Quite a few stories of interest this month, mostly dealing with manned spaceflight. So let’s get to it!
In my last space post I talked about how the Crew 11 astronauts were forced to depart from the International Space Station (ISS) early on the 11th of January because of a medical issue with one of its four members. This emergency left the ISS with only a skeleton crew of three cosmonauts until the Crew 12 team could be readied and launched aboard their Space X Dragon capsule.

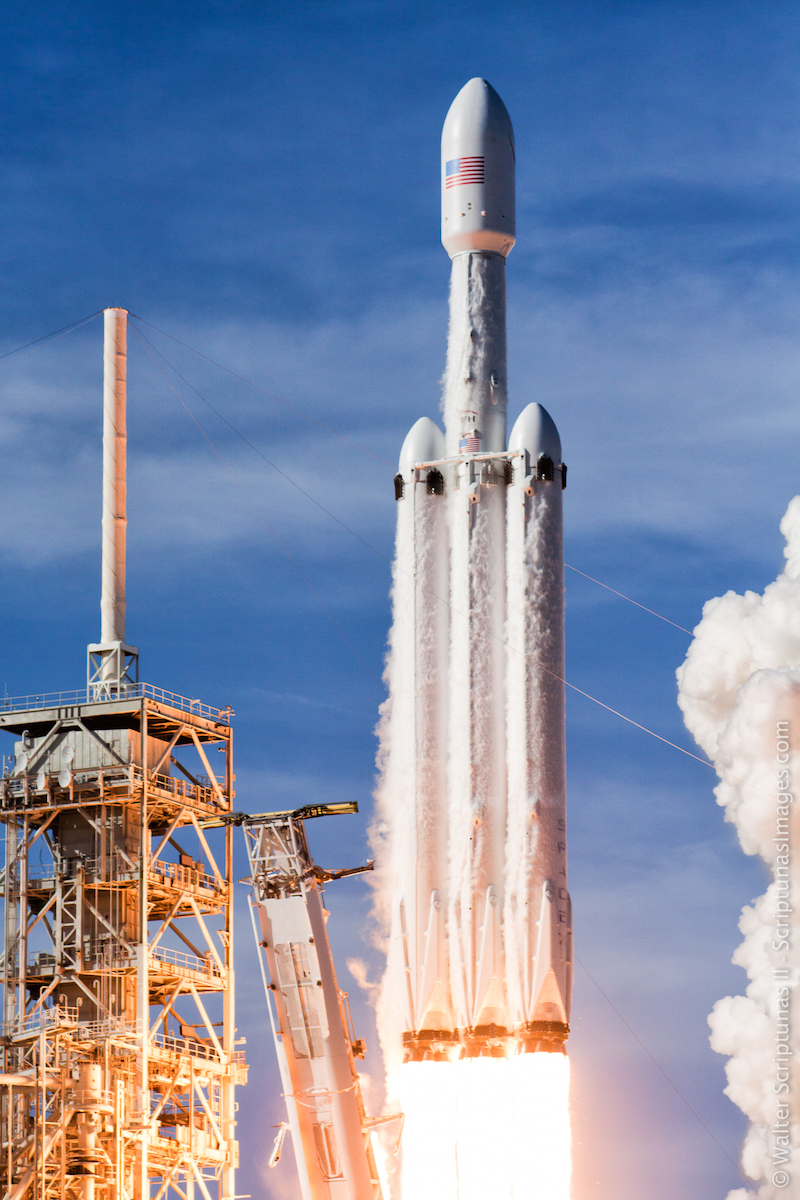
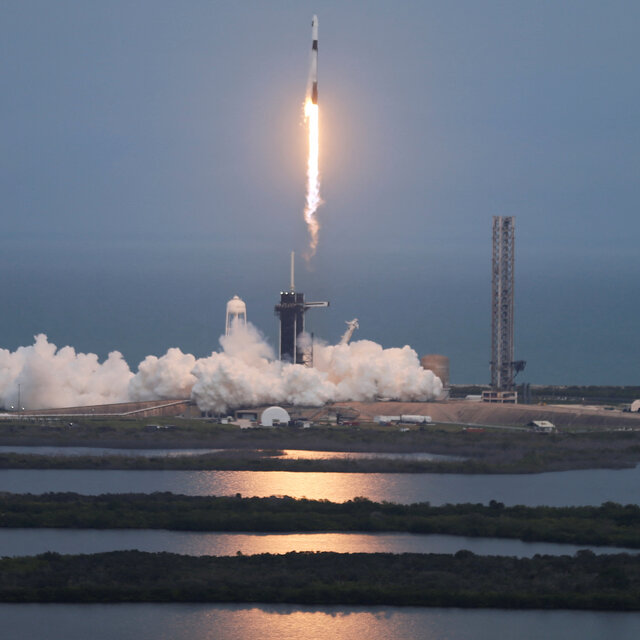
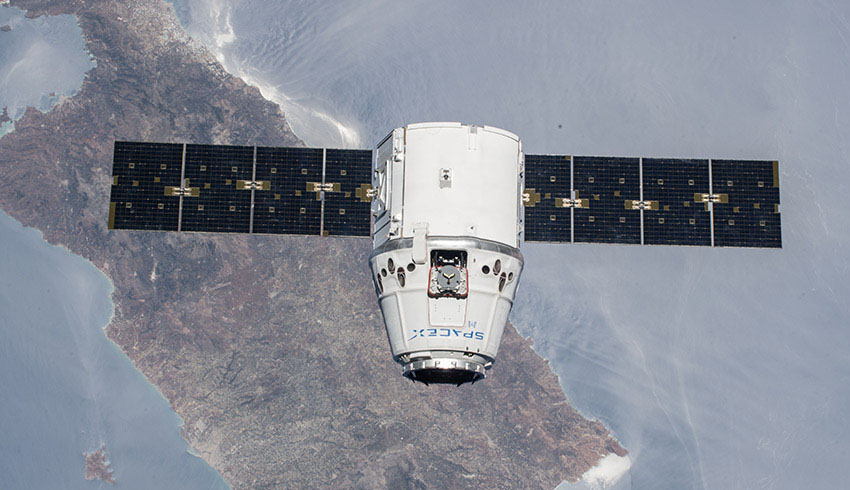
Working quickly NASA and Space X succeeded in moving up the launch of Crew 12 from its original planned date to February 13th. As usual the launch of the Falcon 9 rocket went off without any problem and about a day later on the 14th the Dragon capsule was docked at the ISS. Thanks to Space X and its reusable Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon manned capsule NASA’s commercial crew program is an unqualified success as manned missions to Low Earth Orbit (LOE) are becoming routine.
