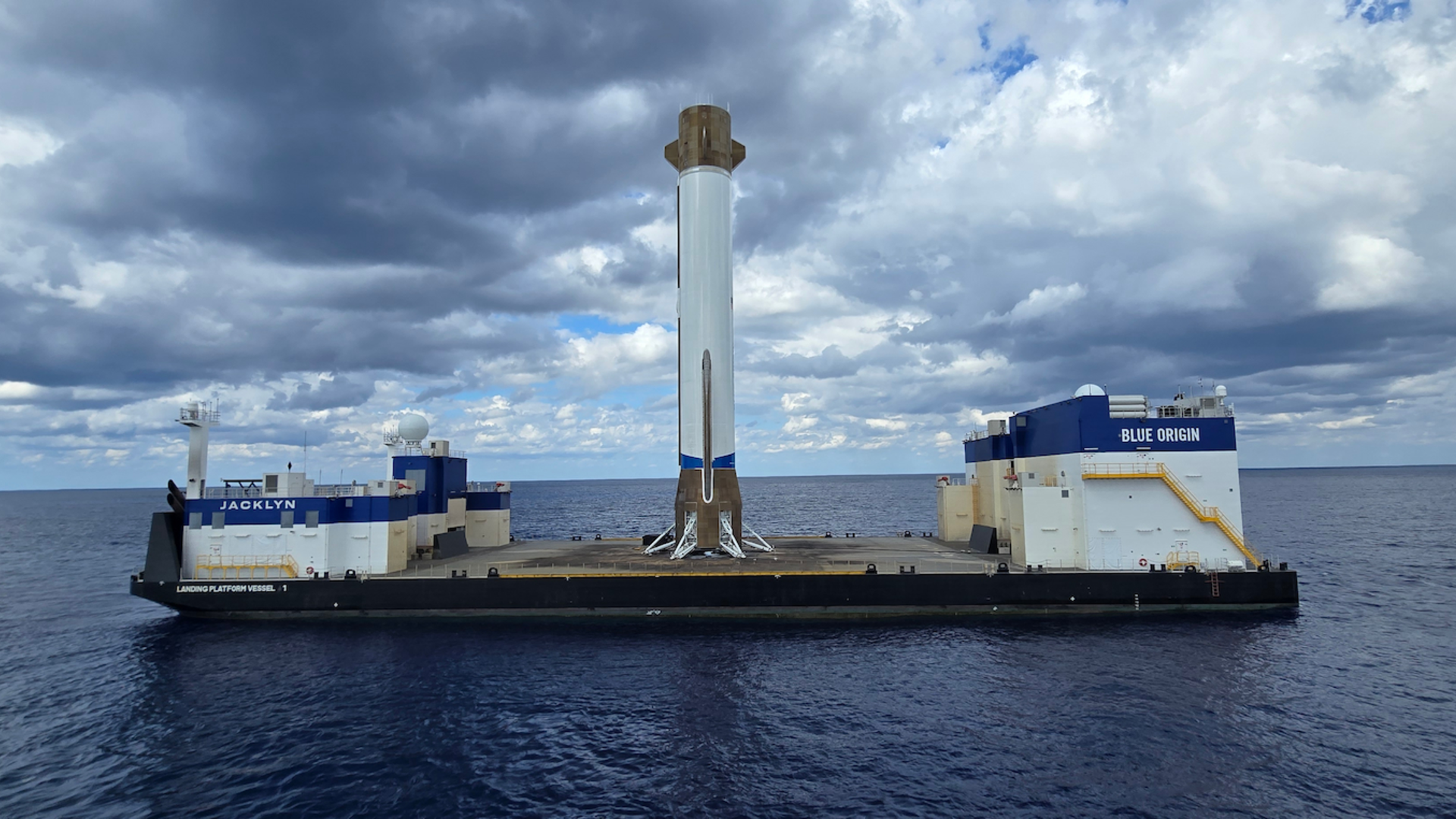

Like the Falcon 9, New Glenn is designed to have a reusable first stage. During the rocket’s first test launch back in January the rocket did succeed in placing a test payload into orbit, however the first stage’s engines failed to reignite so there was no soft landing.
