I’m not certain as to whether or not to classify ‘A City on Mars’ by Kelly and Zach Weinersmith as Science Fiction. You see ‘City on Mars’ is actually an overview of the many problems we humans are going to have to overcome if we really want to settle outer space. Right now we are at the very beginning of that endeavor; we currently have two small, emphasis on small, space stations that are crewed by rotating teams of astronauts about every six months. In other words nobody is actually living in space at this moment. So in a sense that makes ‘A City on Mars’ kinda fictional, doesn’t it?

No matter, Kelly and Zach Weinersmith are a pair of space enthusiasts who have done a lot of delving into the challenges that humans are going to face trying to settle, they don’t like the term colonize because of its political baggage, outer space. Having started out as proponents of space settlement they freely admit that the number and scale of those challenges has made them a lot more cautious.

In ‘A City on Mars’ the problems of space settlement are classified into three broad categories, Physiology or can humans live and multiply long term in space, where to live in space and how, and finally, what are the legal aspects of building a settlement in space. You might wonder about the inclusion of that third class, after all isn’t space the final frontier and therefore kinda lawless? However the legal challenges may be the toughest of all, if we’re going to do it without starting any wars between space powers, nations that just happen to be nuclear powers as well.

Starting with the question of whether humans can live long term in space it’s worth remembering that back in the 1950s, right before the space age began, many medical experts were convinced that humans could not survive for more than a few minutes in zero gravity. Without gravity, they said, you couldn’t even swallow, you’d get disoriented, dizzy and be unable to perform any task. Finally, without gravity your heart would race at double the normal pulse rate until before long you’d have a heart attack.
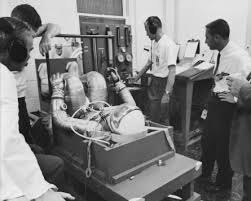
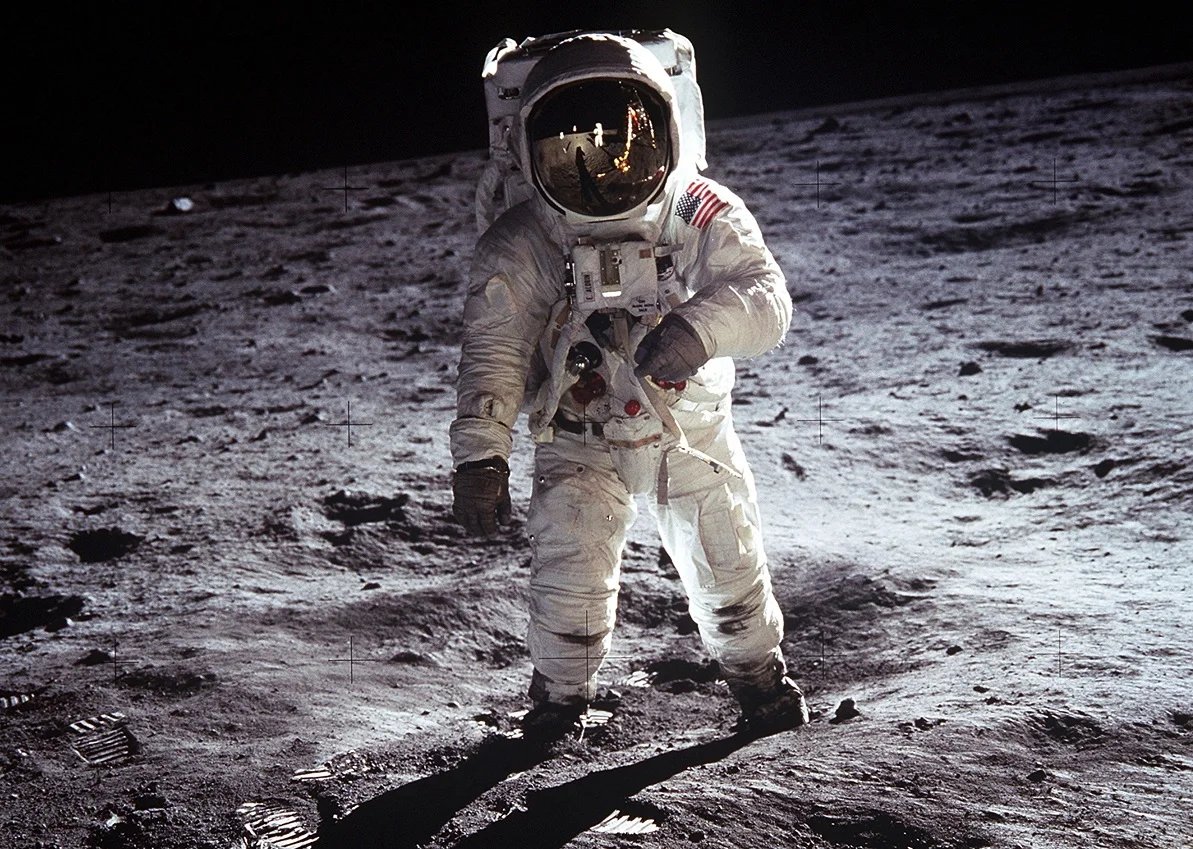
Fortunately it didn’t work out that way. By the time the first men walked on the Moon it was obvious that people could survive zero gravity for several weeks with the only impediment being some temporary weakness when you returned to Earth.
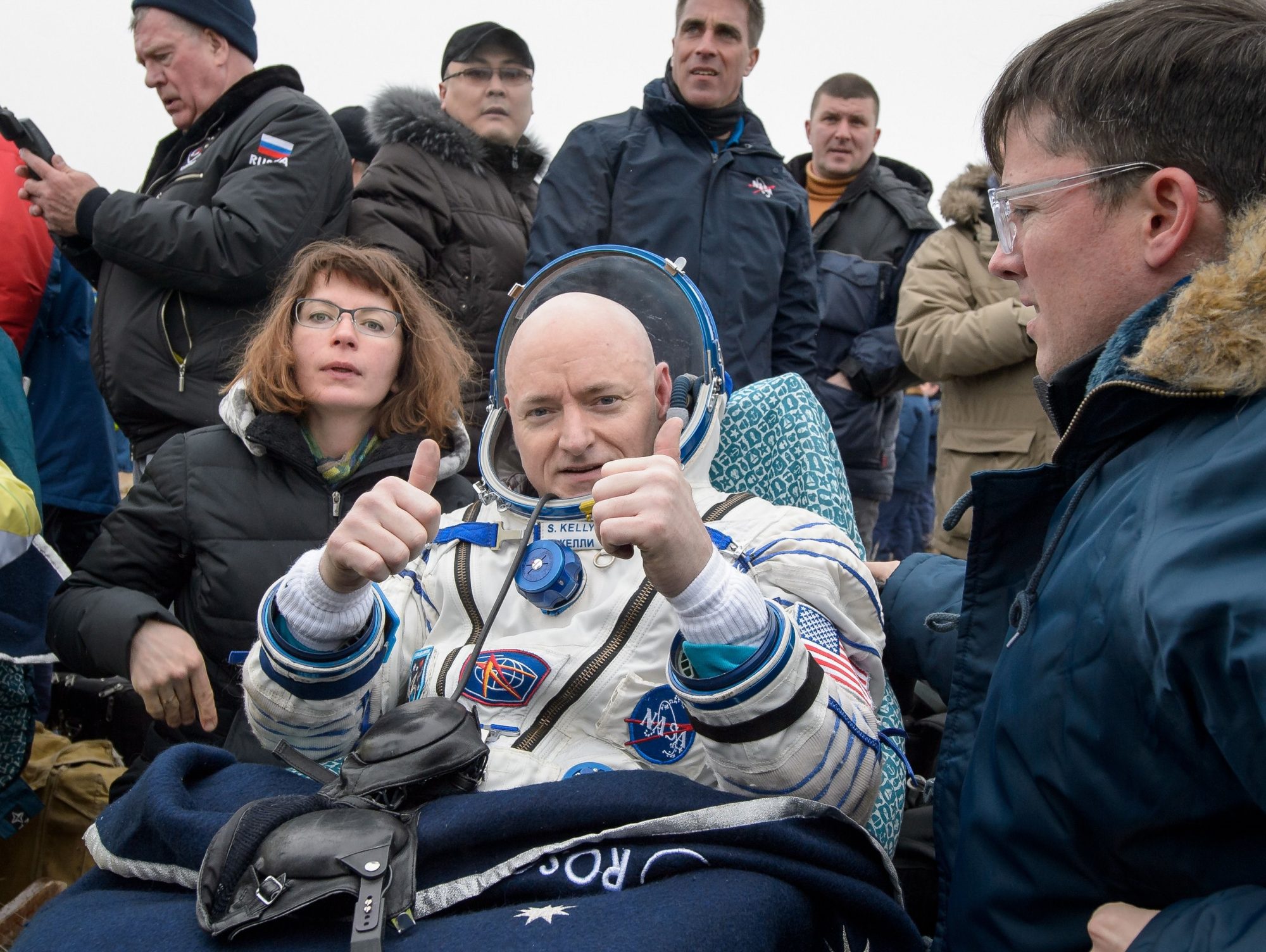

