On Tuesday the 18th of March a Space X Dragon capsule returned to Earth carrying the four Crew 9 astronauts completing their mission at the International Space Station (ISS). Those astronauts had two days earlier been relieved at the ISS by four Crew 10 astronauts who will now crew the station until at least July.
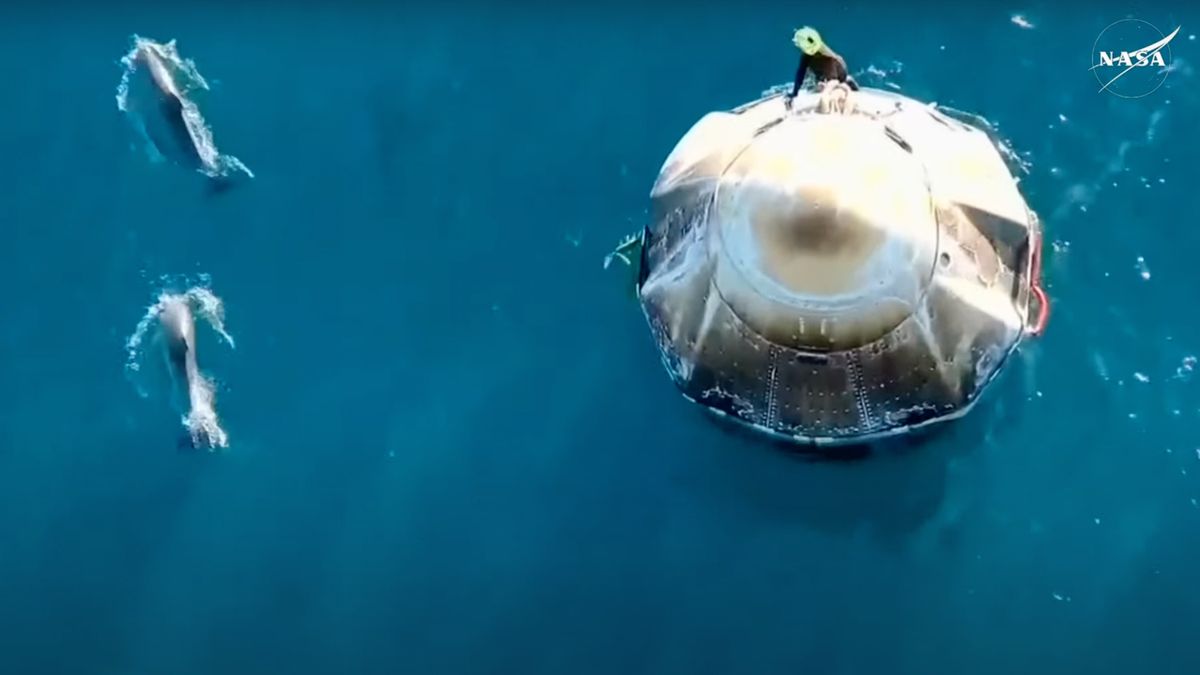

In many ways the splashdown of the Dragon capsule in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Florida represented just another routine crew transfer for Space X. The long saga of Crew 9 however was anything but routine, for two of the astronauts returning to Earth were originally the crew of Boeing’s Starliner capsule on its first manned mission to the ISS. The Starliner crew only became a part of Crew 9 when NASA decided they did not trust Starliner to safely bring them back home.

It’s a long story that I’ve already discussed in several past posts, see my posts of 20 July 2024 and 31 August 2024. In brief astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore were assigned by NASA as the test pilots for Boeing’s Starliner capsule which was intended to both compliment and compete with Space X’s Dragon capsule in transferring astronauts to and from the ISS. After many years of technical problems and delay the Crew Flight Test (CFT) was finally launched on the fifth of June 2024 and reached the ISS after more problems while in orbit.
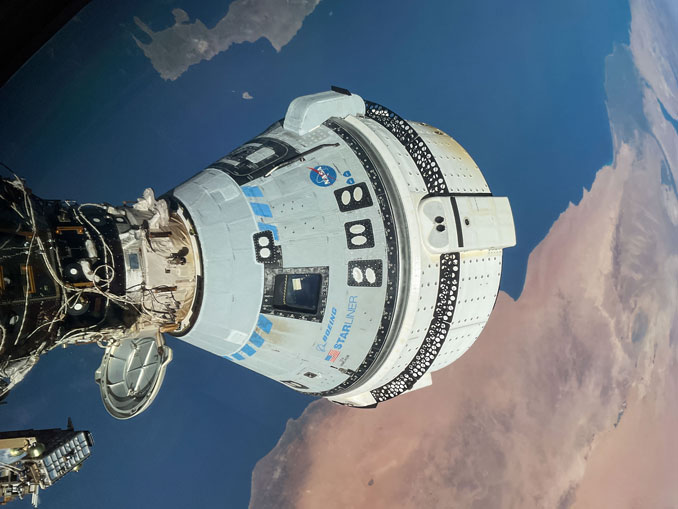

