For over fifty years now the ‘Big Bang Theory’ has been the cornerstone of our understanding of how the Universe came into being. According to the theory a little more than 13 billion years ago an incredibly dense ‘singularity’ exploded hurling matter and energy out into space (Which didn’t exist before the explosion). That matter would slowly cool to form stars and quasars and galaxies and all of the other astronomical objects we see through our telescopes today.
The strongest evidence for the Big Bang comes from observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), literally the leftover heat from that explosion that fills all of space. The image below shows the CMB as measured by the WMAP Satellite.

Still, right from the very first there have been physicists and cosmologists who asked: What was going on before the Big Bang? What in fact caused the Big Bang? (Actually, since on cosmic scales time and space are pretty much the same those two questions can be combined as: What is going on outside of the Big Bang?)
Cosmologists have speculated about cyclic Universes where the expansion of the Big Bang comes to stop, leading to a collapse called a Big Crunch which then rebounds as another Big Bang starting the cycle all over again. Then they are other theories about a ‘Multi-Verse’, where our Big Bang was just one of an infinite number of Big Bangs of various sizes, shapes and properties. My favourite theory is that our Universe is just a Black Hole inside an even bigger Universe. What we call the Big Bang was the instant the Black Hole in that other Universe formed.
If you think these ideas border on crazy, well wouldn’t any theory about how our Universe began sort of have to be! The problem with all of these theories however is that the evidence needed to confirm any of them would have to have come through the Big Bang. In other words that evidence would have had to survive the unimaginable temperatures and pressures at the beginning of our Universe and few physicists thought such survival was possible.
Now however two mathematical physicists think they have found just such evidence buried within the data of the CMB. V.G. Gurzadyan of the Yerevan Physics Institute in Armenia along with Roger Penrose of The Mathematical Institute in Oxford in the UK have been working on a variation of the cyclic Universe that they call Conformal Cyclic Cosmology (CCC). In CCC each Universe, remember we’re talking about a cycle of Universes now, expands until all of the matter has spread so thin that time and space no longer really exist because there is nothing with which to measure them! The Universe has now returned to the initial condition of the Big Bang so another Big Bang occurs to start everything all over again!
One of the interesting things about CCC is that in the theory the Big Bang itself takes a little longer and is therefore less violent. Less violent enough for some traces of really powerful events, like a merger of supermassive black holes for example, to send some evidence through the Big Bang.
It would work like this, see image below. The start of a merger of two supermassive black holes would send a powerful ripple of electromagnetic and gravitational energy spreading through space and time. Once the merger is completed the ripple would cease. As the ripple spread out it would form a cone in space-time which eventually would impact on the next Big Bang causing the formation of concentric circles that could show up on the CMB.

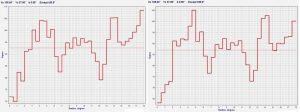
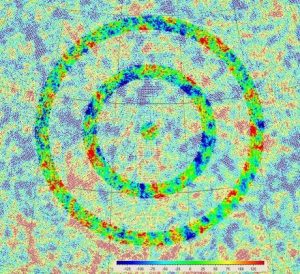
Now searching through all of the CMB data for such traces is the sort of tedious, painstaking work that only a computer could do but Penrose and Gurzadyan believe they have found some. The plots below show some of the evidence, the data peaks being the rings. The image below that shows two superimposed rings on the CMB data. (That means the rings have been artificially placed on the data as an aid to seeing them) I have to admit that I have some trouble seeing the signal through all of the noise but nevertheless I’m intrigued by the possibility of detecting ‘fossils’ of pre-Big Bang existence.
Theories like that of Penrose and Gurzadyan are always greeted with a good deal of skepticism, as they should be. Other physicists and cosmologists will now scrutinize Penrose and Gurzadyan’s math and calculations to see if they can find any flaws. At the same time I’m certain that Penrose and Gurzadyan will be looking for more ‘fossils’, more evidence to support their claims.
If Penrose and Gurzadyan are right it would be one of the biggest finds in science in this century. Only time and more data will tell for sure.