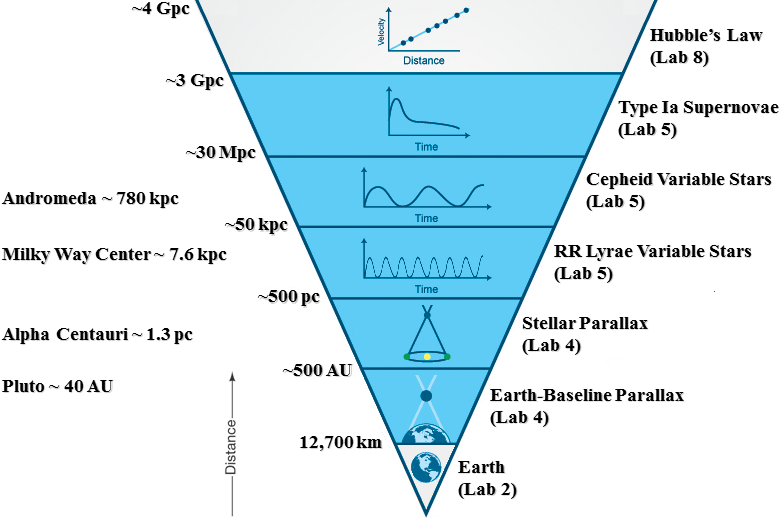
One of the best known tales in the history of science relates how the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes discovered his principal of buoyancy when he stepped into his bath. Noticing the water that had overflowed onto the floor Archimedes realized that the volume of water that was displaced was equal to the volume of his body that had been submerged and the scientist had the solution to his problem. Overjoyed Archimedes got out of his bath and ran naked through the streets of Syracuse crying “Eureka” which is Greek for “I found it!”

Recently a physicist with the California Institute of Technology named Amnon Yariv had an experience somewhat like that of Archimedes while taking his shower at his home in Pasadena, California. Having one of those shower heads that are at the end of a long flexible hose Yariv noticed that when he let the head hang free the force of the flowing water caused it to not only swing back and forth like a pendulum but also twist clockwise and anti-clockwise. Doctor Yariv, who is an expert in Oscillations and periodic motions quickly recognized this behaviour as bimodal, that is two distinct oscillations were moving in synch with each other. Doing a little experimenting Yariv soon discovered a few other interesting characteristics of his phenomenon, one was that the two oscillations were also coupled, any dampening of one would cause a dampening of the other. Also, if he increased the water flow of the shower beyond a certain point the two oscillations began to grow wildly, uncontrollably. Doctor Yariv likens his discovery to two tango dancers, who have to coordinate their dancing with their partner in order to avoid tripping over each other.
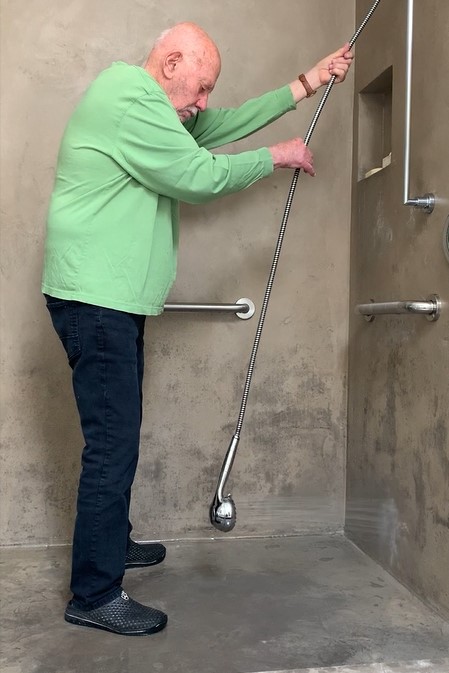


Having discovered his new phenomenon Doctor Yariv spent the next several years modeling it mathematically while also performing some experiments to confirm his model. According to Yariv his oscillation is an bimodal extension of a class of oscillations that were studied by Lord Rayleigh and Michael Faraday a century and a half ago in which a system is excited by a modulation at twice the resonate frequency of the system.