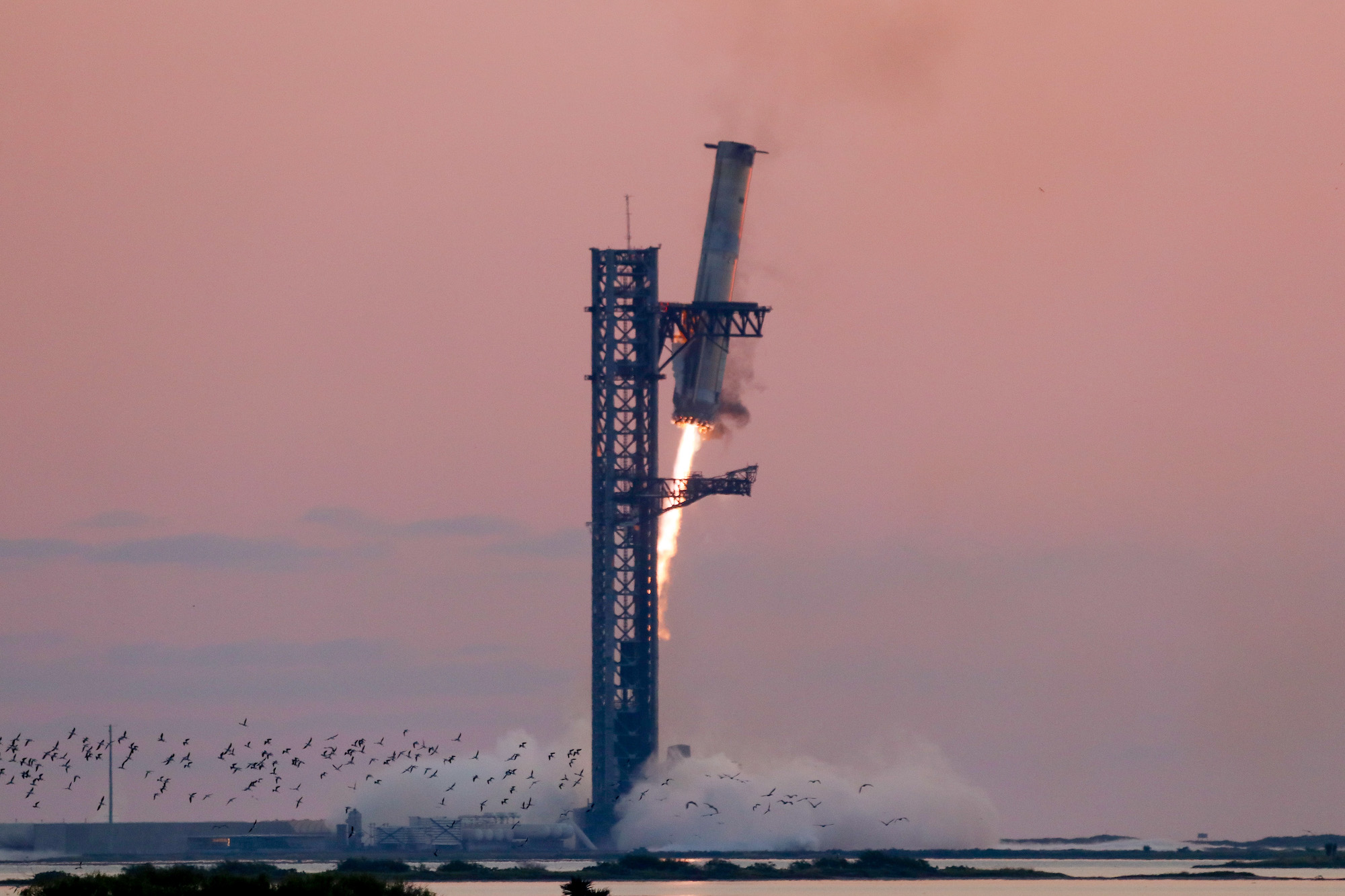

Now just because Blue Origin has managed to successfully land New Glenn’s first stage it doesn’t quite mean that Space X’s monopoly is over, not yet at least. After all it took Space X a couple of years to experiment, try various configurations and gain procedural experience before they got the whole reusability thing down pat. So it will probably take Blue Origin about the same amount of time before it can be reusing New Glenn’s first stages routinely. Still, there’s no doubt that Space X will be hearing footsteps coming up behind them from then on.

With so much to gain by reusability it’s not surprising that others are also working to develop rockets that can soft land and then be reused. China in particular has invested a great deal of money and national prestige in its space program and they are known to be working on a reusable rocket. Of course much of what China does is kept a secret but we do know that several reusable rockets are being developed.