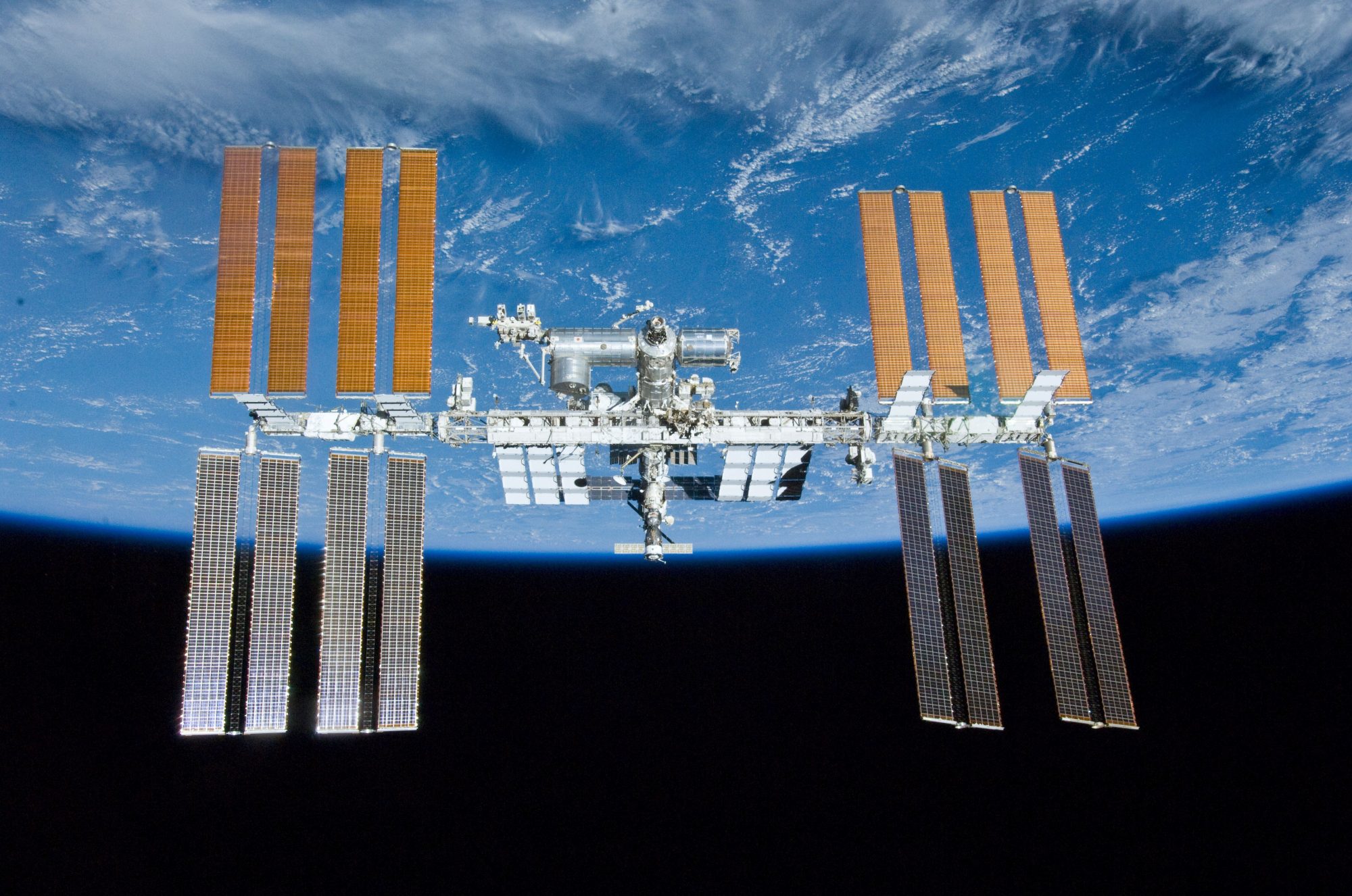

In fact manned missions are becoming so routine that they are no longer solely the province of national space agencies. Private companies or even individuals can, for a large amount of money, charter a manned space mission. There have already been four such missions to the ISS and several other missions that did not go to the ISS.

As a part of this growing commercialization of LOE, NASA and its partners in the ISS have signed contracts for a fifth and sixth private mission to the ISS. The fifth mission, scheduled for no earlier than January of 2027, was awarded to Axiom Space Corporation, the company that charted the first four private missions to the ISS. The sixth mission was awarded to a newcomer, Vast Corporation and is scheduled to launch no earlier than the summer of 2027.