Doctor Yariv was also able to obtain useful work from his oscillations by coupling it to a rotary gear. He hopes that his research may lead to more efficient energy conversion from wind turbines and other green energy systems. Not bad for something discovered in the shower!

Most of the discoveries made by physicists today however require a bit more equipment than a showerhead, often very expensive equipment, even equipment on satellites in outer space. The mystery of Earth’s magnetic field for example has been studied by hundreds of physicists over the last several hundred years with some of the most precise instruments available yet we still known only a little about it. We do know that the core of our planet is composed mainly of liquid iron and nickel, both magnetic materials, and that as our planet spins on its axis currents in that molten core can generate a magnetic field.
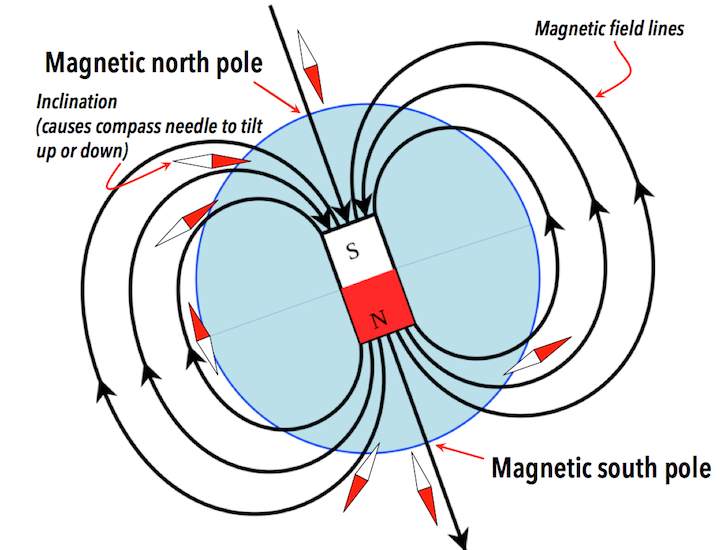
Another thing that we’ve discovered is that every couple of hundred thousand years or so our planet’s magnetic poles swap their positions, the one up north going south and the one down south going north. (By the way, since opposite poles of a magnetic attract each other while similar poles repel, and since the north pole of a compass points north that means that currently there is a south magnetic pole up north and a north magnetic pole down south.)
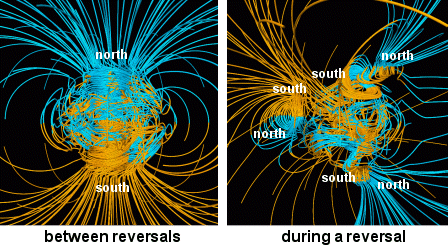
Over the past several decades measurements of the Earth’s magnetic field have shown a steady decline in the strength of that field leading many researchers to think that Earth may be in the initial stages of one of those magnetic pole swaps. In order to get a more precise idea of just how rapidly the Earth’s magnetic field is changing in 2014 the European Space Agency (ESA) launched three satellites that they called the Swarm Constellation that were designed to make the most accurate measurements of our planet’s magnetic field. Over the next six years the satellites made detailed and comprehensive maps of the Earth’s magnetic field from Low Earth Orbit (LOE) and just as importantly monitored how the magnetic field was changing!