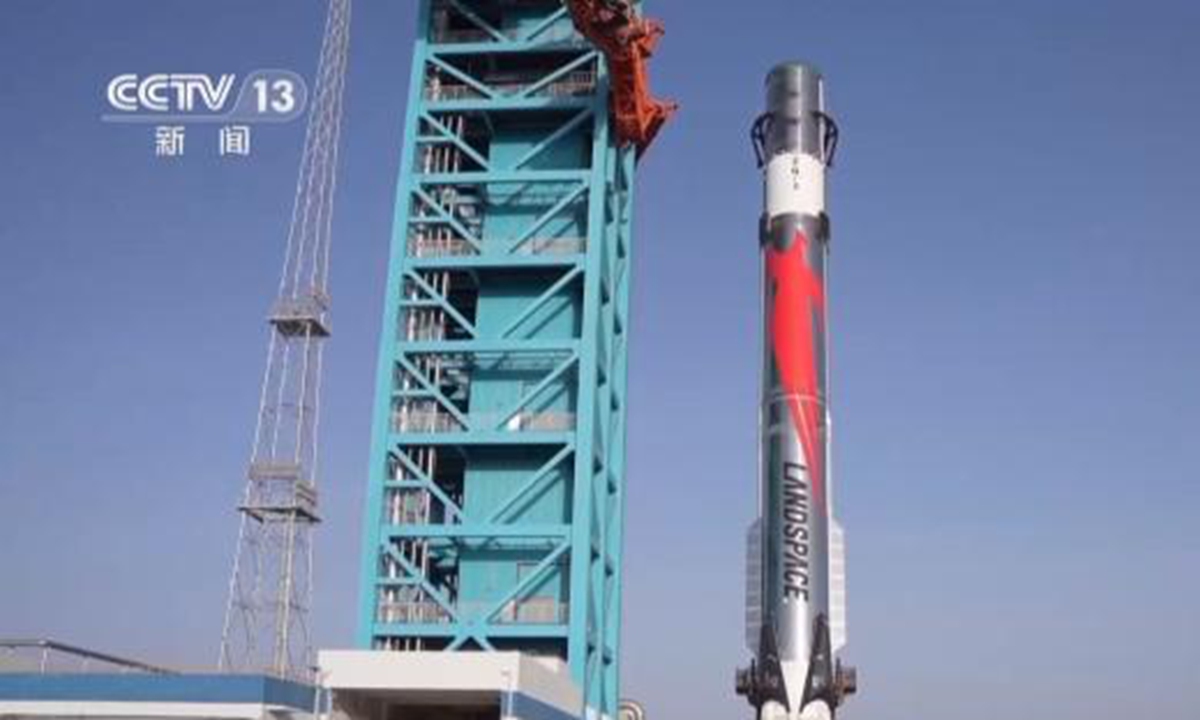

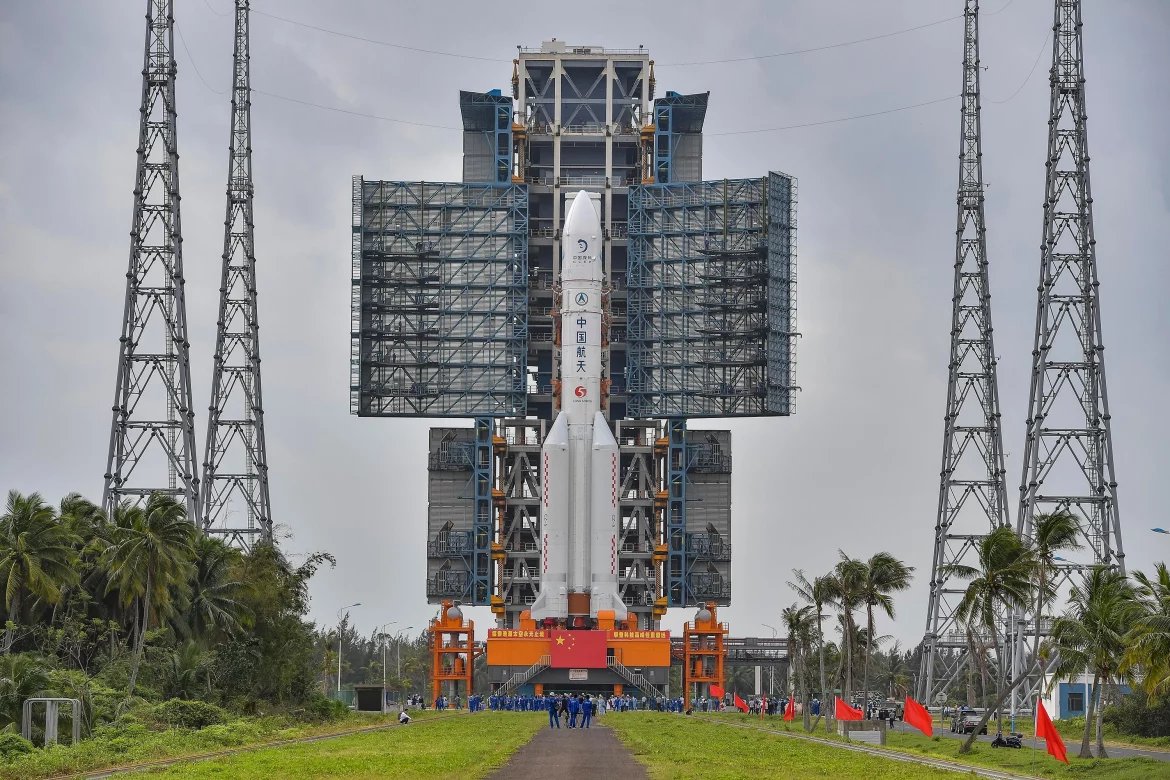
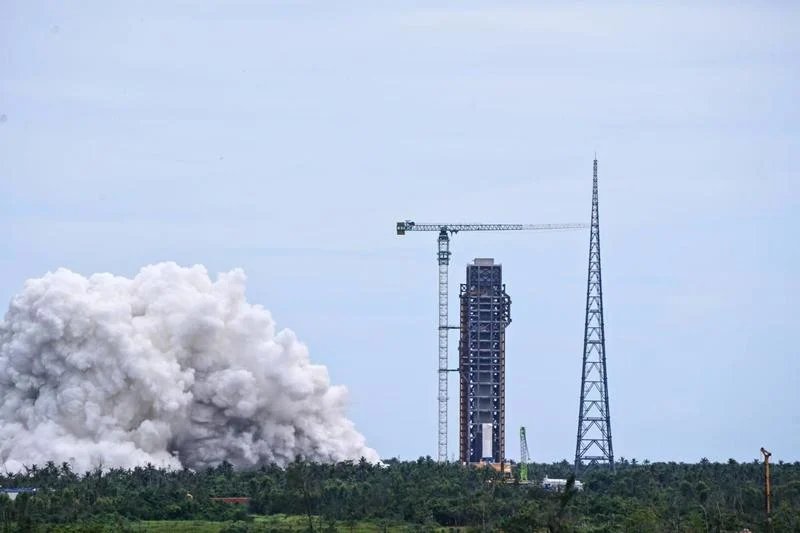
Probably the most advanced Chinese rocket is the Zhuque-3 built by the Chinese aerospace firm LandSpace. Looking a great deal like the Falcon-9, the Zhuque-3’s first stage is intended to be reusable. Back on the 20th of October the Zhuque-3 successfully carried out a static test of its nine Tianque-12A