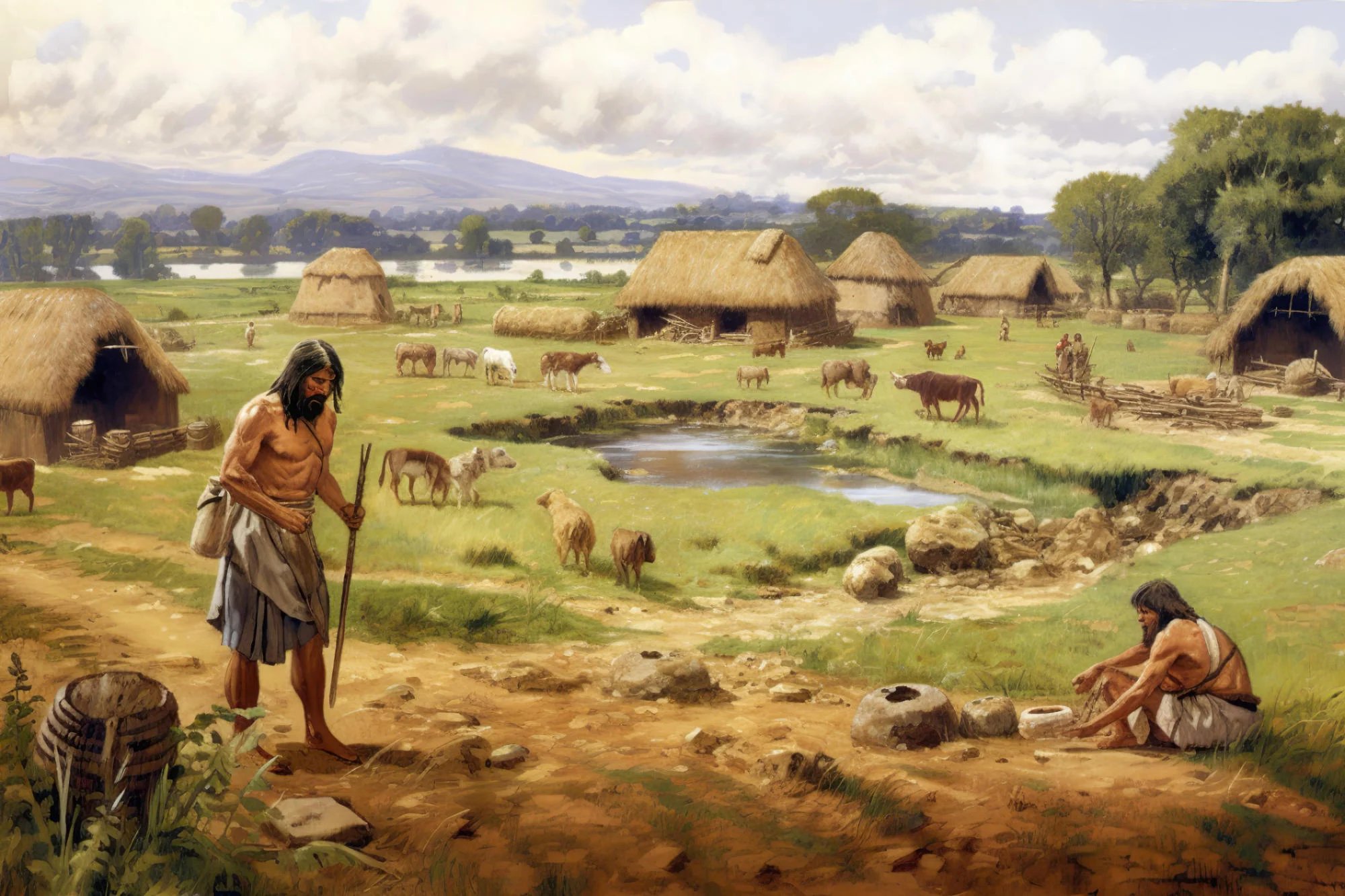
Starting about ten thousand years ago we humans first began to both cultivate crops and domesticate herd animals. These twin achievements allowed our ancestors to end their nomadic, hunter-gatherer lifestyle and settle down into more permanent sites, villages, towns and eventually cities.