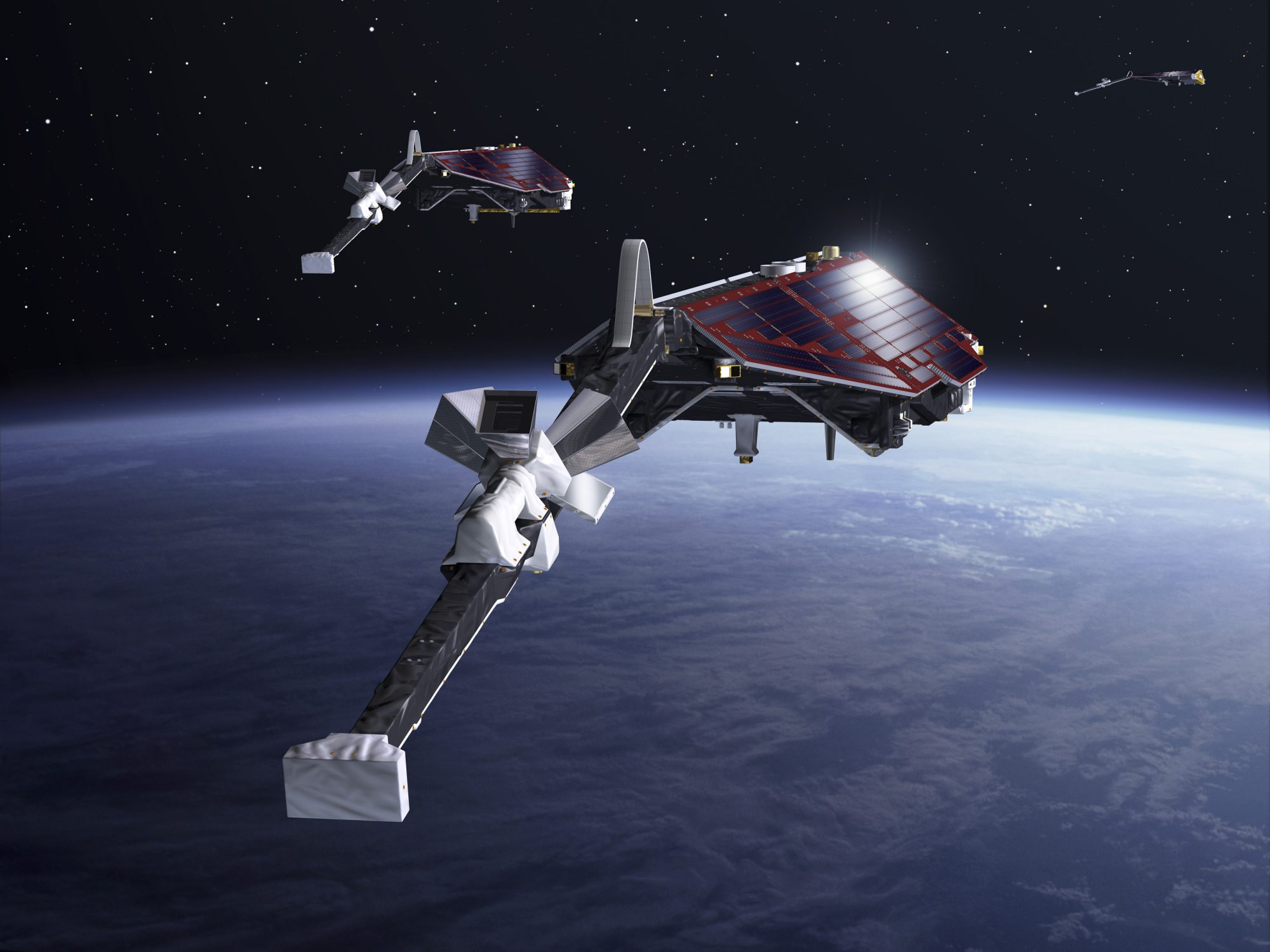

That data has now been analyzed by researchers at the University of Michigan’s department of Climate and Space Sciences and Engineering and compared to the latest model for how we think the Earth’s magnetic field works. That model is known as the International Geomagnetic Reference Field or IGRF-13, the 13 meaning that this is the 13th model in a series. A report on that analysis has recently been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics.