engines in preparation for a maiden flight later on this year. Like Blue Origin on that first flight the Chinese engineers will attempt to safely land the first stage but whether they succeed or not LandSpace is certainly making progress.
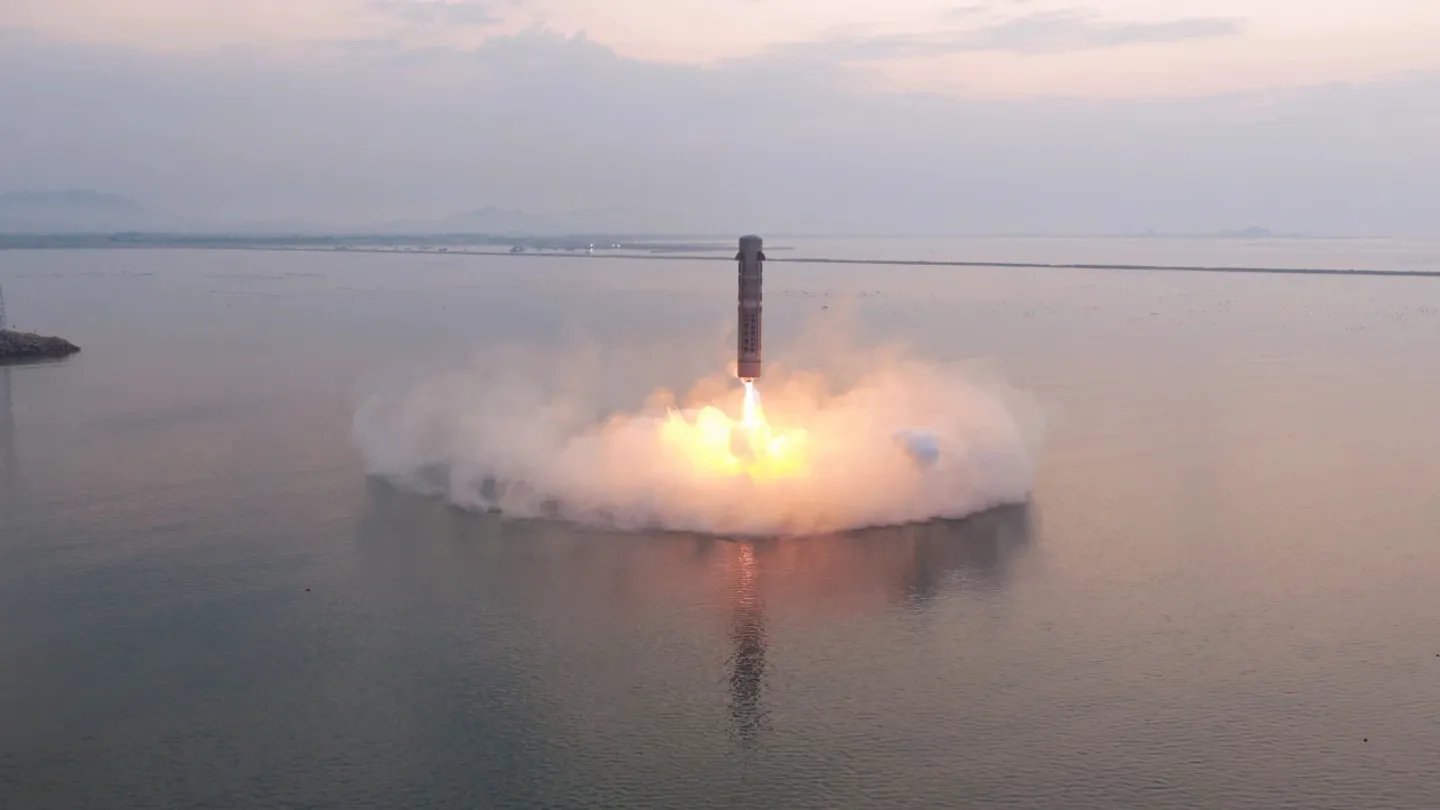

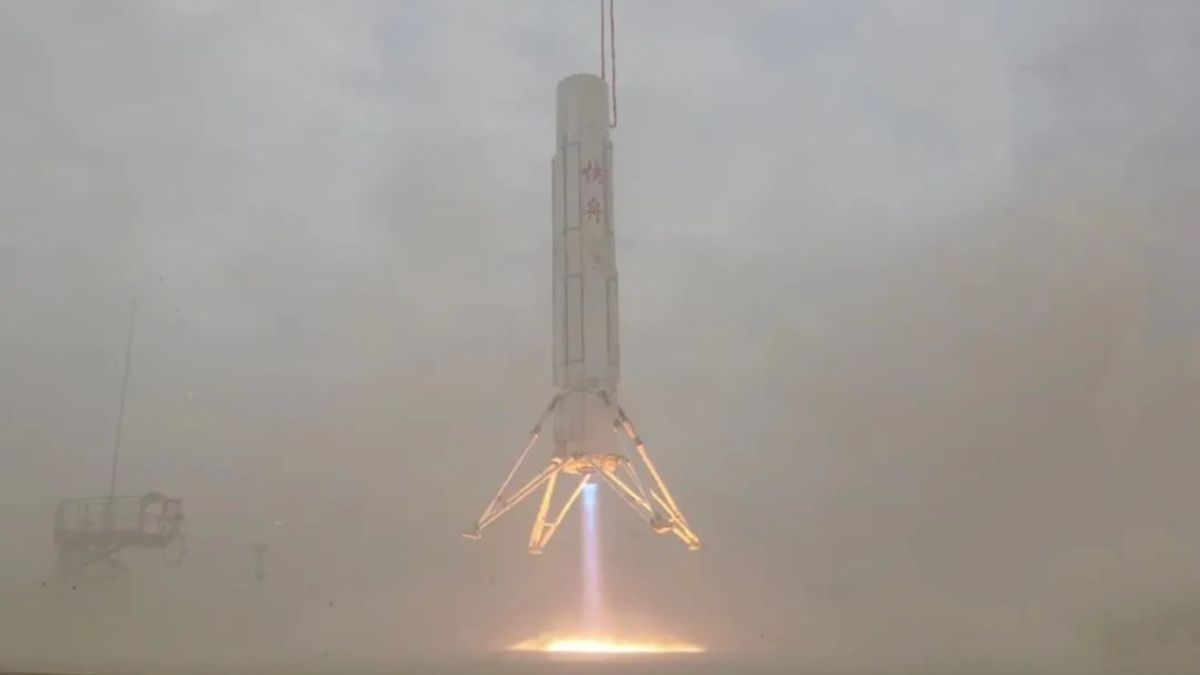
As is another Chinese company called Space Epoch whose sub-orbital test vehicle the Yuanxingzhe-1 was launched back in May from a platform in the Yellow Sea, rose to an altitude of 2.5 km and hovered there before returning to make a soft landing on its original platform. So, one Chinese firm is ready to test a reusable rocket capable of launching a payload to orbit while a second has successfully tested a reusable sub-orbital rocket. It’s only a matter of time before China has a reusable launch system similar to Space X.