However, living in zero gravity for the rest of your life may be another matter. You see, thanks to our space stations we now have lots of data about people living in zero gravity for six months to a year at a time and it’s becoming clear that our bodies aren’t built for living there. Bone mass loss appears to be the biggest problem but there is muscle loss as well, and that’s despite astronauts putting in several hours of exercise every day. There’s also the way that fluids in your body redistribute themselves in zero gravity and that includes the shape of your eyeball causing vision problems. Of course NASA is doing a lot of medical research to find treatments to remedy these problems but it’s clear that our bodies are not built to live in zero gravity long term.

But what if we if build settlements on the Moon or Mars, they have gravity after all, it’s not as strong as Earth’s but it’s still more than zero gravity? Well the problem there is that the longest anymore has spent in partial gravity was about three days on the Moon. We have no idea about whether Lunar or Martian gravity is strong enough to prevent or even lessen any of the problems stated above.

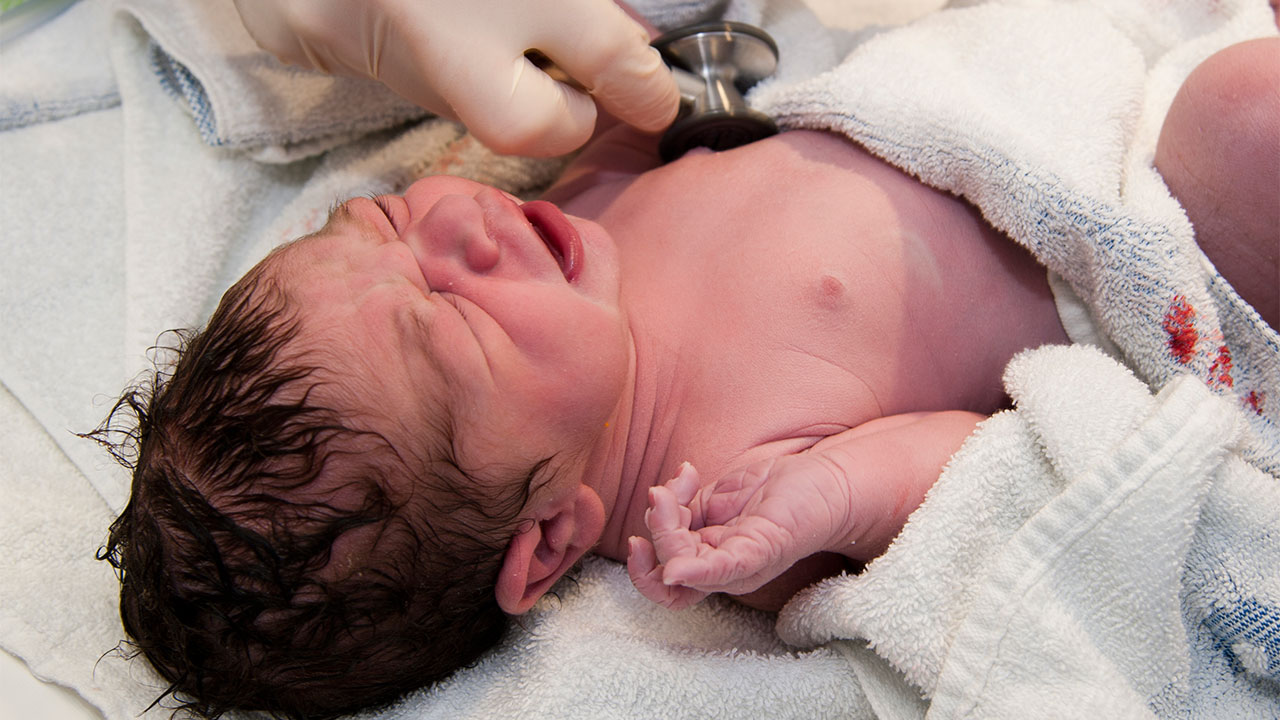
There’s another big issue about which we have no data at all and that’s the question of trying to have children, and raise them in outer space. While it’s true that a fetus in the womb is kinda sorta in zero gravity still there’s that business of the mother’s fluids being redistributed along with her loss of bone and muscle. Then, once the child is born how will they grow in zero or partial gravity, could a child born and raised on Mars ever acquire enough muscle to be able to visit Earth? To date no experiments related to breeding and raising animals have been conducted in space so we literally know nothing about whether it can be done.