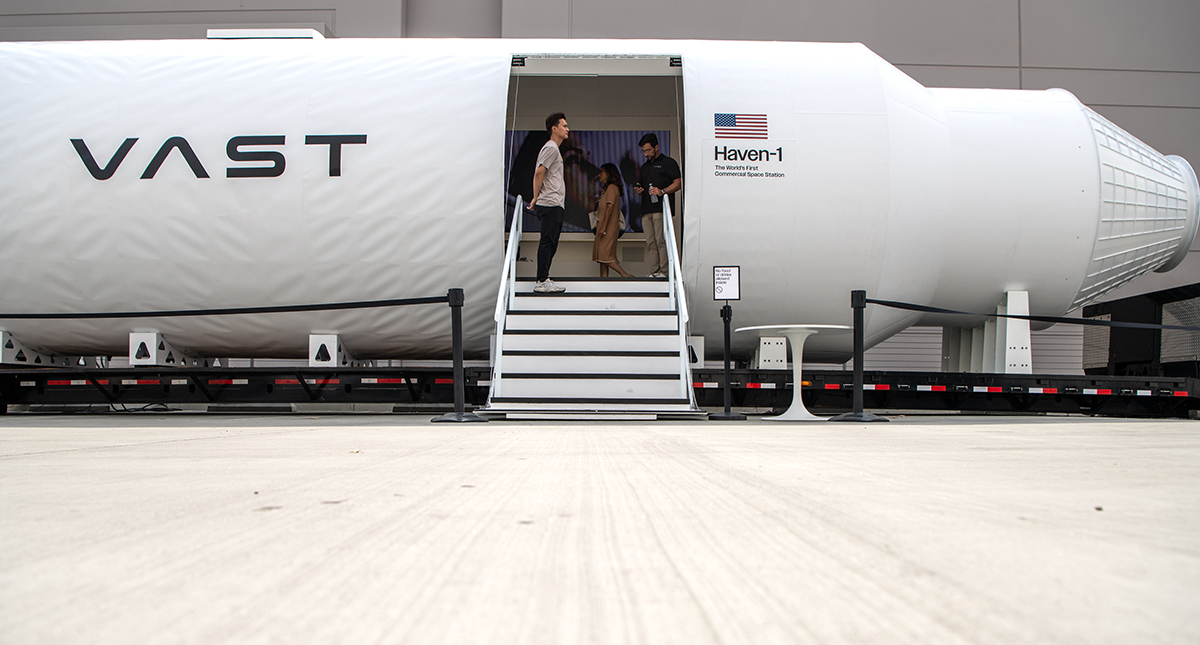

Both of these two missions will spend about 14 days at the ISS and will consist of four crewmembers. Axiom and Vast will purchase mission services from NASA including crew consumables and cargo delivery and storage. Both companies will also have to make flight arrangements with Space X including launch and re-entry missions. In exchange Axiom and Vast will each be allowed to sell four tickets to the ISS, although the private astronauts who are selected must be approved by NASA and will be trained by both NASA and Space X.

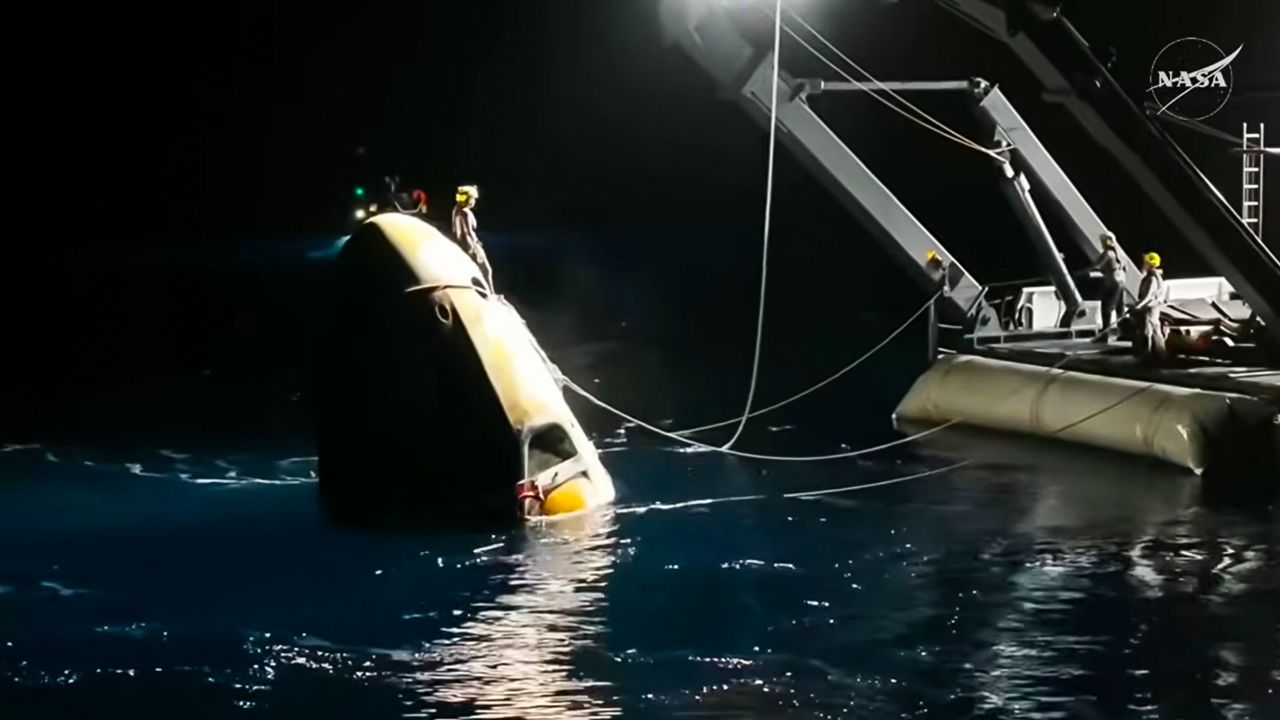
NASA’s commercialization of space was not originally intended to become a Space X monopoly. The plan was for Boeing’s Starliner capsule to also transport both NASA and commercial astronauts to the ISS. However, as I have often mentioned in earlier posts, see my posts of 20July2024, and 12April2025, the Starliner capsule has suffered a seemly unending series of problems. Back in 2024 Starliner finally succeeded in getting two astronauts to the ISS but with so many issues that NASA deemed the capsule to be unsafe for the astronauts to return in. So, the Starliner astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore’s stay at the ISS went from being only a week to more than eight months before they could return to Earth aboard a Space X Dragon capsule.