Meanwhile in Europe there’s the ArianeGroup which is planning a series of short, non-orbital tests of reusable rockets in the hopes of generating interest in the European Space Agency (ESA) for European reusable rockets. The tests will be carried out in Sweden near the Arctic Circle and are built around a reusable methane-oxygen rocket engine named Prometheus that will power three test vehicles named Callisto, Themis and Skyhopper.
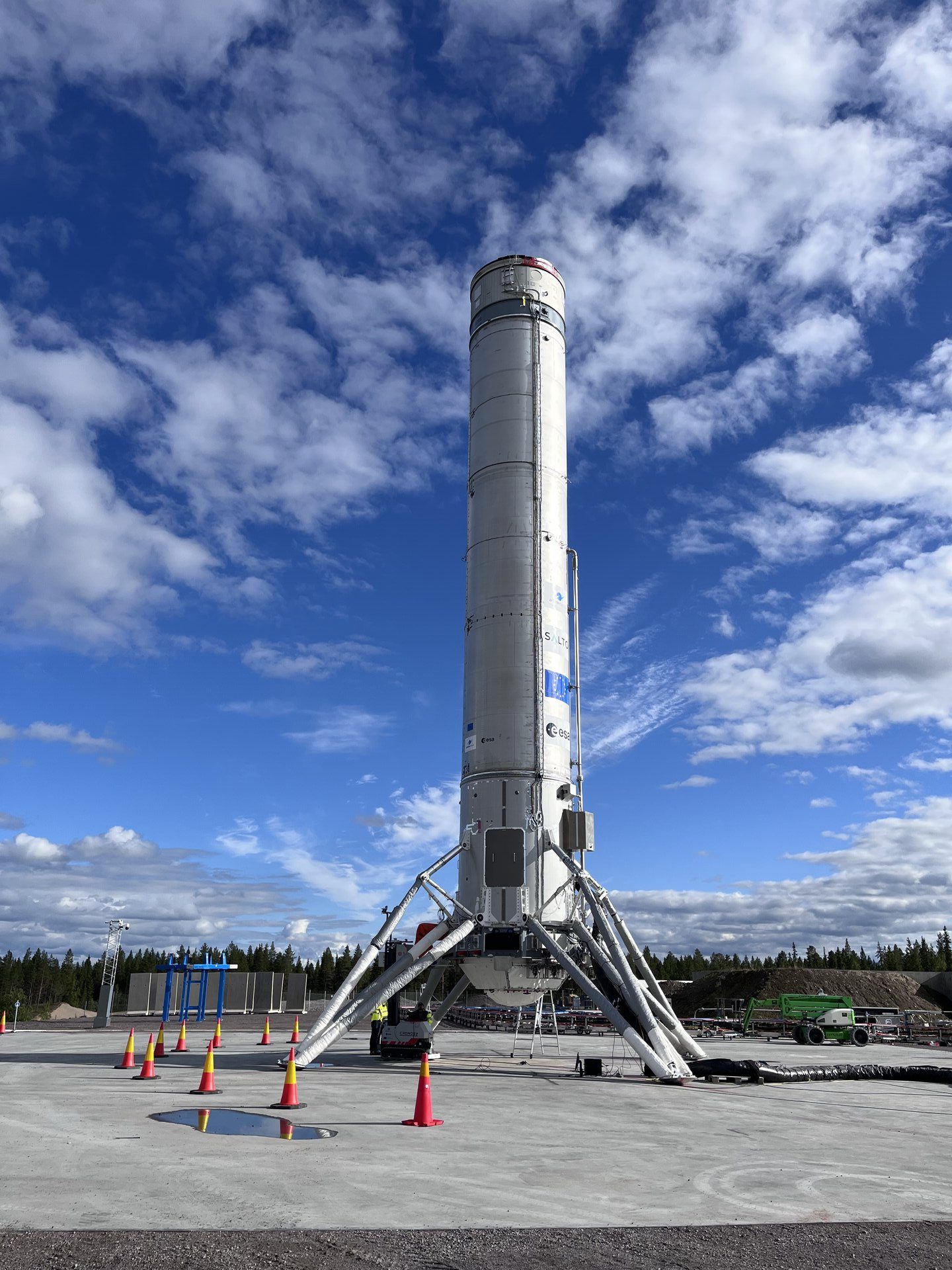

Themis will be tested first on a low altitude flight with a set of permanent landing legs installed while Callisto will have foldable landing legs similar to those on Falcon-9. Skyhopper will be last with a higher altitude, multi-engine flight. The problem with any new rocket developments in Europe is political will. With so many nations involved in the ESA, and the fact that the ESA has always had NASA to fall back on when necessary the ESA has never been able to do anything really big in space.

