The eastern Mediterranean has always been one of the hotbeds of archaeology surrounded as it is by Greece to the north, Egypt to the south and the lands of the bible to the east. Yet despite over two hundred years of intensive study the eastern Mediterranean still manages to surprise us on occasion. In this post I’ll be discussing two new discoveries that have recently been made in the eastern Mediterranean. As usual I will discuss the earliest study first and move forward in time.
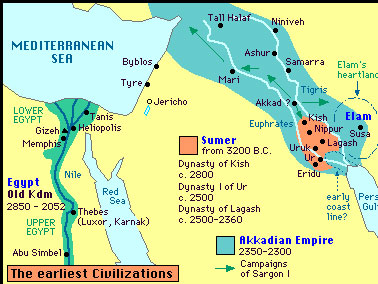
We humans took to traveling on the water long before the beginning of recorded history so the story of how the first boats and ships were built can only be uncovered by archaeology. Based upon underwater excavations of ancient shipwrecks it is known that by the late Bronze Age there were ships capable of sailing hundreds of kilometers and carrying tons of cargo conducting regular trade between the people of Egypt, the Hittite empire, Canaan, Troy and Greece.
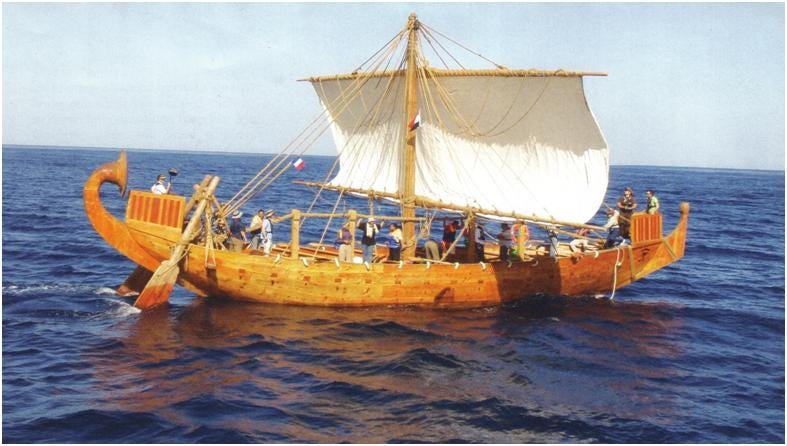

However it was always thought that those ships never sailed out of sight of land but instead hugged the coastline throughout their journeys. The reasons for this timidity are basically twofold; firstly in case of a storm a ship close to shore could quickly find a harbour or even beach itself for safety. In addition the navigators of that time probably lacked the navigational tools necessary to know where they were and what direction they were going once they were out of sight of land.

That’s what makes the recent discovery of a 3,300 year old vessel that had sunk about 90 kilometers off the coast of northern Israel so interesting; the location of the wreck was well out of sight of any land. Another interesting aspect of the discovery is the fact that the wreck was found at a depth of 1,800 meters, with its cargo apparently intact by the London based fossil fuel company Energean which operates underwater natural gas extraction wells in the eastern Mediterranean.