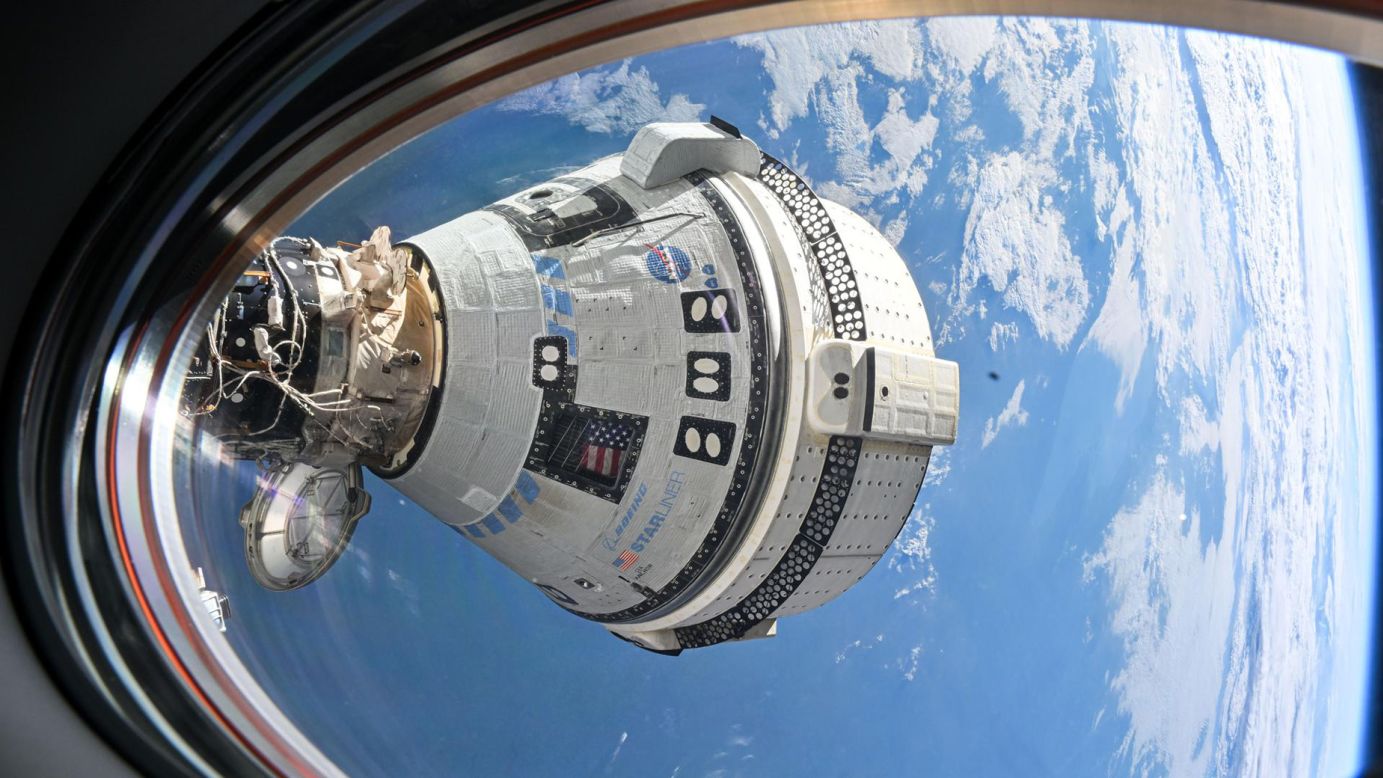

On the 19th of February NASA released its final report on Starliner’s mission and the results were not good for Boeing. Officially Starliner’s mission has been categorized as a ‘Type-A Mishap’, the worst category possible and equivalent to the Challenger and Columbia Space Shuttle disasters! The report details numerous failings that “revealed critical vulnerabilities in Starliner’s propulsion system, NASA’s oversight model, and the broader culture of commercial human spaceflight.” Hither to this report NASA’s Commercial Crew Program had been permitted to investigate itself but now that philosophy is considered to be “inconsistent with NASA safety culture.”

Nevertheless NASA still hopes that Starliner can fulfill some part of its original aspirations. The current plan is for Starliner to conduct one more test mission, to be designated Starliner-1, to the ISS. This test flight however will be unmanned; Starliner will only carry cargo to the ISS. This test flight is scheduled to be conducted no earlier than April.

If everything goes well in this latest Starliner attempt then it is possible that the next ISS crew rotation, planned for August, may be carried out with Starliner rather than a Space X Dragon. For that reason the four astronauts assigned to the next ISS mission are training on both Dragon and Starliner capsules. Whether or not this scheduled plan will be altered because of the 19th of February report remains to be seen.