Of course Japan is also getting in on the act. Back on June the 17th the giant carmaker Honda successfully tested a small, 6.3m in length, reusable rocket. During the test the rocket reached a height of only 300m but touched down only 37cm from its target landing spot. Throughout the test the rocket was completely under control. The company has set its sights on a larger scale, sub-orbital flight in 2029.

Finally let’s just pity poor Russia, which appears to have no plans for developing reusable rockets. Thanks to Vladimir Putin’s mismanagement, to say nothing of his war in Ukraine, Russia’s economy is in such a bad state that the first nation in space is now steadily falling behind.

So there you have it, while Space X has built themselves a dominant position in space based upon their reusable Falcon 9 rocket that dominance could soon start to slip now that other nations and companies have seen the advantages of reusable rockets.
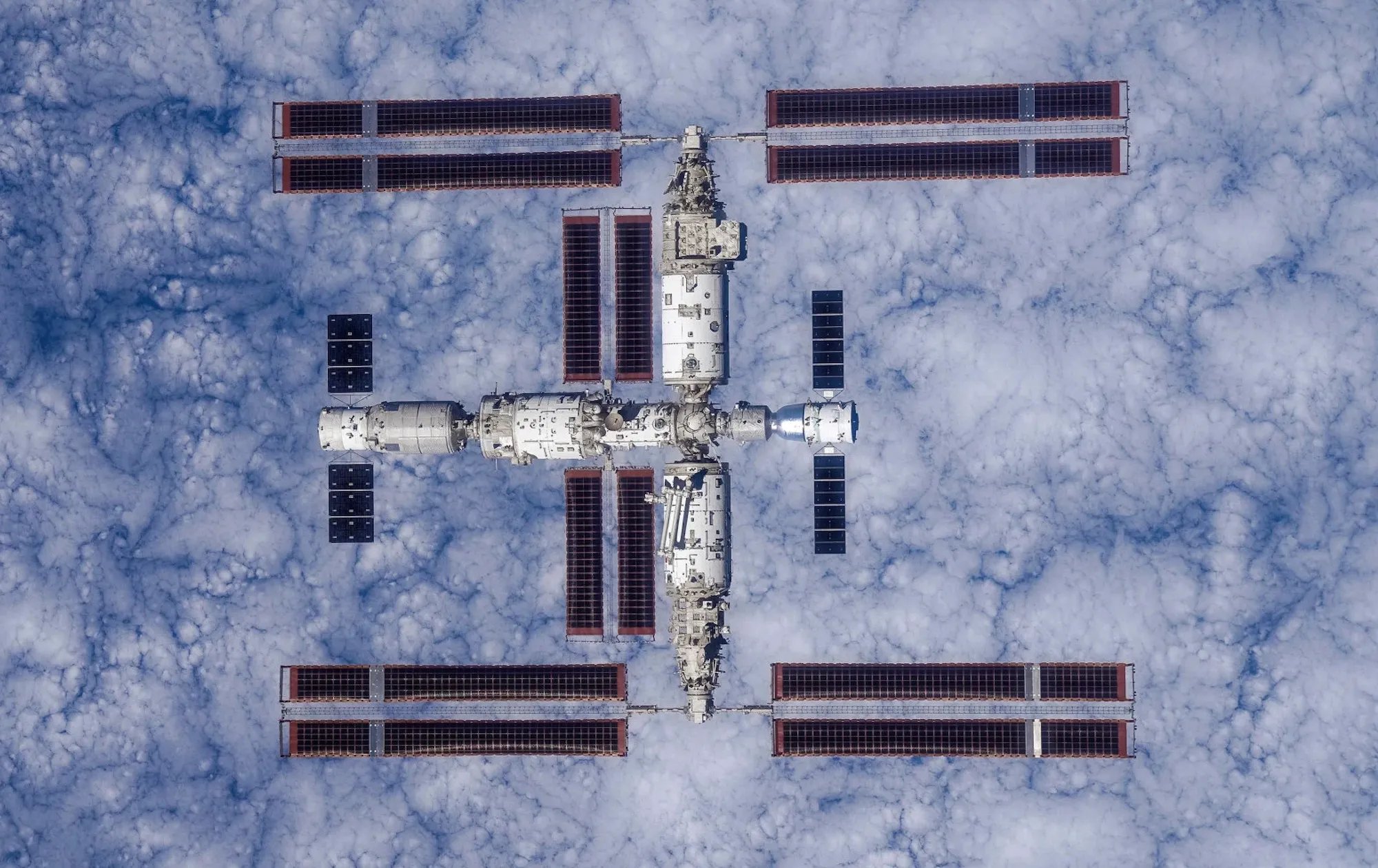