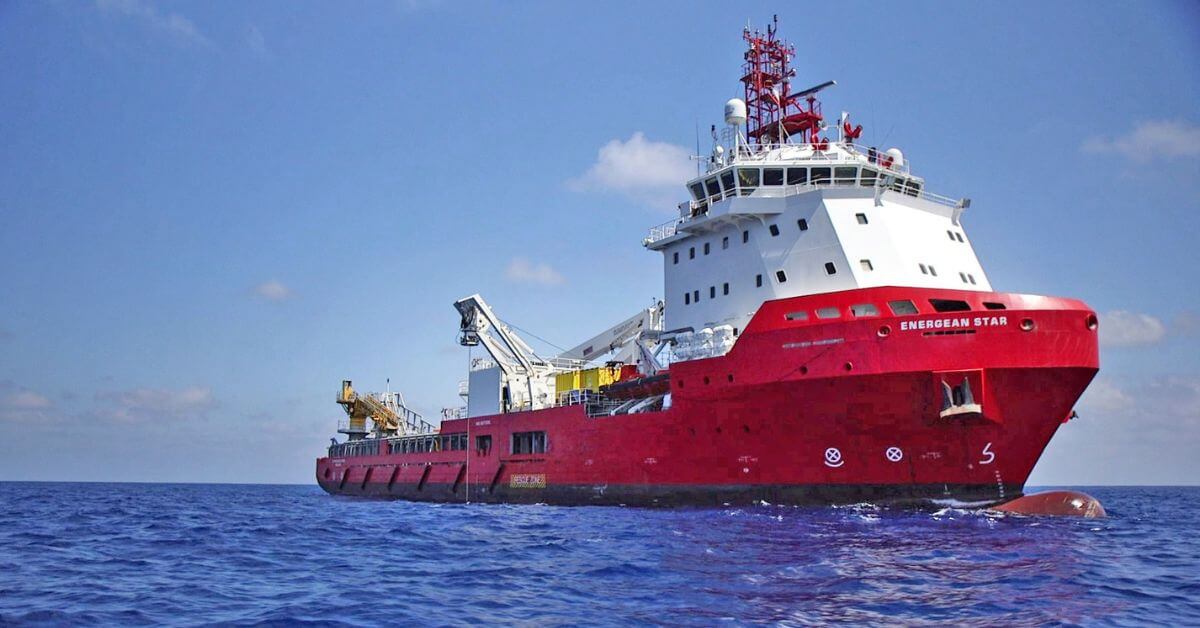

Energean was searching in an area off the coast of Israel for likely new sites for gas wells using an underwater robot when the robot just happened upon the ancient wreck. From what the robot could see the ship is approximately 12-14 meters in length and lays on the ocean floor surrounded by hundreds of earthenware jars that must have held the ships cargo of oil, wine or perhaps fruit.
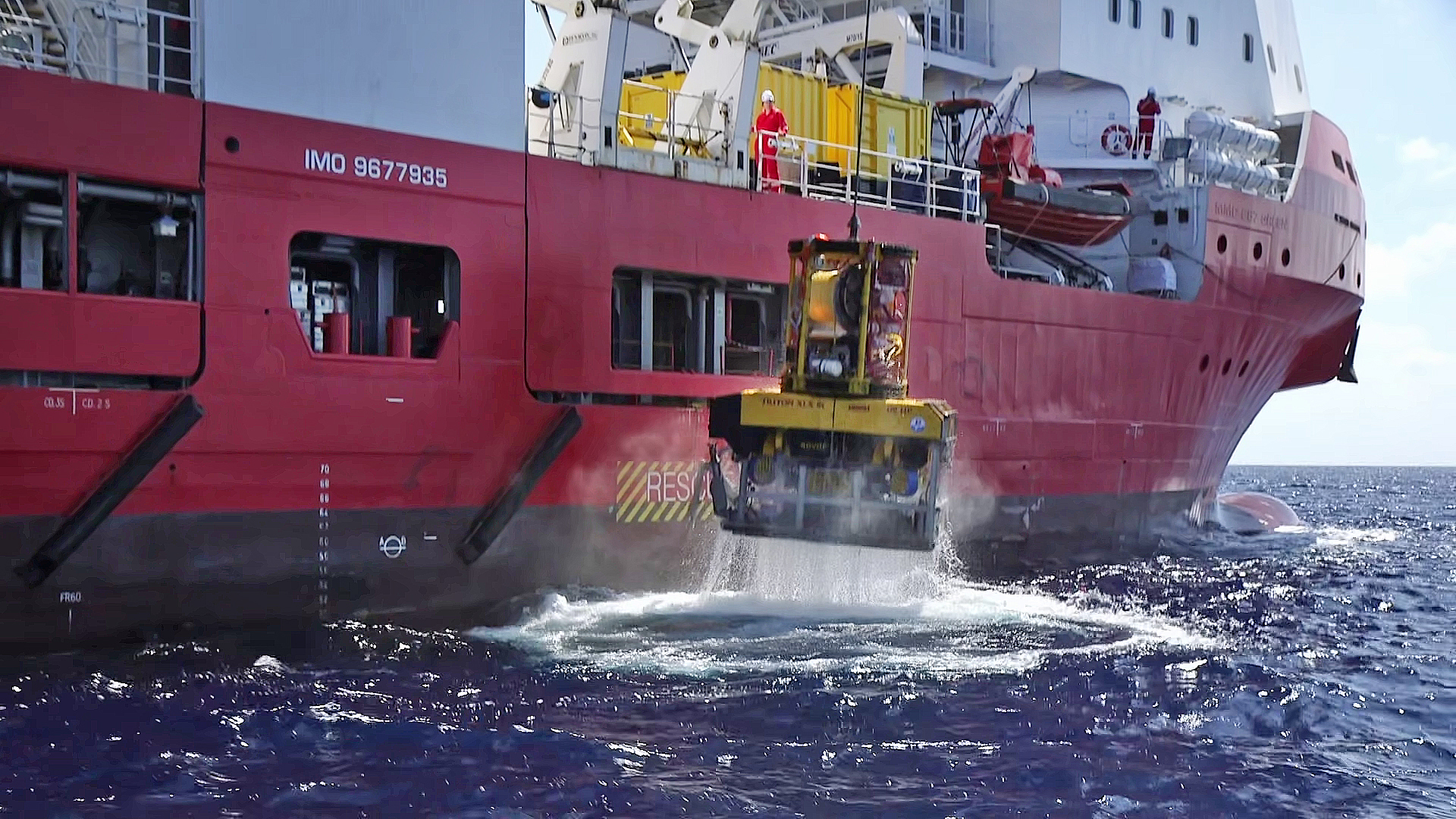

Once the engineers from Energean realized what they had come across they contacted the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) who announced the discovery of the wreck on the 20th of June. The wreck itself is so deep