Assuming we can live and multiply somewhere in space the question now becomes where and how. After a quick review of the various choices in our solar system ‘A City on Mars’ settles on the Moon and Mars because the two of them are the closest to Earth in both distance and conditions. The problem is that even then the Moon and Mars are horrible places to live. As far as trying to live there is concerned they are both airless, waterless deserts where even the sky and ground are trying to kill you. Any people living there will have to build themselves strong shelters equipped with the means of providing air, water and food while keeping a livable temperature, oh and shielding its inhabitants from cosmic radiation.
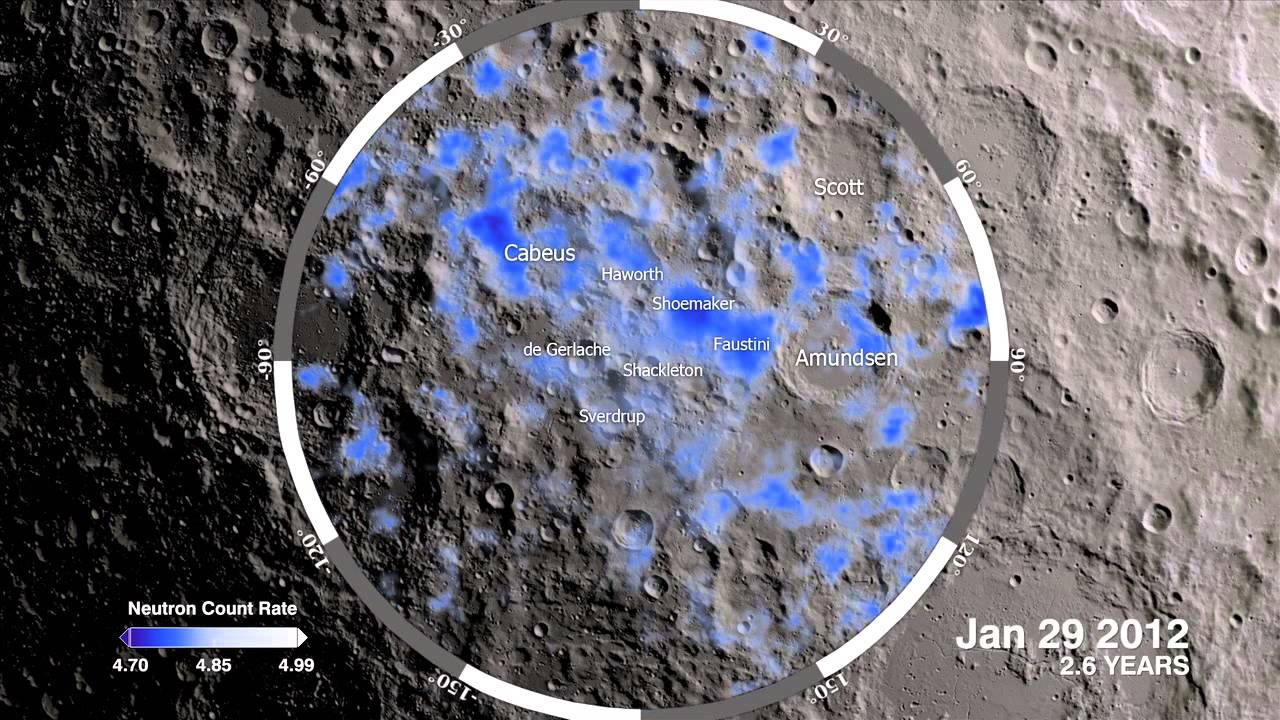
‘A City on Mars’ also takes a chapter to discuss the choicest real estate on the Moon. You may have heard recently about how space nations are really interested in the Moon’s south pole. That’s because it’s thought that the bottom of some of the craters there may have been in complete darkness for billions of years so that there may be water there in the form of ice. Also, some of the peaks of those craters may be in almost perpetual sunlight making them the perfect places to build solar arrays for power. The fact that those areas represent less than one tenth of one percent of the Moon’s surface makes them extremely valuable, valuable enough to be the cause of violence?