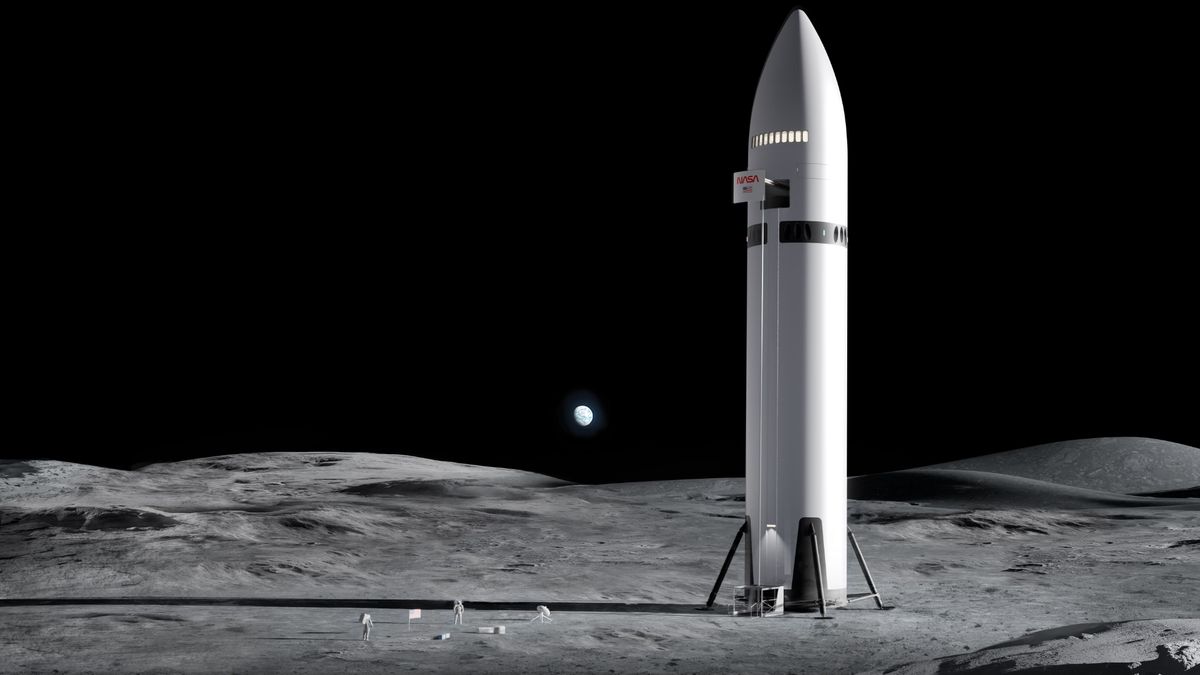
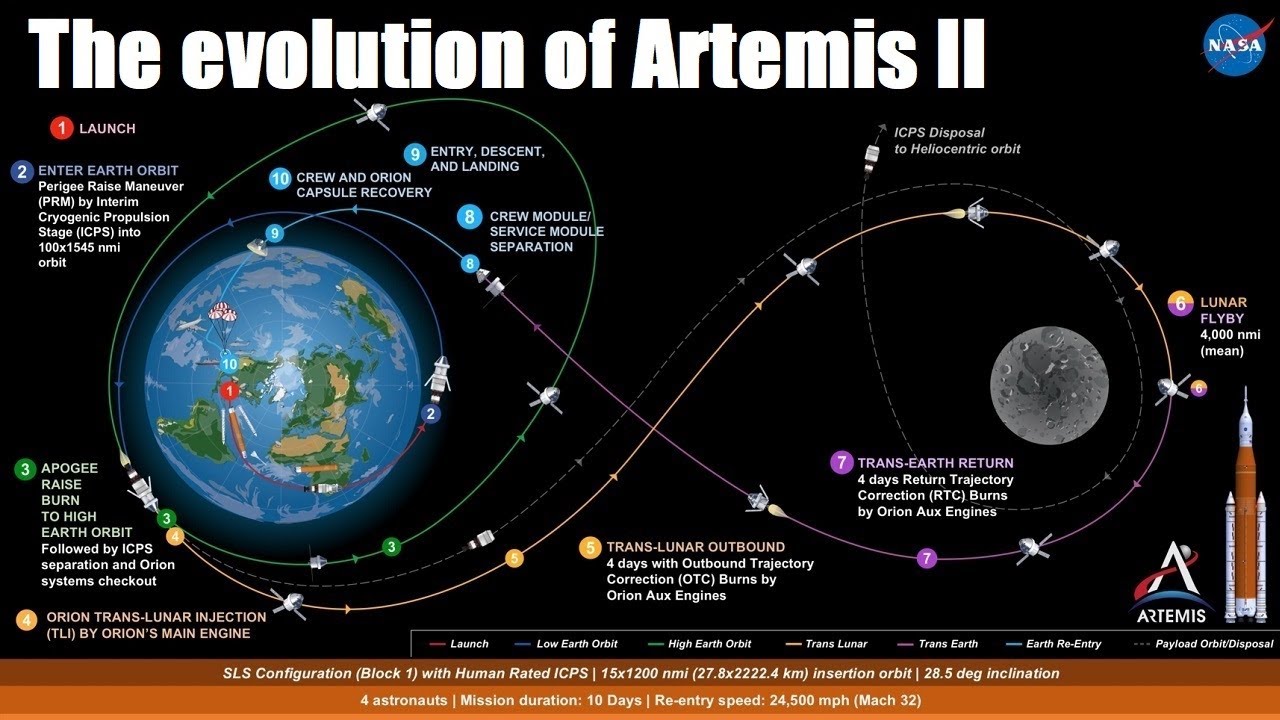
So far all of my news in this post have dealt with space flights to LOE, begging the question of when will we be getting back into deep space, getting back to the Moon and beyond. Well, the Artemis II rocket and Orion capsule are currently sitting on their launch pad undergoing final testing before launching four astronauts out of LOE for a trip around the Moon similar to Apollo eight’s mission back in 1968.