beneath the ocean’s surface that a comprehensive examination of the ship is probably impossible. However the Energean robot did succeed in bringing up two of the ship’s jars that archaeologists with the IAA have identified as being of Canaanite origin and from about the year 1,300 BCE.
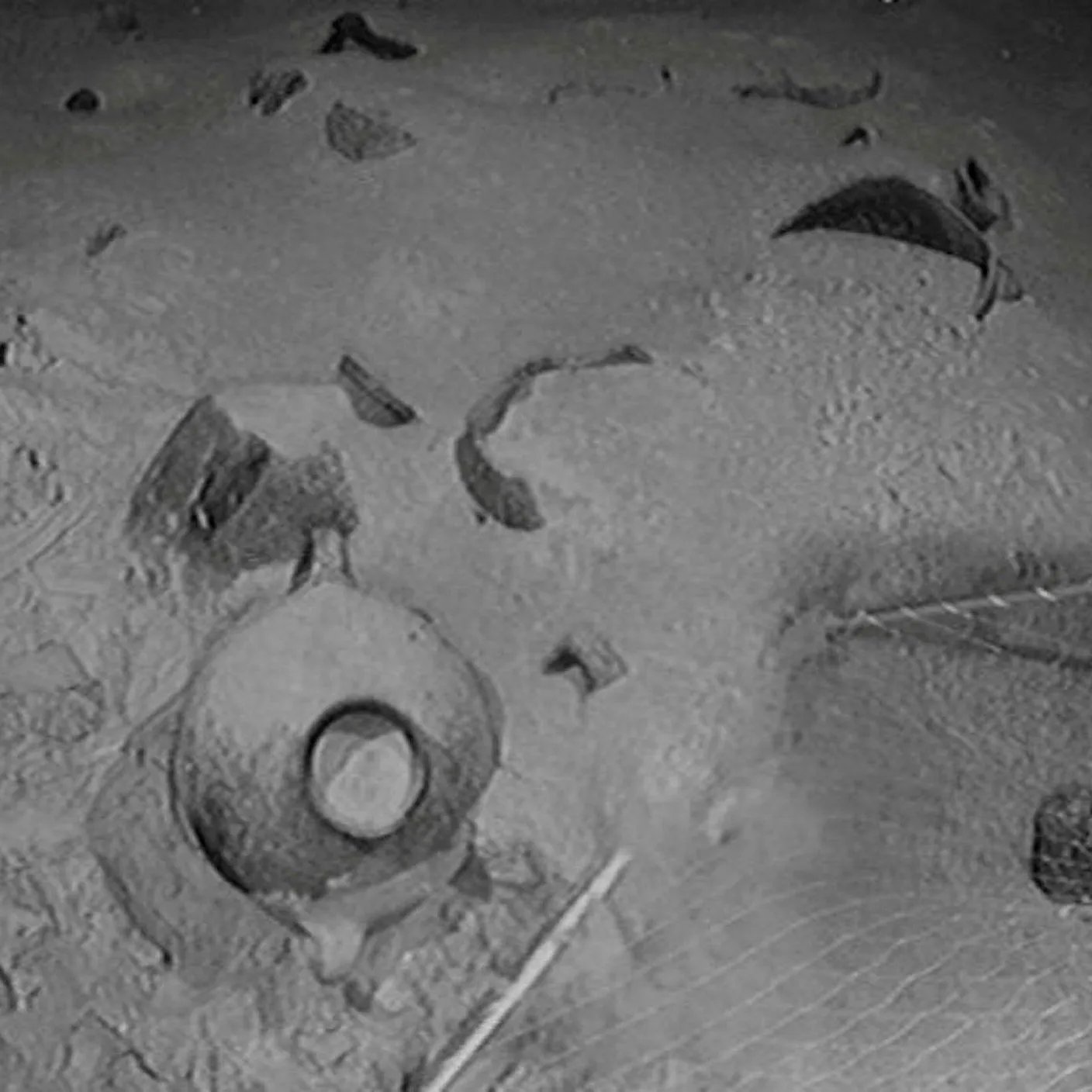

The Canaanites were of course the Bronze Age enemies of the Hebrews who lived along the coast of modern Israel and Lebanon. The fact that the wreck was discovered so far from land clearly shows that the ancient mariners of the Bronze Age were not as timid as we had though and that they probably could use the position of the Sun and stars to navigate when they were away from land.