Astronauts Williams and Wilmore were only supposed to remain on the ISS for eight days but NASA engineers spent more than a month trying to understand and fix the problems with Starliner’s thrusters. In the end it was decided that Starliner was too untrustworthy to risk returning from orbit with astronauts aboard so the Starliner capsule was brought back unmanned.
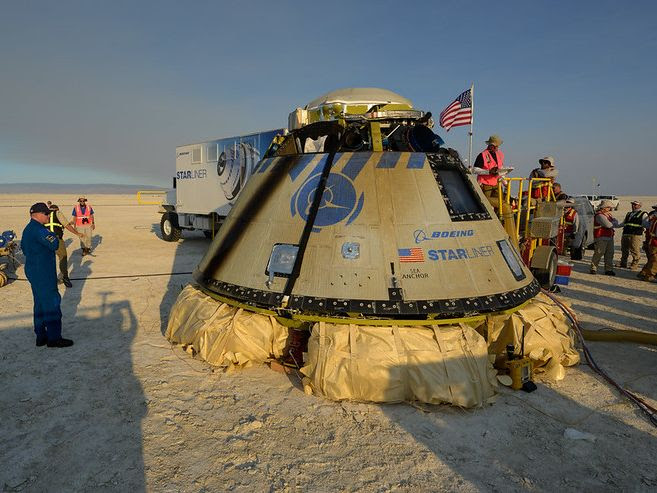

A special rescue mission using a Space X Dragon capsule was considered but in the end NASA decided to send the next scheduled crew transfer mission, Crew 9, with only two rather than the usual four astronauts. Williams and Wilmore then became the other two Crew 9 astronauts and would return to Earth when Crew 9 was relieved by Crew 10. In all, the eight-day mission for Williams and Wilmore turned into a nine month mission.

So with Williams and Wilmore now safely back on Terra Firma the question for NASA is, what to do with Starliner. Boeing has yet to demonstrate that the eight billion dollar capsule can complete a mission without problems. To make matters worse for Boeing the ISS is scheduled to be de-orbited in five years so there are a maximum of about eleven regular crew transfer missions left for Starliner to take part in.

Currently NASA is considering their options. At a briefing on March 9th, shortly before the launch of Crew 10, it was announced that Boeing and the space agency were “making good progress” and had resolved 70% of the issues that Starliner had developed during its CFT. If that is so it seems that another CFT is unlikely to be carried out before this time next year and even if everything in that test goes smoothly a regular crew transfer mission can hardly be set up before early 2027.

There are even rumours coming from Boeing that the aerospace corporation might be considering giving up on Starliner. After all there is now little chance that Boeing can recoup the losses that they have incurred due to Starliner on a few missions to the ISS before it is de-orbited. Add to that the damage to Boeing’s reputation if there are any further problems with Starliner. At the same time however there are plans in the works for several commercial space stations to replace the ISS and Boeing would certainly like to use Starliner to secure a portion of the business of taking astronauts back and forth to them.

A few paragraphs above I mentioned that the current plan for the ISS is to de-orbit the aging space station in or around 2030. Space X has already been awarded the contract to modify the cargo version of their Dragon capsule to provide the necessary power to bring the ISS down for a landing in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. On February 21st however Space X’s CEO Elon Musk announced that in his opinion that the ISS should be brought down “as soon as possible”, within two years if not sooner. Musk’s claims that the ISS has served its purpose and is now taking money and resources away from his chief goal of reaching Mars. Musk has even argued that NASA should forget about the Artemis program’s goal of returning astronauts to the surface of the Moon, again with the intent of getting to Mars as quickly as possible.

NASA’s new director Jared Isaacman, who has ridden into space twice via commercial flights onboard Space X’s Dragon, also feels that the space agency needs to concentrate on a long term goal of Reaching Mars. Meanwhile Trump has publicly stated that although the idea of missions to the red planet “are of interest” they are not currently “a top priority”. Once again we see the possibility of a political change in Washington upending all of NASA’s long term goals, resulting in a waste of money, resources and worst of all time.

And to top it off Space X has conducted another private space mission designated as Fram2. That mission was funded by Chun Wang a Chinese born cryptocurrency billionaire and the crew consisted of three of his friends, Eric Phillips of Australia, Jannicke Mikkelsen of Norway and Rabea Rogge of Germany. This latest billionaire joyride was distinguished by its planned orbital path, which will for the first time take astronauts over Earth’s polar regions. The mission launched on the first of April and successfully splashed down on the April fourth.

This post turned out to be entirely about manned space flight but that doesn’t mean that there isn’t a lot going on with robotic space probes. Hopefully I’ll be able to catch up with them soon.