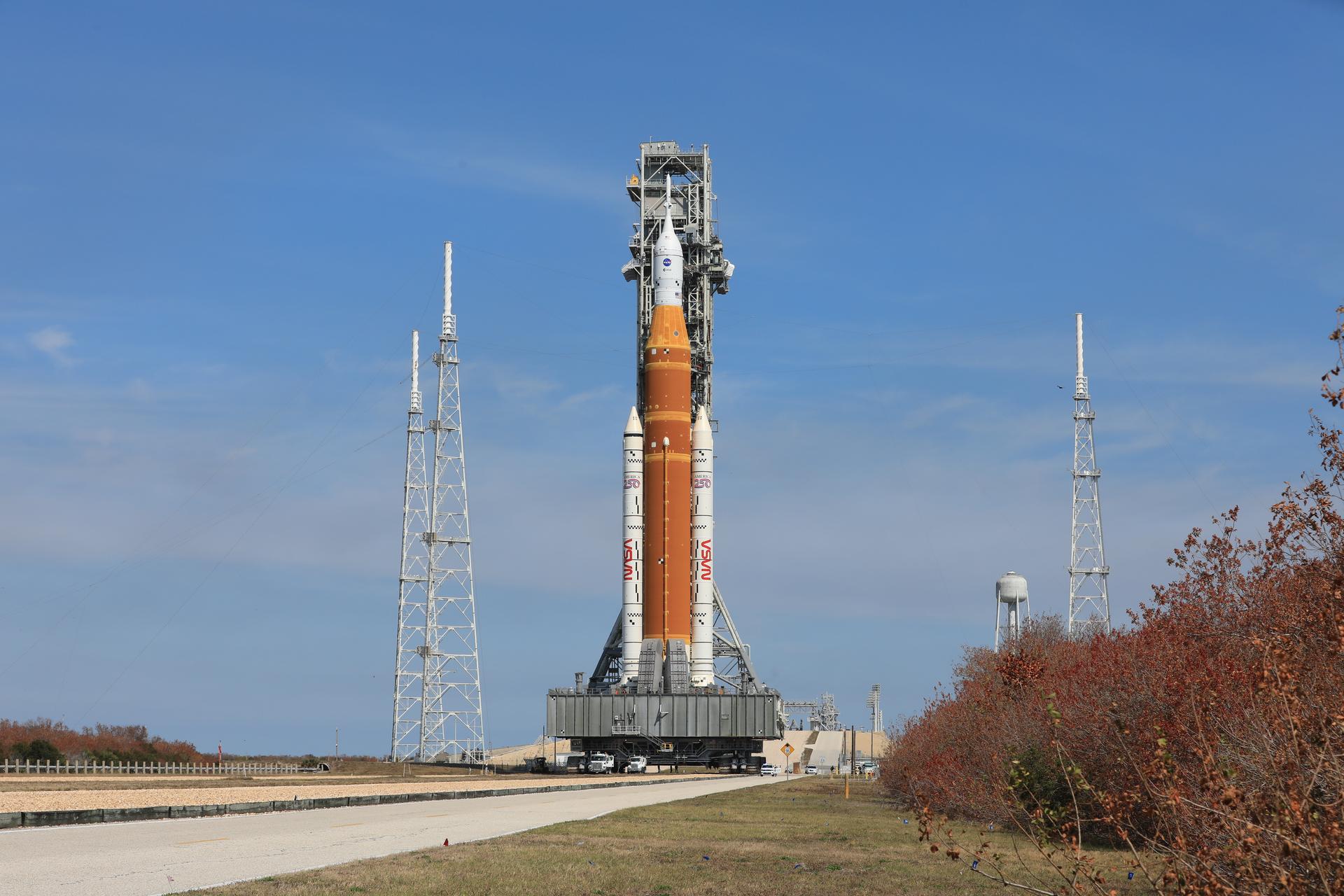

As a final test before launch NASA conducted a wet dress rehearsal on February 12th, that’s a full fueling of the rocket. Unfortunately during that test a series of hydrogen leaks occurred forcing the test to be terminated early. This same problem occurred during testing of the Artemis I unmanned mission back in November of 2022.
A second wet dress rehearsal was carried out from February 17th to the 20th and at first it appeared that the hydrogen leak problem had been resolved, the mission was put on a schedule for a launch on March 11th. However on the very next day the leak problem reappeared in the Artemis II’s second stage and the decision has been made to roll Artemis back into the Vehicle Assembly Building for repairs. How long of a delay this will cause to the Artemis II’s launch is just guesswork at the moment.