Speaking of the enemies of the ancient Hebrews as the Bronze Age turned into the Iron Age the people of Israel and Judah acquired enemies who were much more powerful than the Canaanites. The Iron Age in the Middle East was a time of empires starting with Egypt and followed by the Assyrians, Babylon and Persia.
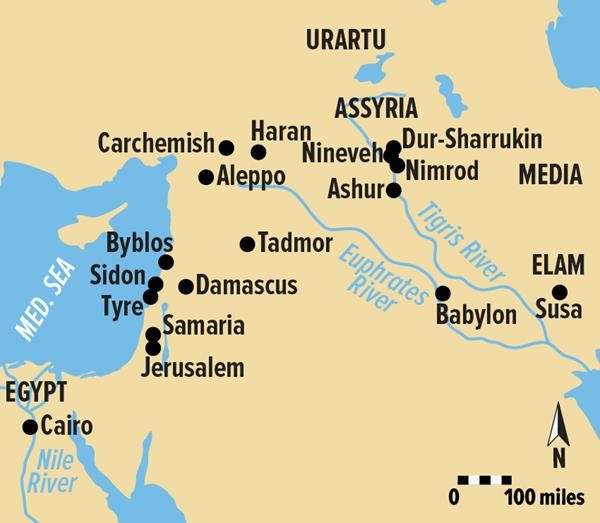
According to the bible the Assyrians tried to conquer the two Hebrew kingdoms several times before finally subjugating the kingdom of Israel, giving rise to the legend of the ‘lost ten tribes of Israel’. They never succeeded in defeating Judah however despite their king Sennacherib laying siege to Jerusalem in 701 BCE. As told in 2Kings 19:35 the Assyrian army was encamped outside the walls of the city when “the angel of the Lord went out and put to death a hundred and eighty-five thousand in the Assyrian camp.”
The Assyrians tell it a little bit differently. Cuneiform tablets have been found in excavations at the Assyrian capital of Nineveh that relate how king Hezekiah of Judah paid Sennacherib a large tribute, and promised to behave as the Assyrian king’s vassal in order to save the city.

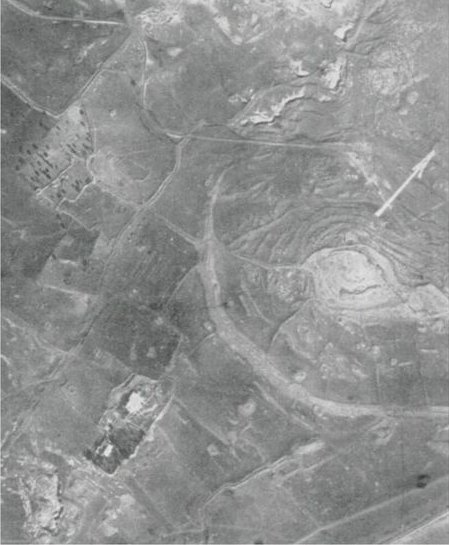
The truth is probably somewhere in-between but regardless an independent scholar who specializes in Near Eastern Archaeology named Stephen Compton has written an article in the journal Near Eastern Archaeology where he claims to have found the campsite of Sennacherib’s army. Now Mister Compton didn’t go digging around in Israel, instead he studied aerial photographs from the mid 20th century of the area between Jerusalem and the Hebrew town of Lachish that Sennacherib also laid siege to searching for clues as to where the Assyrian army might have camped.