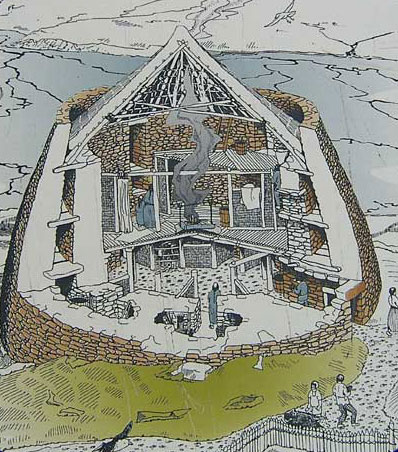
This change from temporary housing in caves or portable huts to long-term structures obviously is a great boon to present day archaeologists. Think about it, a cave where an extended family lived for a few months out of the year certainly won’t contain as much archaeological evidence for an excavator to find as would a cluster of dwellings where many families lived for decades or longer. Nevertheless the details of exactly when and how that change from wanderers to homesteaders took place are still fuzzy, which is why a great deal of the efforts of archaeologists today are geared towards the study of how humans built those first urban areas.

As I mentioned above one of the advancements that enabled the first villages and towns to be built was domesticating animals that could be herded like sheep or goats or even reindeer in the north. Now the raising and handling of such large groups of animals requires not only pastures for grazing but also corrals for confining them when it becomes time for sheering, branding, slaughtering or even just counting how many of them you have.

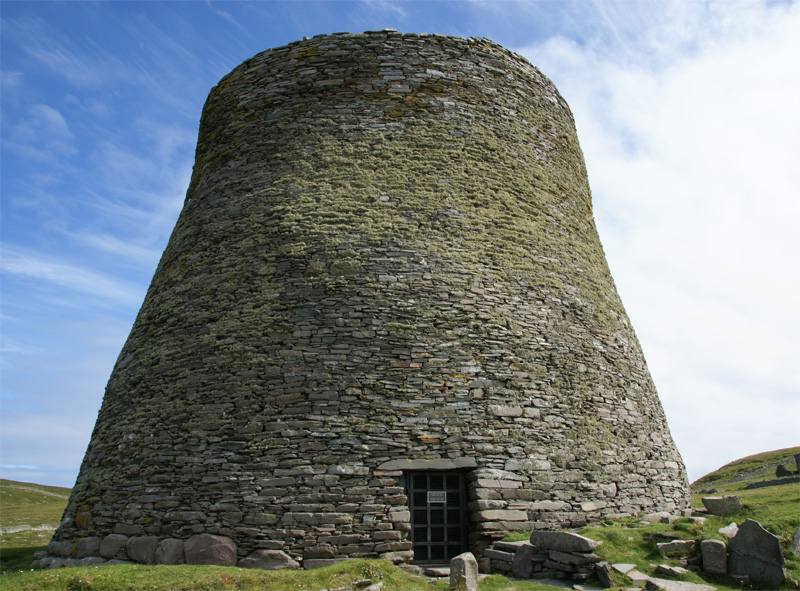
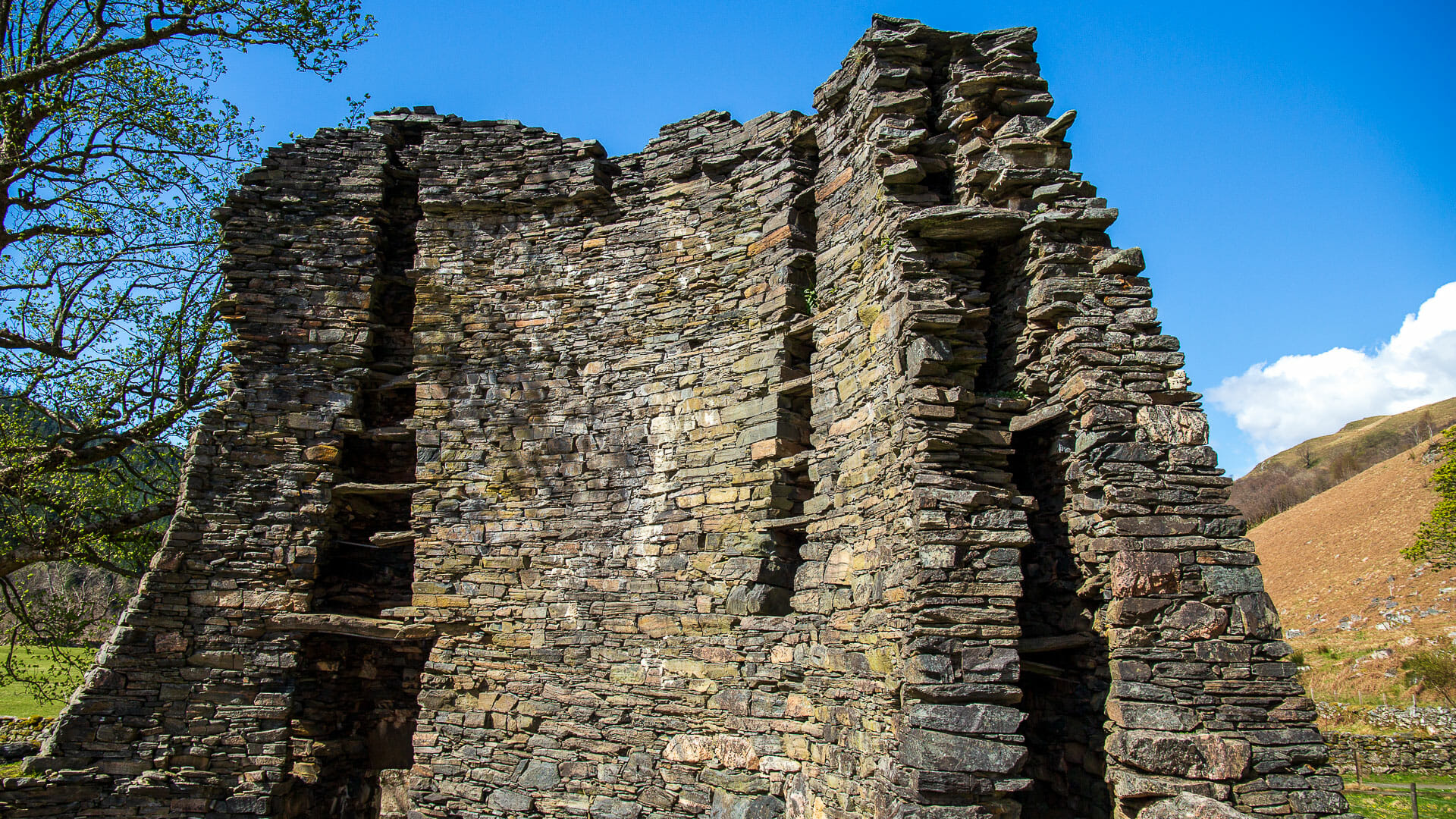
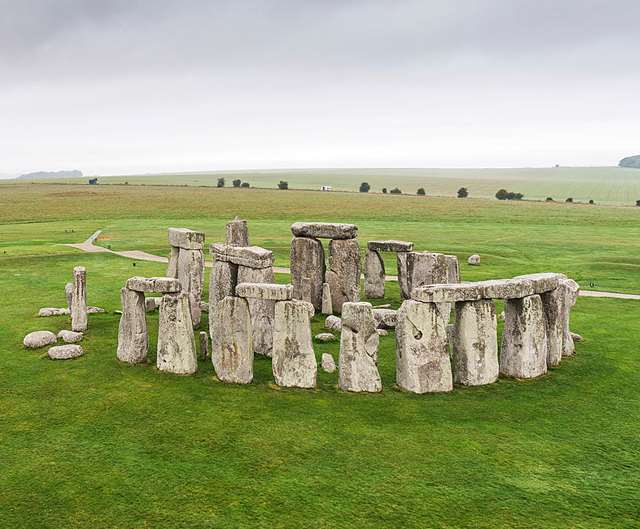
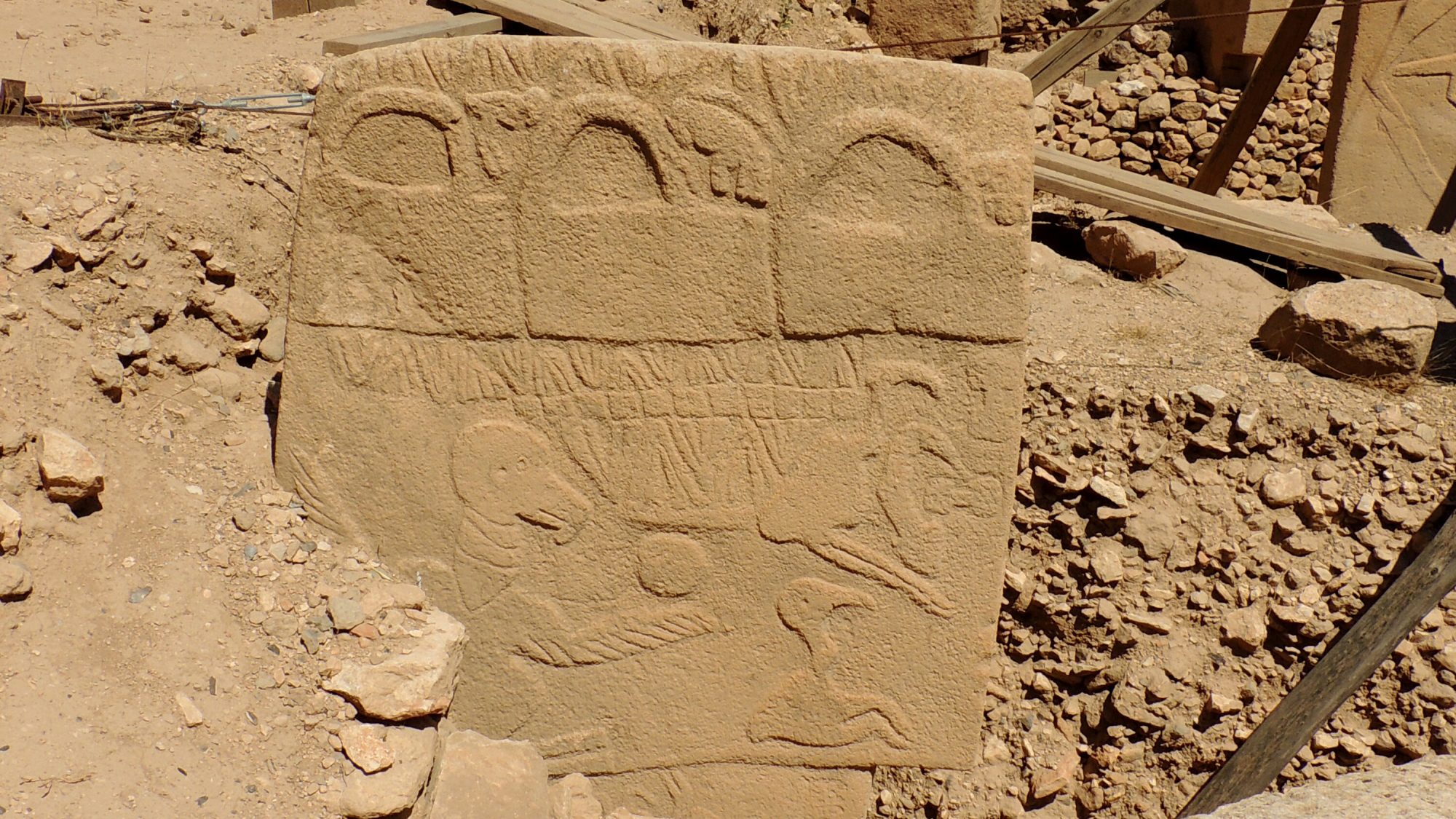
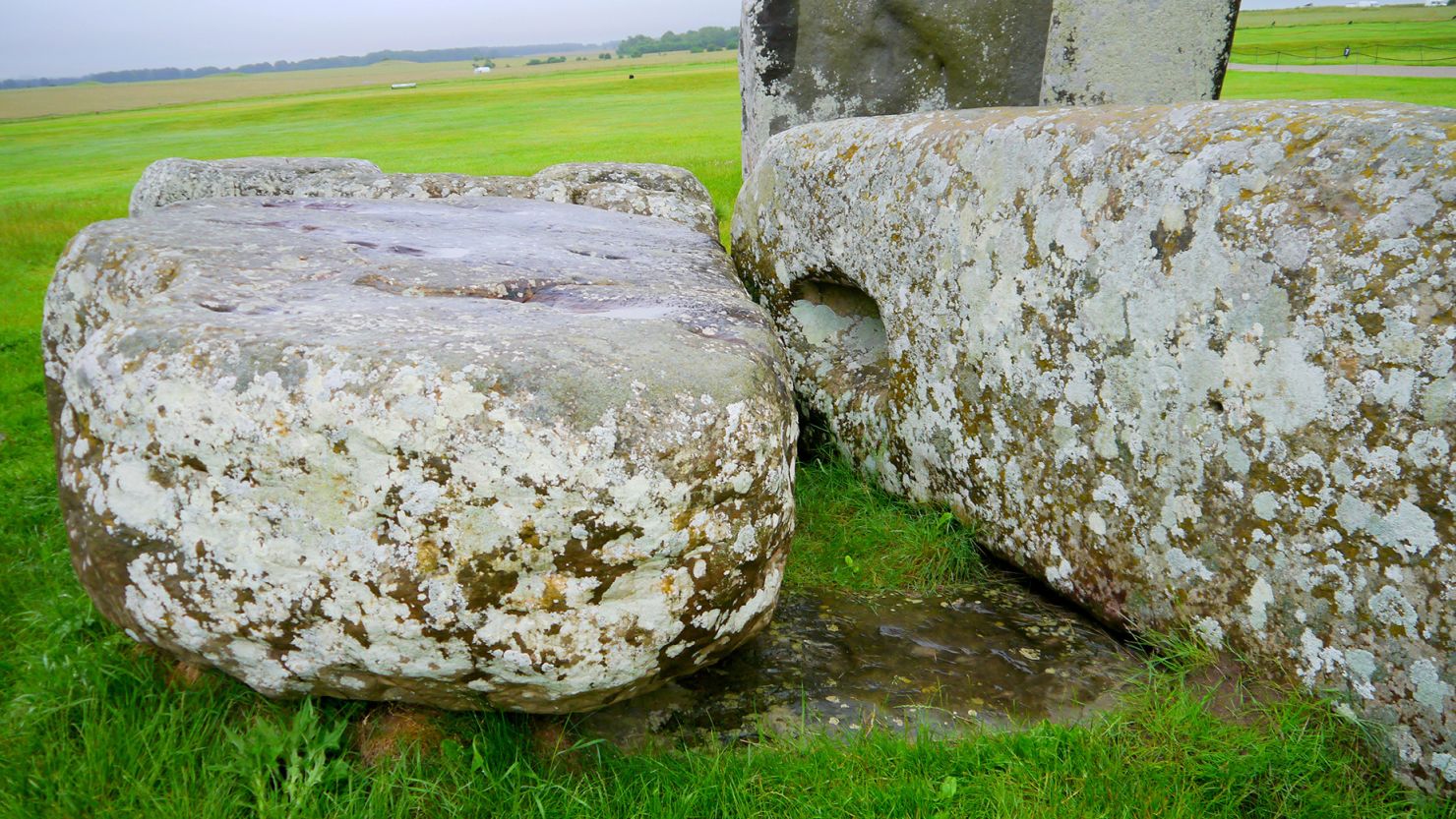
A recent study by archaeologists at Tel Aviv University and Ben Gurion University of the Negev in Israel has upended long held ideas about a late Stone-Age, early Bronz Age, 4-5 thousand year old mysterious site in the Golan Heights known as the ‘Gilgal Refaim’, which is Hebrew for the ‘Wheel of Giants’. For decades now the 100-meter in diameter site had been interpreted as an astronomical observatory like the famous Stonehenge in England. Indeed the site is often referred to as the ‘Wheel Stonehenge’.