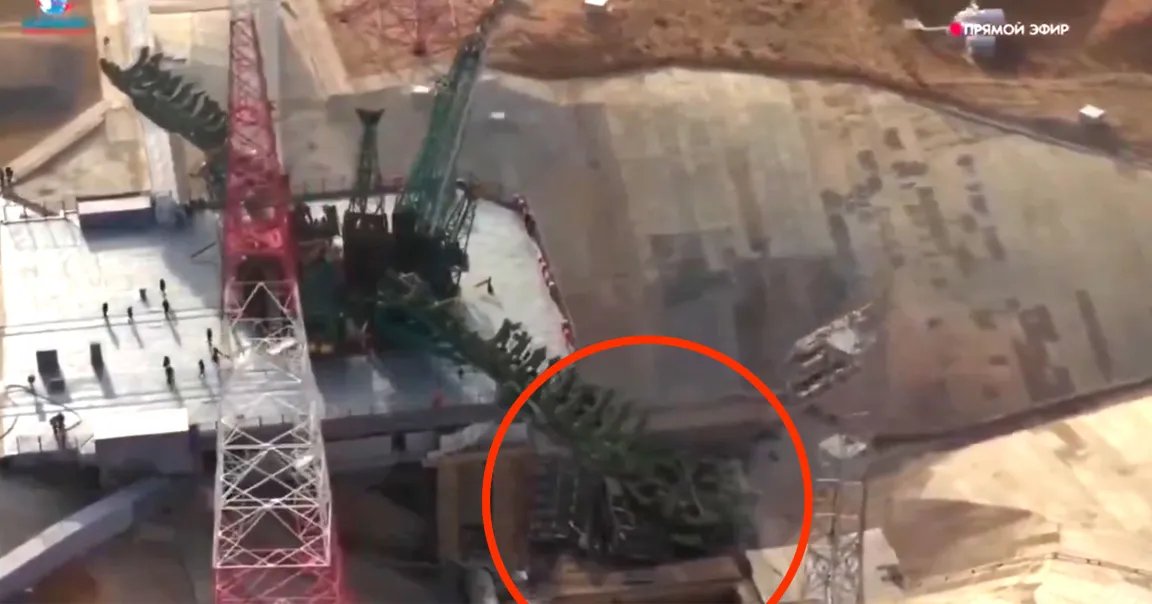
All of the stories above concerned either NASA or American commercial aerospace corporations but there is also news coming from China’s space agency as well. On the 12th of February China successfully tested two components of their future manned Lunar exploration missions simultaneously.

Like NASA’s Artemis program China is designing a large rocket called the Long March 10 along with a crew capsule called the Mengzhou and a Lunar lander called the Lanyue. The test conducted on the 12th consisted of an abort systems test for the Mengzhou capsule along with a test of the re-usability of a scaled down version of the Long March 10 rocket.
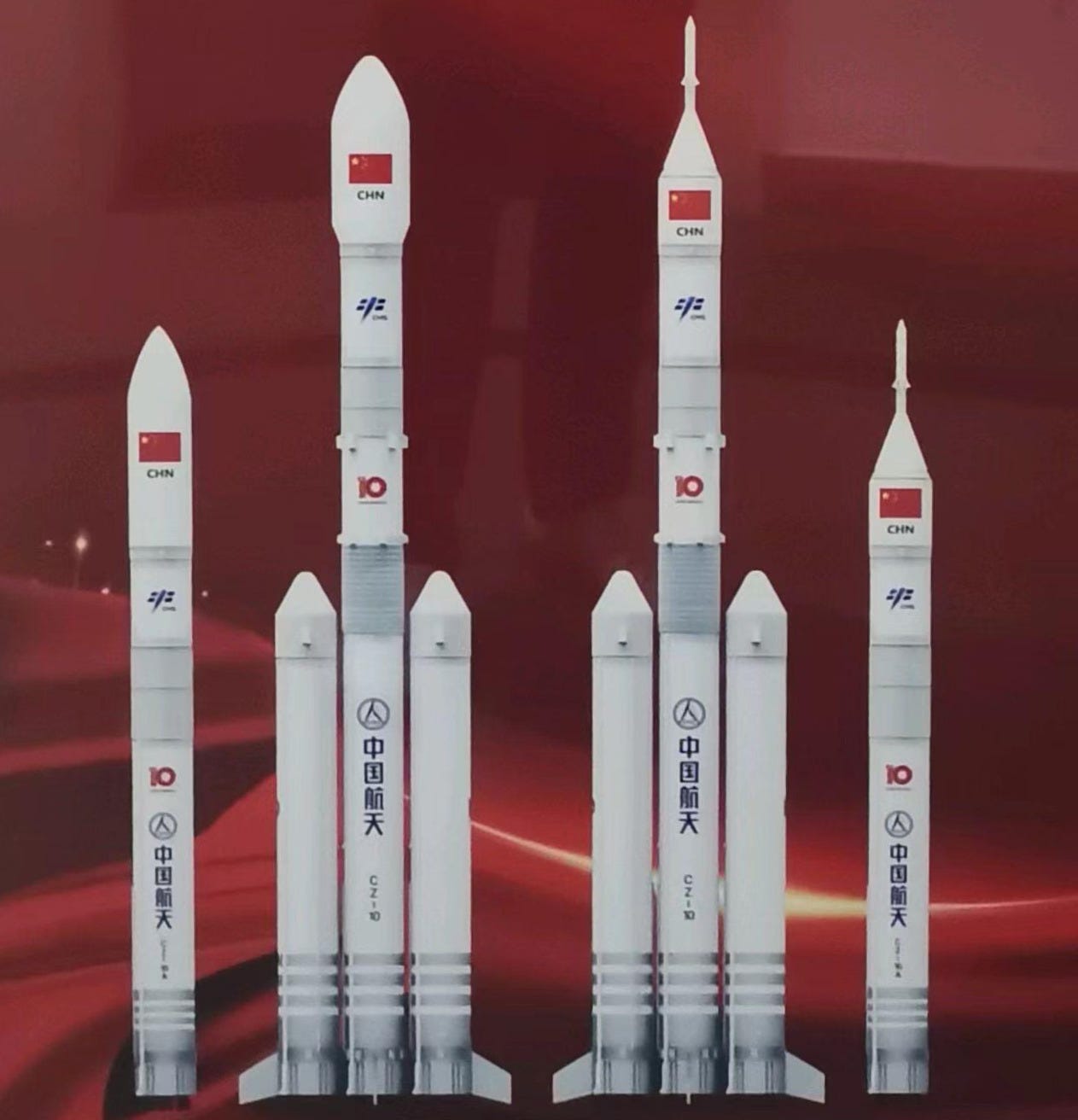

The abort test of the Mengzhou capsule is a standard test for manned spacecraft, both the Space X Dragon and Artemis’ Orion capsules underwent such testing. If during a launch anything should go wrong with the first stage rocket, or if there’s a problem with jettisoning the first stage and igniting the second stage, solid fuel rockets on the capsule will fire pulling it away from the launch vehicle and allowing the capsule and crew to safely land. The test of the abort system is usually carried out during the launch at what is called ‘Max Q’ which is the moment when aerodynamic pressure on the entire launch vehicle is greatest.