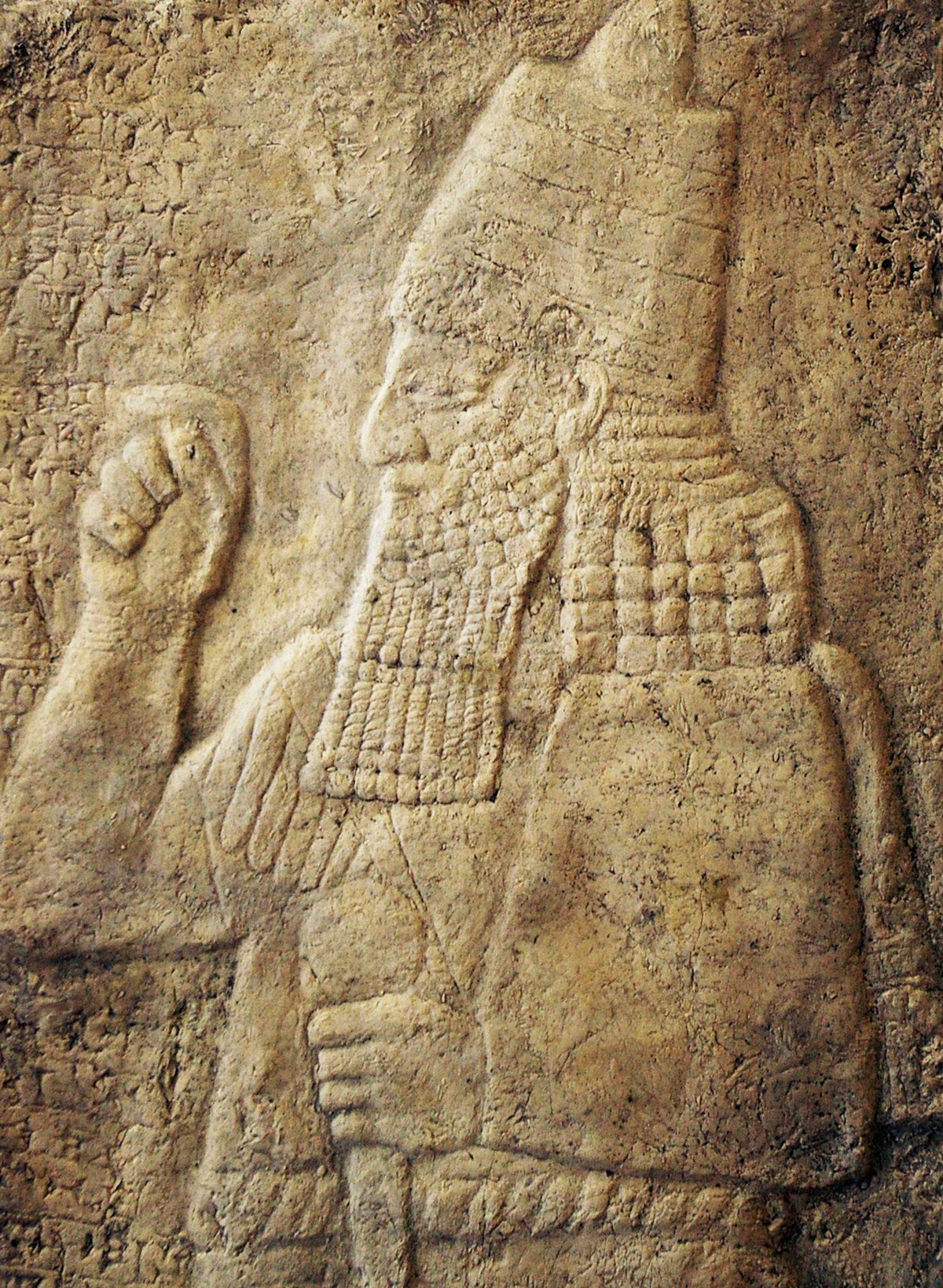

What Mr. Compton was looking for in particular was a simple oval wall encompassing an area large enough for an army to camp in but without any permanent structures inside. A temporary city in other words, which is pretty much what an army camp is. Stone reliefs from Nineveh have been found that show that the Assyrians did in fact build oval shaped temporary fortifications for their army during campaigns. The location that Mr. Compton has identified is known locally as the Khirbet al Mudawwara where Mudawwara is an Arabic word that can mean a place where a sultan has placed his army. A memory perhaps of the Assyrians even after 2700 years!