The new study however took into account the way that Plate Tectonics, working at a slow rate of 8-15 mm per year has over the last 4-5 thousand years moved and even rotated the wheel. So looking at the way that the wheel was orientated back in the Neolithic the archaeologists found that there were no alignments to any celestial objects or events like solstices or equinoxes that would be important to a newly agricultural society. Instead the researchers maintain that Gilgal Refaim was a corral, a place that shepherds or goatherds could bring their flocks. The researchers also surveyed the surrounding area within 30km of the site and found other, smaller examples of such stone wheels averaging 20m in diameter. So perhaps Gilgal Refaim is simply the largest of a whole class of structures in the area used to concentrate livestock.

At the same time the archaeologists also recognize that structures like corrals can often serve as locations where people gather and interact. Remember the first rodeos were just people having fun at corrals while working with their livestock. So there is every possibility that Gilgal Refaim could have been used as a gathering place for nearby clans, either for religious of social events.

Another way in which the lives of human beings changed as they began to live in settled communities is the spread of communicable diseases. Think about it, a small group of nomads, say 12-15 people, who wander from one place to another with the seasons as different resources become available will probably only encounter other such groups three, maybe four times a year. Those are hardly the conditions that would allow an infectious disease to spread rapidly.

When humans started living in larger communities of hundreds or thousands of people however infectious organisms could multiply more easily, allowing the evolution of more diseases that could inflict our species. Indeed there is considerable DNA evidence that illnesses like salmonella, tuberculosis and even the bubonic plague all began to infect humans during the Neolithic period, the time of the first villages.

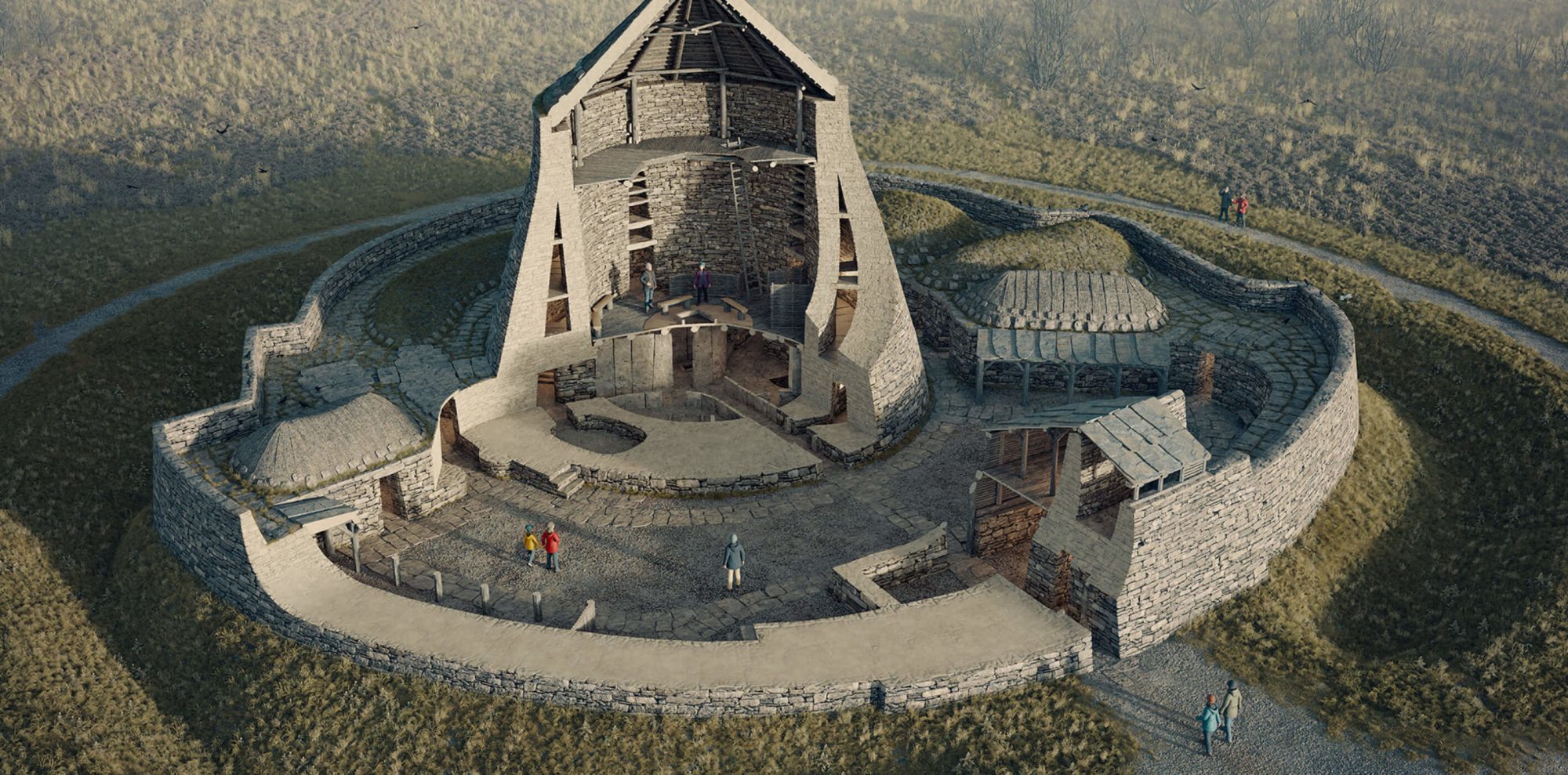
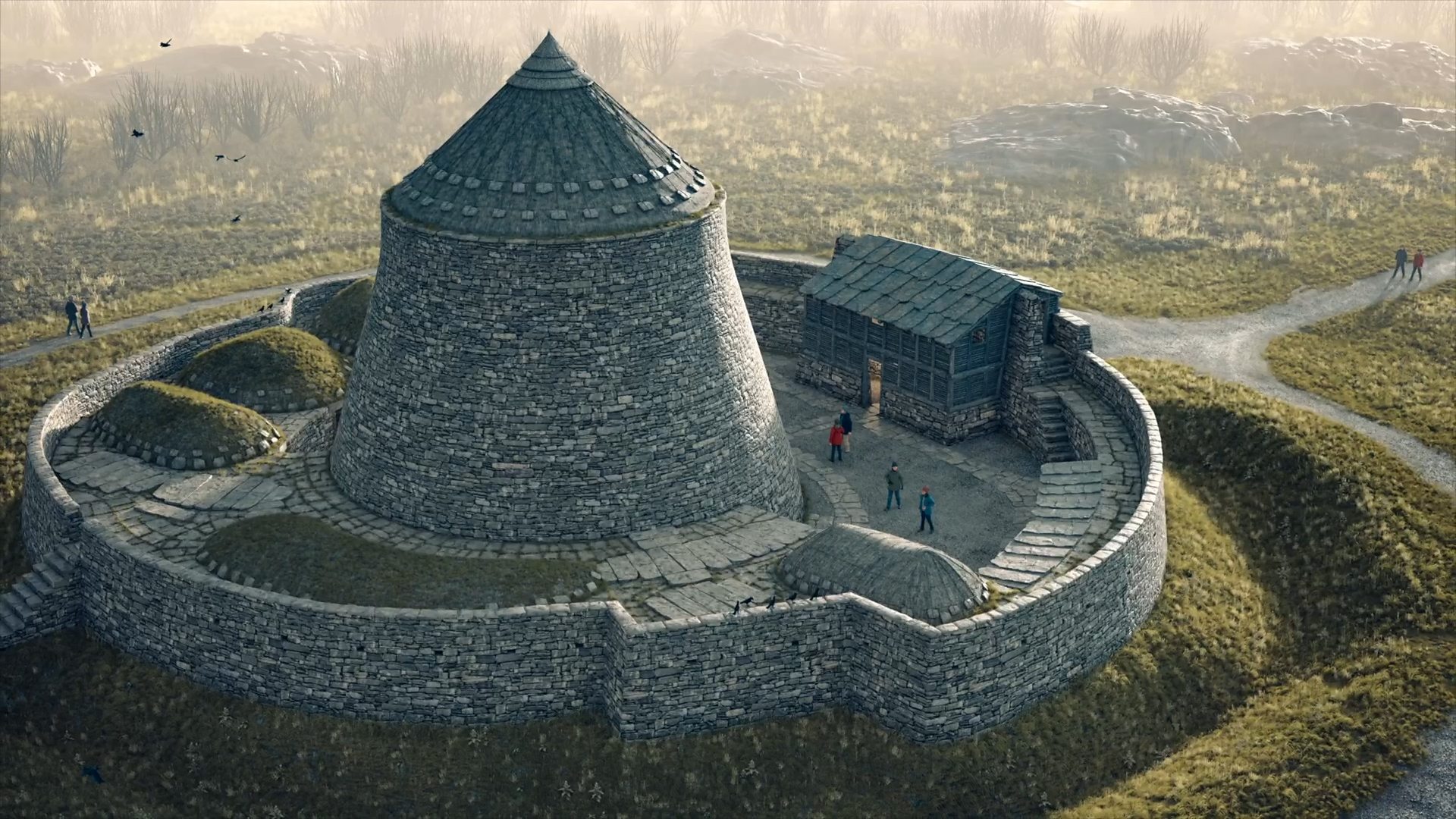
Now there is also evidence that humans began to adapt to these new, potential epidemic conditions by adopting a policy of ‘social distancing’ familiar to all of us thanks to Covid-19. A team of researchers from the University of Tennessee, Cambridge University, Durham University and Texas A&M have studied the patterns of settlement during the Neolithic ‘Trypillia’ culture of eastern Ukraine. Their results have been published in the ‘Journal of the Royal Society Interface’. During the late Stone Age this area contained a number of proto-towns or even proto-cities that have been well studied by archaeologists.