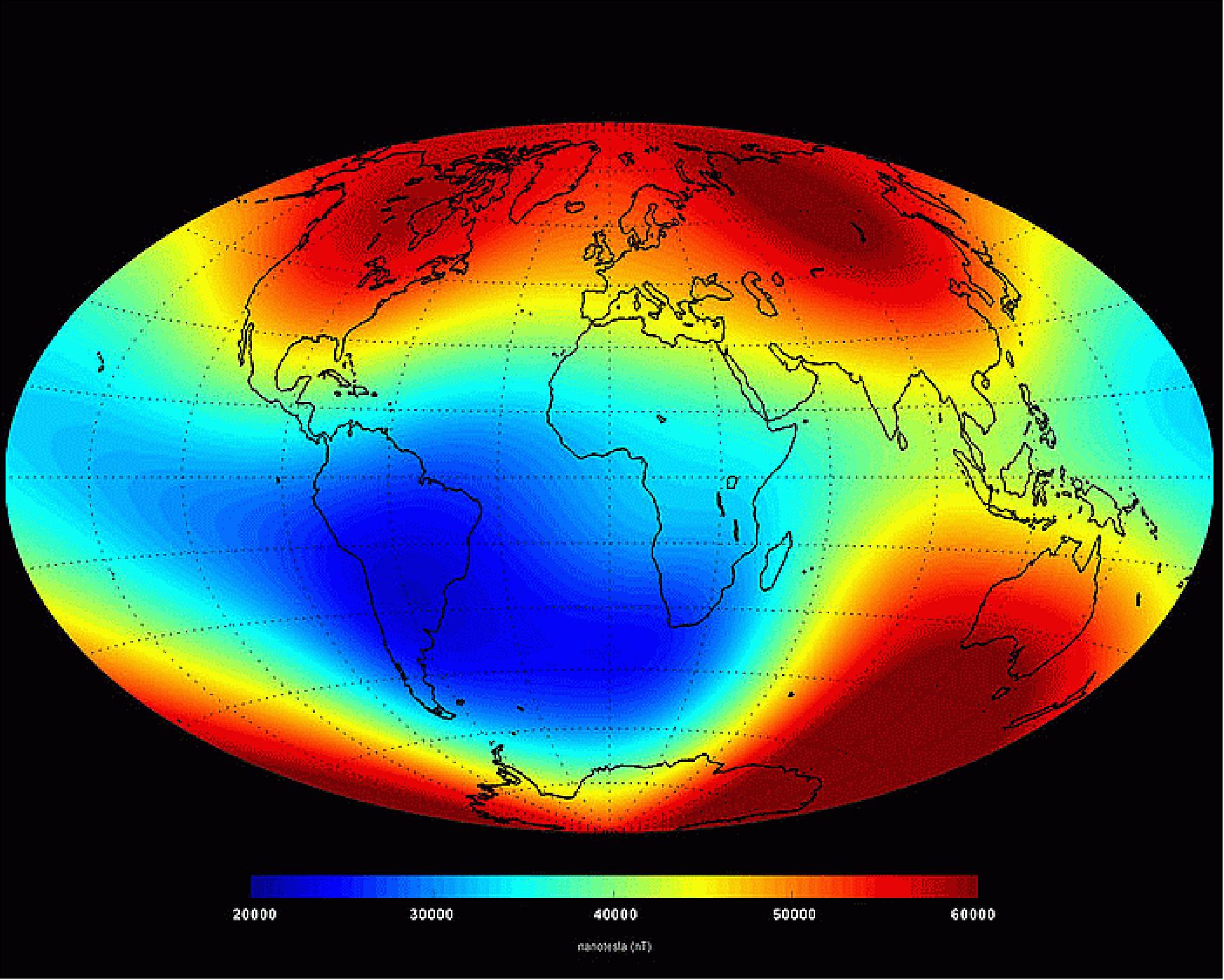
Through their examination of the data from the Swarm Constellation satellites the researchers discovered a number of discrepancies between the data and the model many of which were caused by a surprising error in the model. You see, although the physical North and South Poles, as defined by the Earth’s axis of rotation, are exactly on opposite sides of our globe, the same is not quite true of the North and South magnetic poles. Currently the north magnetic pole is situated at 84º of latitude and 169º of longitude, for the south magnetic pole to be exactly opposite it on our globe it would have to be at -84º and 11º of longitude but it is in fact at -74º latitude and 19º longitude. At least some of the reason for this asymmetry in Earth’s magnetic field comes from the observed fact the both magnetic poles move, currently the north magnetic pole is moving at a speed of about 45km per year.