Which brings me to the legal aspects of settling space. Of course so far there hasn’t been much need for the long arm of justice in space. That’s because there are only three nations that have the ability to send people into space and those nations have all made certain that the people they send are law abiding and can be expected to behave themselves while in space. Nevertheless, as more actors gain access to space, such as Space X, the race to obtain what little resources there are in space may lead to conflict.

The governing legal document covering the exploration of space right now is actually called the Outer Space Treaty or OST and it was ratified in 1967 by the only two space powers at the time, the USA and the USSR. Since that time another 110 countries have signed on including all of the major space nations. Shortly after its creation the OST was supplemented by several other agreements known as the Rescue Agreement, the Liability Convention and the Registration Convention.

So how are these treaties going regulate the way that human beings settle space? The short answer is that the OST forbids anyone from owning any part of any celestial object, in other words no ‘I claim this crater in the name of King and Country’. On the other hand anyone can explore and make use of space, so Ireland for example has the right to set up a exploratory outpost basically anyway on the Moon, but they don’t even control the ground directly beneath that outpost! Obviously that could lead to a fair amount of misunderstanding if Vietnam decides to set up their outpost in exactly the same spot as Ireland’s!

What the authors of ‘A City on Mars’ have discovered is that there isn’t a lot of rules and regulations that will govern how we settle space, which could lead to a ‘wild west’ scenario complete with shoot outs that trigger full-scale wars, between nuclear powers, back here on Earth. Remember Spain, Portugal, France, Holland and England fought a number of wars in Europe that began in the New World.

So there are a lot of problems that are going to have to be solved before humans settle space and most of them do not involve rockets or robots or spacesuits or cool technical things like that. If you’d like to know more about those nasty little details, and some of the possible solutions I think you’d like to read ‘A City on Mars’.