As I mentioned above both the Dragon and Orion capsules underwent this test and in those tests the launch rocket was simply jettisoned after the capsule was pulled away. The Chinese however wanted to try for more than that. Currently the Chinese are working very hard to develop a re-usable rocket similar to Space X’s Falcon 9. So they decided to conduct a full flight of the Long march 10 rocket, after the Mengzhou capsule was pulled away. Therefore, about five minutes after the Mengzhou capsule had completed its test the Long March 10 rocket re-ignited its engines and was able to make a controlled splashdown in the waters off China’s Hainan Island. Two successful tests for the price of one.
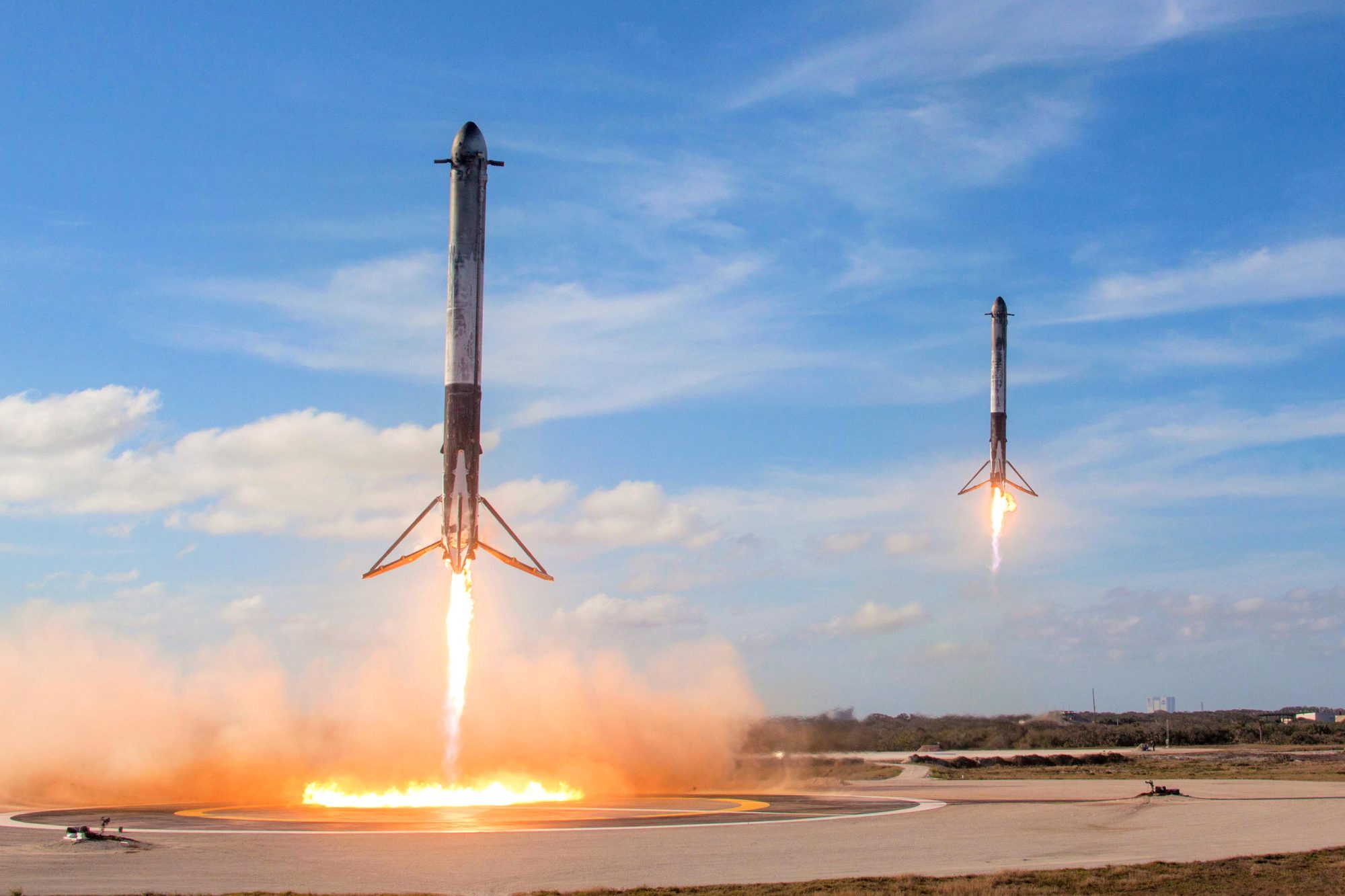

The race to get back to the Moon is heating up, as is the effort to commercialize space. The future will belong not to whoever is first but whoever keeps going and finishes the job.