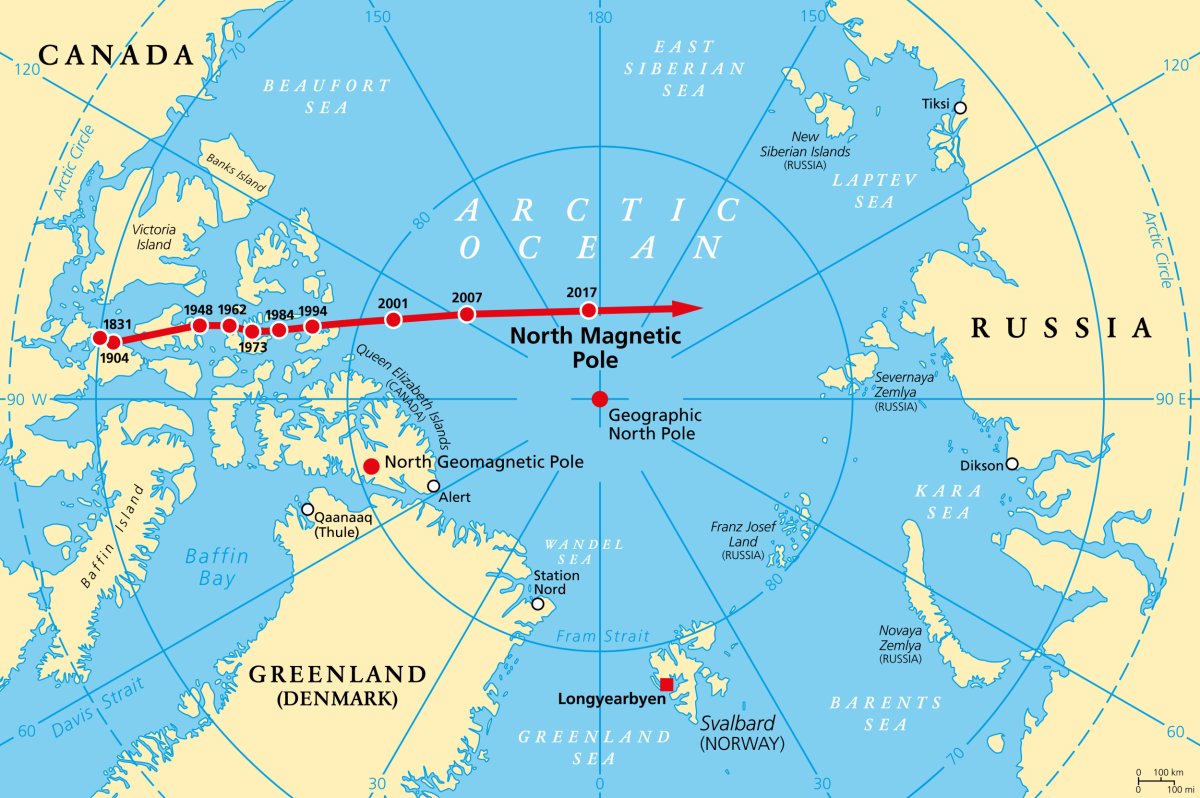
The discovery of this error in the model will certainly help with further improvements in the model but another find by the scientists may be even more important and that is the speed with which the Earth’s magnetic field is changed. As outlined in the report noticeable shifts in both the strength and polarity of the magnetic field can be observed even over as short a period as six months. In fact the rapid changes in the magnetic field are already causing problems in navigation for both ships and aircraft, especially for those whose paths take them close to the Polar Regions.

Earth’s magnetic field is a dynamic phenomenon whose pace of change is increasing. In the years to come those changes could impact our daily lives in other ways than just making navigation more difficult. Only by learning more about our planet’s magnetic field physicists can we prepare ourselves for the changes to come.