The researchers focused on one settlement known today as Nebelivka, which possessed thousands of wooden dwellings that were identified as being arranged in concentric patterns and clustered in pie shaped neighborhoods. Using computer programs designed to both study the spread of diseases as well as model urban planning to minimize that spread the team discovered that the inhabitants of Nebelivka were well aware of the hygienic benefits of ‘social distancing’. “This clustered layout is known by epidemiologists to be a good configuration to contain disease outbreaks.” According to Lead Author Alex Bentley of the University of Tennessee. “This suggests and helps explain the curious layout of the world’s first urban areas. It would have protected residents from emerging diseases of the time.”

The team also conducted a more detailed simulation of what would occur in Nebelivka if a food borne illness such as salmonella was to break out there. Carrying out millions of computer simulations what they discovered was that the pie shaped clustering of houses in Nebelivka helped to reduce the spread of such diseases.

The study’s result may also help to explain why the residents of Nebelivka are known to have burned down their dwellings on a regular basis and replaced them with new wooden houses. Fire has long been used as a means of fighting infectious disease.

What both of these two studies show is that the people of the Neolithic period were every bit as smart as we are. That they used what technology they had to solve the problems that they faced and occasionally they developed new technology that they passed on. We are the inheritors of their knowledge and wisdom, we should be a little more grateful.