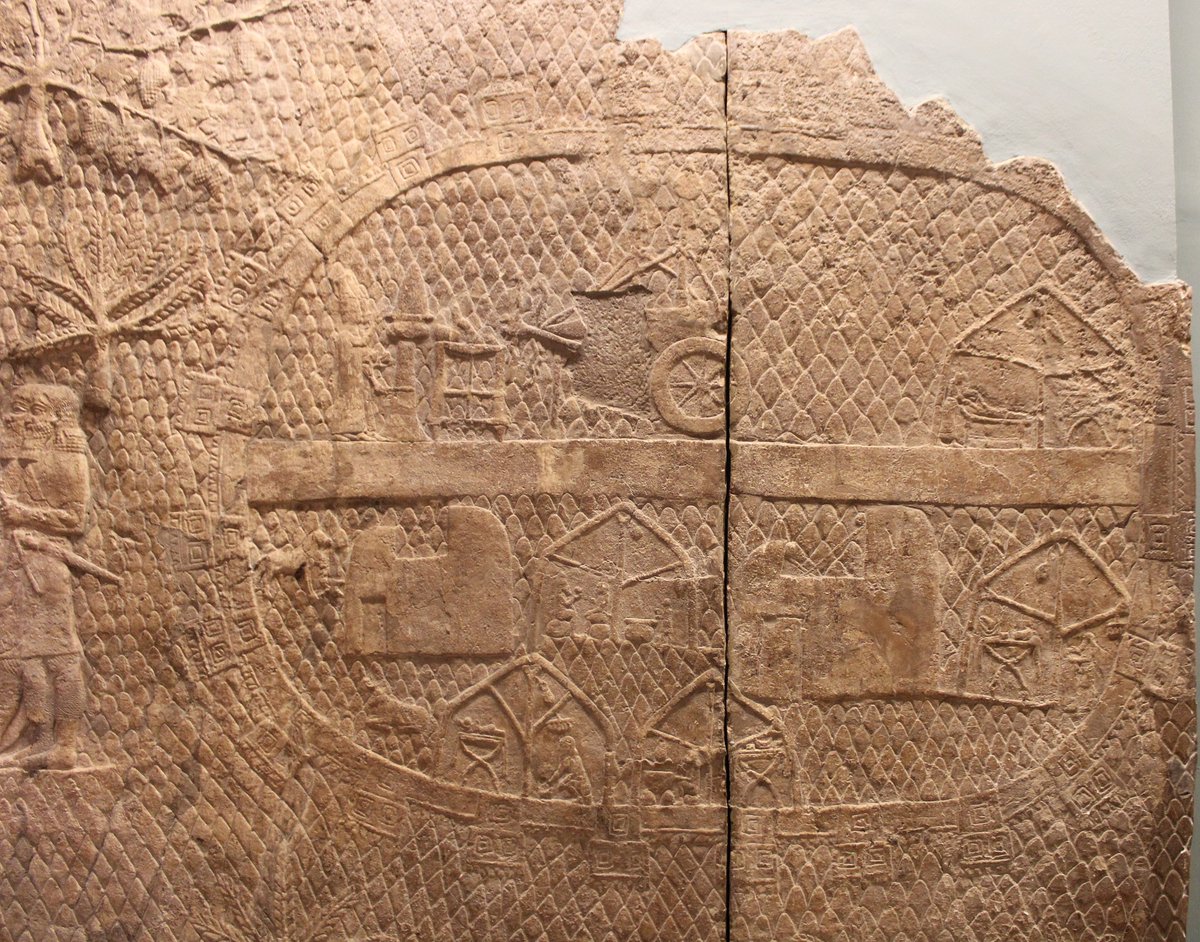


If Mr. Compton’s discovery does turn out to be true it will be good evidence that the bible, like Homer’s tales, can be used as a guide for the ancient history of the Near East. Provided that is you take into account spin doctoring, exaggeration and the occasional outright falsehood.