This post was intended to be about developments in reusable rockets but recent happenings at the Chinese Tiangong space station require a bit of discussion. On the 31st of October a new crew of three Taikonauts arrived at the Tiangong space station aboard their Shenzhou 21, relieving the Shenzhou 20 crew. However, as the two crews were both aboard the station the Shenzhou 20 capsule was struck by space debris.

Officials with the Chinese space agency immediately ordered a delay in the return of the Shenzhou 20 crew while engineers analyzed the data to determine if the capsule was safe. After more than a week of delay it was decided that the Shenzhou 20 capsule was unsafe and the Shenzhou 20 crew would return to Earth aboard the Shenzhou 21 capsule.
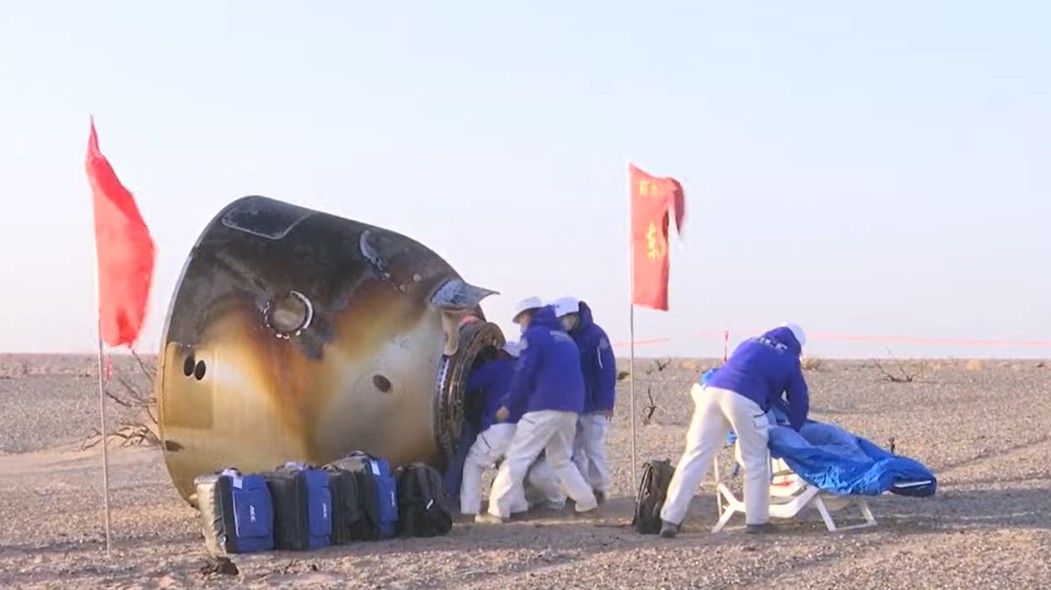

On the 14th of November the Shenzhou 20 crew did safely land back on our planet but in doing so they left the Shenzhou 21 crew stranded on Tiangong without a safe capsule in which to return if an emergency should occur. As you can imagine China is now rushing to launch an unmanned Shenzhou capsule, the one slated for the Shenzhou 22 mission, to Tiangong as quickly as possible. The Chinese space agency has announced a tentative date of November 25 for the launch of that unmanned mission.